Author:
Ellen Moore
Date Of Creation:
20 January 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 4: Two Numbers: The Simple Method
- Method 2 of 4: Two numbers: the detailed method
- Method 3 of 4: Three or More Numbers: The Simple Method
- Method 4 of 4: Three or More Numbers: Using Logarithms
- Tips
Geometric mean is a mathematical quantity that can be easily confused with the more commonly used arithmetic mean. Follow the methods below to calculate the geometric mean.
Steps
Method 1 of 4: Two Numbers: The Simple Method
 1 Take two numbers, the geometric mean of which you want to find.
1 Take two numbers, the geometric mean of which you want to find.- For example, 2 and 32.
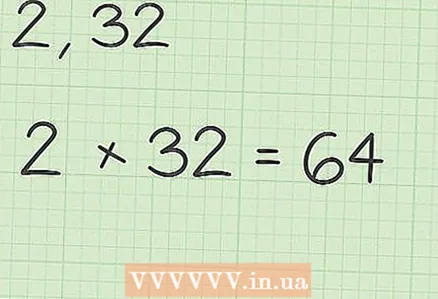 2 Multiply them.
2 Multiply them.- 2 x 32 = 64.
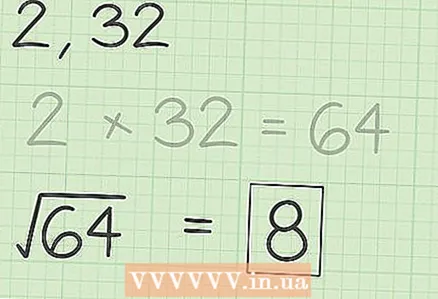 3 Extract Square root from the resulting number.
3 Extract Square root from the resulting number.- √64 = 8.
Method 2 of 4: Two numbers: the detailed method
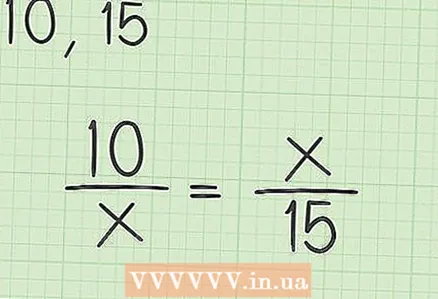 1 Plug the numbers into the above equation. If these are, say, 10 and 15, then substitute them as shown in the figure.
1 Plug the numbers into the above equation. If these are, say, 10 and 15, then substitute them as shown in the figure. 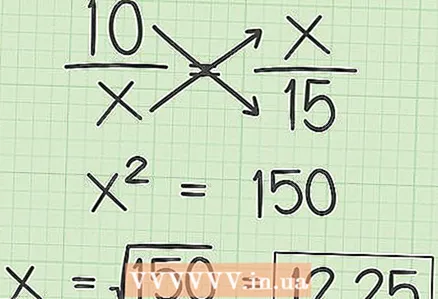 2 Find "x". Start by multiplying crosswise, which means multiplying pairs of numbers along the diagonal and placing the results of the multiplication on opposite sides of the = sign. Since x * x = x, the equation is reduced to the form: x = (the result of multiplying your numbers). To calculate x, take the square root of the multiplication of the numbers used. If the root is an integer, great. If not, give your answer in decimal form or write it down with a root sign (depending on what your instructor requires). The answer in the figure above is written as a simplified square root.
2 Find "x". Start by multiplying crosswise, which means multiplying pairs of numbers along the diagonal and placing the results of the multiplication on opposite sides of the = sign. Since x * x = x, the equation is reduced to the form: x = (the result of multiplying your numbers). To calculate x, take the square root of the multiplication of the numbers used. If the root is an integer, great. If not, give your answer in decimal form or write it down with a root sign (depending on what your instructor requires). The answer in the figure above is written as a simplified square root.
