Author:
Bobbie Johnson
Date Of Creation:
6 April 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 3: Precautions for Examining Newborn Puppies
- Method 2 of 3: Physical examination of sex characteristics
- Method 3 of 3: Behavioral Differences in Puppies of Different Genders
- Tips
Determining the sex of an adult dog is quite easy, it only requires paying attention to its external sexual characteristics and behavior. However, when it comes to puppies under six months old, finding out their gender becomes somewhat more difficult. To determine the sex of a puppy, you need to carefully examine it and understand which genitals it possesses. Certain behaviors can also tell you the sex of the puppy, but they are less reliable than the results of a close physical examination of the animal.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Precautions for Examining Newborn Puppies
 1 Wait a few weeks before examining your newborn puppy. It will be easier for you to determine the sex of your puppy when he is a little older. Try to wait at least 3-4 weeks before starting your physical exam to increase your chances of getting accurate results.
1 Wait a few weeks before examining your newborn puppy. It will be easier for you to determine the sex of your puppy when he is a little older. Try to wait at least 3-4 weeks before starting your physical exam to increase your chances of getting accurate results. - It is best to wait until the puppy is 8 full weeks of age, as by this time the male genitals are fully visible.
- If the puppy still has an umbilical cord on its belly, see if it has signs of a penis centimeter below the umbilical cord. In the first few weeks of a puppy's life, the penis looks like a small bulge in the middle of its abdomen. Unlike males, girls (bitches) do not have any genitals on their belly at all.
 2 Pick up the puppy carefully. Newborn puppies are quite fragile, so extra care must be taken when handling them. Before handling your puppy, wash and dry your hands. Hold your puppy carefully and very securely so as not to accidentally injure him.
2 Pick up the puppy carefully. Newborn puppies are quite fragile, so extra care must be taken when handling them. Before handling your puppy, wash and dry your hands. Hold your puppy carefully and very securely so as not to accidentally injure him. - Make sure that the whelping bitch doesn't mind if you take her puppies. Some dogs behave very aggressively when a stranger touches their puppies.
- If your dog is upset about touching her puppy, return it to the mother immediately and try another time.
 3 Keep your puppy warm. The physical examination of the puppy should be done in a warm room to prevent the puppy from catching a cold. Also, keep your arms warm when you pick them up. Small puppies can easily get sick if they get too cold.
3 Keep your puppy warm. The physical examination of the puppy should be done in a warm room to prevent the puppy from catching a cold. Also, keep your arms warm when you pick them up. Small puppies can easily get sick if they get too cold. - For the same reason, the puppy should not be removed from the mother for more than 5-10 minutes. Longer examination may cause the puppy to freeze too much.
- If the puppy begins to shiver or cry, return it immediately to the side of the mother or to a warm puppy pen.
 4 Lay the puppy on its back. To do this, either place a clean, soft towel on a stable work surface, or turn the puppy right in your arms. Gently grab the puppy and flip it over onto its back to expose its belly.
4 Lay the puppy on its back. To do this, either place a clean, soft towel on a stable work surface, or turn the puppy right in your arms. Gently grab the puppy and flip it over onto its back to expose its belly. - It is only possible to securely hold the puppy on its back directly in the hand if it is small and calm enough.
- Be sure to support your puppy's head well when holding him on his back.
- The towel you are using should be warm. If necessary, heat the towel for a few minutes on a radiator, coil, or tumble dryer before placing your puppy on it. Do not use a cold, hot, or wet towel.
 5 Try to distinguish between the penis and the umbilical cord. One of the most common mistakes in sex determination of young puppies is caused by people mistaking the umbilical cord for the penis. Although both look like a bulge on the puppy's belly, the place where the umbilical cord (navel) is attached is directly under the ribcage, while the penis should be lower in the abdomen, located between the hind legs.
5 Try to distinguish between the penis and the umbilical cord. One of the most common mistakes in sex determination of young puppies is caused by people mistaking the umbilical cord for the penis. Although both look like a bulge on the puppy's belly, the place where the umbilical cord (navel) is attached is directly under the ribcage, while the penis should be lower in the abdomen, located between the hind legs. - Moreover, puppies of both sexes will have at least one bulge on their abdomen, since they all must have navels. But males should have a second bulge between the navel and the hind legs. Also, males will only have one hole under the tail, not two as bitches should.
- However, if you need to find out the gender of a very young puppy, it is best to rely on the opinion of a veterinarian, breeder or other experienced dog-handling professional.
Method 2 of 3: Physical examination of sex characteristics
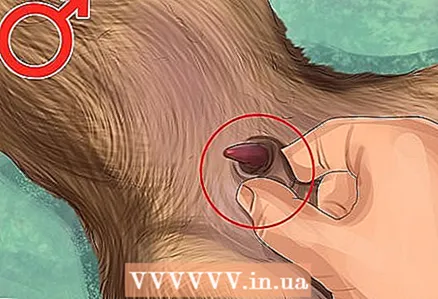 1 Examine the animal for male genitalia. Examine the area between the puppy's navel and tail to reveal the penis and scrotum. In older dogs, these sexual characteristics are very pronounced, while they can be extremely miniature and practically invisible in very small puppies.
1 Examine the animal for male genitalia. Examine the area between the puppy's navel and tail to reveal the penis and scrotum. In older dogs, these sexual characteristics are very pronounced, while they can be extremely miniature and practically invisible in very small puppies. - The scrotum should be located under the anus, practically between the hind legs.
- However, if the male has been neutered (so as not to participate in reproduction), he will not have a clearly visible scrotum.
