Author:
Sara Rhodes
Date Of Creation:
13 February 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 3: Finding Height by Base and Area
- Method 2 of 3: Finding the Height in an Equilateral Triangle
- Method 3 of 3: Finding Height Using Angles and Sides
- Additional articles
To calculate the area of a triangle, you need to know its height. If it is not given, you can calculate it using the values you know! In this article, we will show you several ways to find the height of a triangle from known values of other quantities.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Finding Height by Base and Area
 1 Let us recall the formula for calculating the area of a triangle. The area of a triangle is calculated by the formula: A = 1 / 2bh.
1 Let us recall the formula for calculating the area of a triangle. The area of a triangle is calculated by the formula: A = 1 / 2bh. - A is the area of the triangle
- b is the side of the triangle to which the height is lowered.
- h - the height of the triangle
 2 Look at the triangle and think about what values you already know. If you are given an area, designate it with the letter "A" or "S". You should also be given the meaning of the side, mark it with the letter "b". If you are not given an area and a side, use another method.
2 Look at the triangle and think about what values you already know. If you are given an area, designate it with the letter "A" or "S". You should also be given the meaning of the side, mark it with the letter "b". If you are not given an area and a side, use another method. - Keep in mind that the base of a triangle can be any side to which the height is lowered (regardless of how the triangle is located). To understand this better, imagine that you can rotate this triangle. Turn it so that the side you know faces down.
- For example, the area of a triangle is 20, and one of its sides is 4. In this case, "A = 20", "b = 4".
 3 Plug the given values into the formula for calculating the area (A = 1 / 2bh) and find the height. First multiply side (b) by 1/2 and then divide area (A) by that value. This way you will find the height of the triangle.
3 Plug the given values into the formula for calculating the area (A = 1 / 2bh) and find the height. First multiply side (b) by 1/2 and then divide area (A) by that value. This way you will find the height of the triangle. - In our example: 20 = 1/2 (4) h
- 20 = 2h
- 10 = h
Method 2 of 3: Finding the Height in an Equilateral Triangle
 1 Remember the properties of an equilateral triangle. In an equilateral triangle, all sides and all angles are equal (each angle is 60˚). If you draw the height in such a triangle, you get two equal right-angled triangles.
1 Remember the properties of an equilateral triangle. In an equilateral triangle, all sides and all angles are equal (each angle is 60˚). If you draw the height in such a triangle, you get two equal right-angled triangles. - For example, consider an equilateral triangle with side 8.
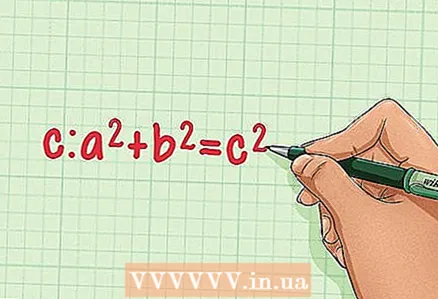 2 Remember the Pythagorean theorem. The Pythagorean theorem says that in any right-angled triangle with legs "a" and "b" the hypotenuse "c" is equal to: a + b = c... This theorem can be used to find the height of an equilateral triangle!
2 Remember the Pythagorean theorem. The Pythagorean theorem says that in any right-angled triangle with legs "a" and "b" the hypotenuse "c" is equal to: a + b = c... This theorem can be used to find the height of an equilateral triangle!  3 Divide an equilateral triangle into two right-angled triangles (draw the height for this). Then mark the sides of one of the right-angled triangles. The side of an equilateral triangle is the hypotenuse "c" of a right-angled triangle. Leg "a" is equal to 1/2 of the side of an equilateral triangle, and leg "b" is the desired height of an equilateral triangle.
3 Divide an equilateral triangle into two right-angled triangles (draw the height for this). Then mark the sides of one of the right-angled triangles. The side of an equilateral triangle is the hypotenuse "c" of a right-angled triangle. Leg "a" is equal to 1/2 of the side of an equilateral triangle, and leg "b" is the desired height of an equilateral triangle. - So, in our example with an equilateral triangle with a known side of 8: c = 8 and a = 4.
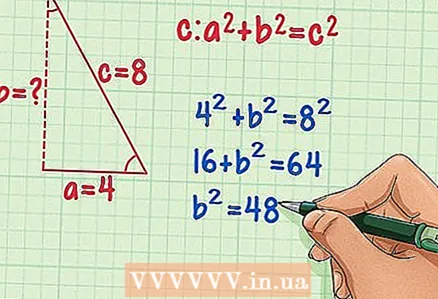 4 Plug these values into the Pythagorean theorem and calculate b. First, square "c" and "a" (multiply each value by itself). Then subtract a from c.