Method 3 of 4: Three or More Numbers: The Simple Method
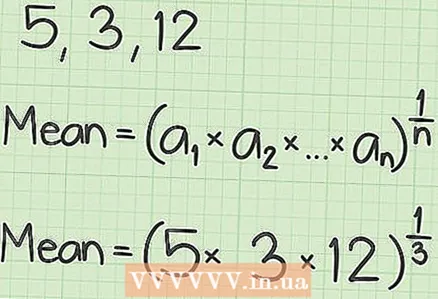 1 Plug the numbers into the above equation.Geometric mean = (a1 × a2 ... ... ... an)
1 Plug the numbers into the above equation.Geometric mean = (a1 × a2 ... ... ... an) - a1 is the first number, a2 - the second number and so on
- n - total number of numbers
 2 Multiply the numbers (a1, a2 etc).
2 Multiply the numbers (a1, a2 etc).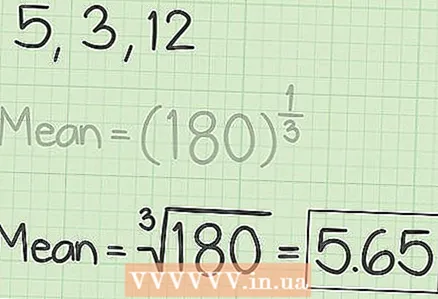 3 Extract the root n degrees from the resulting number. This will be the geometric mean.
3 Extract the root n degrees from the resulting number. This will be the geometric mean.
Method 4 of 4: Three or More Numbers: Using Logarithms
 1 Find the logarithm of each number and add the values together. Find the LOG key on your calculator. Then enter: (first number) LOG + (second number) LOG + (third number) LOG [+ as many numbers as given] =... Remember to press =, or the result shown will be the logarithm of the last entered number, not the sum of the logarithms of all numbers.
1 Find the logarithm of each number and add the values together. Find the LOG key on your calculator. Then enter: (first number) LOG + (second number) LOG + (third number) LOG [+ as many numbers as given] =... Remember to press =, or the result shown will be the logarithm of the last entered number, not the sum of the logarithms of all numbers. - For example, log 7 + log 9 + log 12 = 2.878521796
 2 Divide the addition by the total of the originally given numbers. If you've added the logarithms of three numbers, divide your result by three.
2 Divide the addition by the total of the originally given numbers. If you've added the logarithms of three numbers, divide your result by three. - For example, 2.878521796 / 3 = 0.959507265
 3 Calculate the antilogarithm of the result obtained. On the calculator, press the shift key (activates the upper case functions - above the keys), and then press LOGto get the antilogarithm value. This result will be the geometric mean.
3 Calculate the antilogarithm of the result obtained. On the calculator, press the shift key (activates the upper case functions - above the keys), and then press LOGto get the antilogarithm value. This result will be the geometric mean. - For example, antilog 0.959507265 = 9.109766916. Therefore, the geometric mean of 7, 9, and 12 is 9,11.
Tips
- Differences between arithmetic mean and geometric mean:
- To calculate arithmetic mean, for example, numbers 3, 4 and 18, you need to add them 3 + 4 + 18, and then divide by 3 (because initially three numbers are given). The answer is 25/3, or about 8.333; this means that if you add 8.3333 three times in a row, then the answer will be the same as when adding the numbers 3, 4, and 18. The arithmetic mean answers the question: “If all quantities have the same value, then what should this value be to add one result? "
- Against, geometric mean answers the question: "If all quantities have the same value, then what should this value be in order for multiplication to get one result?" Therefore, to find the geometric mean of 3, 4, and 18, we multiply these numbers: 3 x 4 x 18. We get 216. Then we take the cube root of the result of the multiplication (cube root, since there are three numbers involved). The answer is 6. In other words, since 6 x 6 x 6 = 3 x 4 x 18, then 6 is the geometric mean of 3, 4, and 18.
- The geometric mean is always less than or equal to the arithmetic mean. Read more here.
- Geometric mean is calculated only for positive numbers. The scheme for solving various applied problems using the geometric mean will not work in the presence of negative numbers.