 2 Pay attention to the female genitals. If the puppy is a bitch, you should notice a vulva when viewed belly up. Gently lift the puppy's hind legs so you can see the anus. If a leaf-like formation is noticeable between the paws near the anus, then this is the vulva characteristic of the bitch.
2 Pay attention to the female genitals. If the puppy is a bitch, you should notice a vulva when viewed belly up. Gently lift the puppy's hind legs so you can see the anus. If a leaf-like formation is noticeable between the paws near the anus, then this is the vulva characteristic of the bitch. 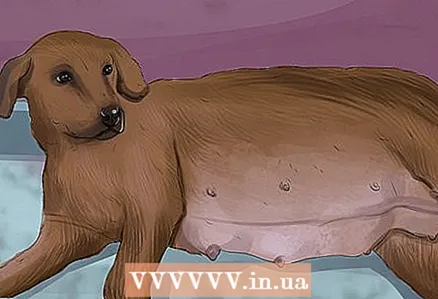 3 Identify physical signs pregnancy. If a dog is pregnant, then without any doubt it can be said that she is a bitch. Signs of pregnancy include a very large belly, which has grown despite the absence of changes in nutrition, as well as the birth itself.
3 Identify physical signs pregnancy. If a dog is pregnant, then without any doubt it can be said that she is a bitch. Signs of pregnancy include a very large belly, which has grown despite the absence of changes in nutrition, as well as the birth itself.  4 Do not use any other physiological trait to determine the sex of the dog. You may want to use some additional physiological clues to find out the sex of the animal. However, any other sex differences in dogs will be so subtle that they will be difficult to detect by someone who is not a professional breeder of a particular breed. Because of the subtle differences between other sex characteristics of different genders, it is better to rely on other more significant indicators.
4 Do not use any other physiological trait to determine the sex of the dog. You may want to use some additional physiological clues to find out the sex of the animal. However, any other sex differences in dogs will be so subtle that they will be difficult to detect by someone who is not a professional breeder of a particular breed. Because of the subtle differences between other sex characteristics of different genders, it is better to rely on other more significant indicators. - For example, both females and males have nipples, so by the presence of nipples you cannot say that you are a bitch.
- In addition, a large constitution for a dog of a particular breed and well-developed muscle mass does not mean that this is a male dog. In dogs, differences in size between animals of different sexes are minimal.
Method 3 of 3: Behavioral Differences in Puppies of Different Genders
 1 Pay attention to how the puppy urinates when he is at least 6 months old. Small puppies urinate in the same way regardless of gender. However, after six months, most males begin to lift their paws to urinate, while females continue to sit down.
1 Pay attention to how the puppy urinates when he is at least 6 months old. Small puppies urinate in the same way regardless of gender. However, after six months, most males begin to lift their paws to urinate, while females continue to sit down. - In the first few weeks of life, puppies are not yet able to control their bowels and bladder, so at this stage it is useless to try to find out their gender from the habit of urinating.
- Even when the puppies are old enough to stand confidently on their paws and learn to control themselves, for the first couple of months they will all sit down to urinate.
- Many males take up to six months to develop the habit of urinating the way adults of the same sex do.
 2 Pay attention to the tendency to mark your territory. Once young males are a few months old, they can begin to mark territory. This is a fairly good behavioral marker of gender, since this instinct is not typical for young bitches.
2 Pay attention to the tendency to mark your territory. Once young males are a few months old, they can begin to mark territory. This is a fairly good behavioral marker of gender, since this instinct is not typical for young bitches. - The need to mark territory is especially strong in young males that have not been neutered. The neutering of the puppy significantly reduces this need for him.
- The exact age at which males begin to mark territories varies from animal to animal, but in most cases this occurs between two and six months.
- A dog that urinates quickly in many places is more likely to mark territory, especially if it does so on purpose after carefully examining each specific area for smell.
- Dogs that only urinate once or twice usually do not mark their territory, even if they stop in many places during the walk to study their smell.
 3 Watch for signs of heat. Bitches that have not been neutered will go into heat once every six months. The first heat usually falls between six and ten months of age. Moreover, each estrus lasts about 3 weeks. Signs of heat in a bitch include changes in behavior, swelling of the vulva and discharge from it.
3 Watch for signs of heat. Bitches that have not been neutered will go into heat once every six months. The first heat usually falls between six and ten months of age. Moreover, each estrus lasts about 3 weeks. Signs of heat in a bitch include changes in behavior, swelling of the vulva and discharge from it. - Possible behavioral changes in a bitch during estrus include increased anxiety and obsession.
- Discharge from bitches during estrus can be clear, brown or bloody (it all depends on what stage of the reproductive cycle they are in).
 4 Do not use the personal characteristics of the general behavior of the dog as an indicator of gender. Both males and females can be equally affectionate, aggressive in defense, active or calm. These individual behaviors do not in any way relate to the sex of the animal.
4 Do not use the personal characteristics of the general behavior of the dog as an indicator of gender. Both males and females can be equally affectionate, aggressive in defense, active or calm. These individual behaviors do not in any way relate to the sex of the animal. - For example, often even bitches can climb on other animals and imitate intercourse, which is usually referred to as a characteristic feature of males.
Tips
- If you handle your puppy too often under 3 weeks old, you may leave too much of your scent on it, masking its own scent. When a puppy smells too much of a human, the mother may refuse him. In addition, if the puppy is very often taken away from the mother, he may become hypothermic and sick.
- Remember that both bitches and males have nipples, so this trait cannot be relied upon to determine the sex of a puppy.