4 Plug these values into the Pythagorean theorem and calculate b. First, square "c" and "a" (multiply each value by itself). Then subtract a from c. - 4 + b = 8
- 16 + b = 64
- b = 48
 5 Take the square root of b to find the height of the triangle. To do this, use a calculator. The resulting value will be the height of your equilateral triangle!
5 Take the square root of b to find the height of the triangle. To do this, use a calculator. The resulting value will be the height of your equilateral triangle! - b = √48 = 6,93
Method 3 of 3: Finding Height Using Angles and Sides
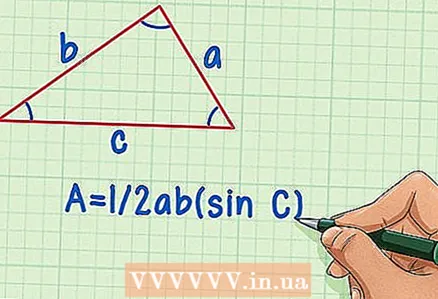 1 Think about what values you know. You can find the height of a triangle if you know the values for the sides and angles. For example, if you know the angle between the base and the side. Or if the values of all three sides are known. So, let's designate the sides of the triangle: "a", "b", "c", the corners of the triangle: "A", "B", "C", and the area - the letter "S".
1 Think about what values you know. You can find the height of a triangle if you know the values for the sides and angles. For example, if you know the angle between the base and the side. Or if the values of all three sides are known. So, let's designate the sides of the triangle: "a", "b", "c", the corners of the triangle: "A", "B", "C", and the area - the letter "S". - If you know all three sides, you need the area of the triangle and Heron's formula.
- If you know the two sides and the angle between them, you can use the following formula to find the area: S = 1 / 2ab (sinC).
 2 If you are given values for all three sides, use Heron's formula. This formula will have to perform several actions. First you need to find the variable "s" (we will denote by this letter half of the triangle's perimeter). To do this, plug the known values into this formula: s = (a + b + c) / 2.
2 If you are given values for all three sides, use Heron's formula. This formula will have to perform several actions. First you need to find the variable "s" (we will denote by this letter half of the triangle's perimeter). To do this, plug the known values into this formula: s = (a + b + c) / 2. - For a triangle with sides a = 4, b = 3, c = 5, s = (4 + 3 + 5) / 2. The result is: s = 12/2, where s = 6.
- Then, by the second action, we find the area (the second part of Heron's formula). Area = √ (s (s-a) (s-b) (s-c)). Replace the word “area” with the equivalent formula for finding area: 1 / 2bh (or 1 / 2ah, or 1 / 2ch).
- Now find the equivalent expression for height (h). For our triangle, the following equation will be valid: 1/2 (3) h = (6 (6-4) (6-3) (6-5)). Where 3 / 2h = √ (6 (2 (3 (1))). So 3 / 2h = √ (36). Use the calculator to calculate the square root. In our example: 3 / 2h = 6. It turns out that the height (h) is 4, side b is the base.
 3 If by the condition of the problem you know two sides and an angle, you can use a different formula. Replace area in the formula with the equivalent expression: 1 / 2bh. Thus, you get the following formula: 1 / 2bh = 1 / 2ab (sinC). It can be simplified to the following form: h = a (sin C) to remove one unknown variable.
3 If by the condition of the problem you know two sides and an angle, you can use a different formula. Replace area in the formula with the equivalent expression: 1 / 2bh. Thus, you get the following formula: 1 / 2bh = 1 / 2ab (sinC). It can be simplified to the following form: h = a (sin C) to remove one unknown variable. - Now it remains to solve the resulting equation. For example, let "a" = 3, "C" = 40 degrees. Then the equation will look like this: "h" = 3 (sin 40). Use a calculator and a sine table to calculate the value for "h". In our example, h = 1.928.
Additional articles
 How to apply the Pythagorean theorem
How to apply the Pythagorean theorem  How to find the area of a quadrilateral
How to find the area of a quadrilateral  How to find the volume of a pyramid
How to find the volume of a pyramid  How to find the area of a triangle
How to find the area of a triangle  How to calculate the circumference of a circle
How to calculate the circumference of a circle  How to calculate the diameter of a circle
How to calculate the diameter of a circle  How to calculate square meters
How to calculate square meters  How to calculate the diagonal of a rectangle
How to calculate the diagonal of a rectangle  How to find the volume in cubic meters
How to find the volume in cubic meters  How to find the hypotenuse
How to find the hypotenuse  How to calculate angles
How to calculate angles  How to calculate the volume of a cube
How to calculate the volume of a cube  How to find the center of a circle
How to find the center of a circle  How to find the area of a polygon
How to find the area of a polygon



