Author:
Eric Farmer
Date Of Creation:
10 March 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 2: Determining the number of neutrons in atoms (not isotopes)
- Method 2 of 2: Determining the Number of Neutrons in Isotopes
- Tips
In atoms of the same element, the number of protons is constant, while the number of neutrons can vary.By knowing how many neutrons a particular atom contains, you can determine if it is a regular atom or an isotope that will have fewer or more neutrons. Determining the number of neutrons in an atom is quite simple. All you need to do to calculate the number of neutrons in an atom or isotope is to follow our instructions and keep the periodic table handy.
Steps
Method 1 of 2: Determining the number of neutrons in atoms (not isotopes)
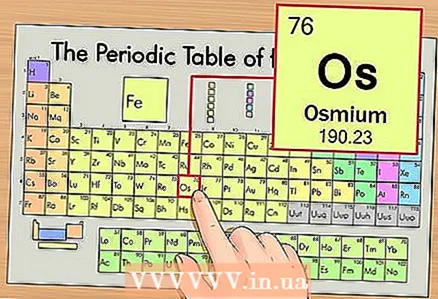 1 Find the element on the periodic table. As an example, we will consider osmium (Os), which is in the sixth period (sixth row from the top).
1 Find the element on the periodic table. As an example, we will consider osmium (Os), which is in the sixth period (sixth row from the top).  2 Find the atomic number of the element. This is usually the most noticeable number in the cell of an element and is usually located above its symbol (in the version of the periodic table that we use in our example, there are no other numbers). The atomic number is the number of protons in one atom of that element. For osmium, this number is 76, that is, there are 76 protons in one osmium atom.
2 Find the atomic number of the element. This is usually the most noticeable number in the cell of an element and is usually located above its symbol (in the version of the periodic table that we use in our example, there are no other numbers). The atomic number is the number of protons in one atom of that element. For osmium, this number is 76, that is, there are 76 protons in one osmium atom. - The number of protons is unchanged, and this is what makes an element an element.
 3 Find the atomic mass of an element. This number is usually found below the element symbol. Note that in the version of the periodic table in our example, the atomic mass is not given (this is not always the case; in many versions of the periodic table, the atomic mass is indicated). The atomic mass of osmium is 190.23.
3 Find the atomic mass of an element. This number is usually found below the element symbol. Note that in the version of the periodic table in our example, the atomic mass is not given (this is not always the case; in many versions of the periodic table, the atomic mass is indicated). The atomic mass of osmium is 190.23.  4 Round the atomic mass to the nearest whole number. In our example, 190.23 is rounded to 190.
4 Round the atomic mass to the nearest whole number. In our example, 190.23 is rounded to 190. - Atomic mass is the average number of isotopes of a particular element, usually it is not expressed as an integer.
 5 Subtract the atomic number from the atomic mass. Since protons and neutrons account for the absolute fraction of the atomic mass, subtracting the number of protons (that is, the atomic number, which is equal to the number of protons) from the atomic mass gives the number of neutrons in the atom. The numbers after the decimal point refer to the very small mass of electrons in an atom. In our example: 190 (atomic weight) - 76 (number of protons) = 114 (number of neutrons).
5 Subtract the atomic number from the atomic mass. Since protons and neutrons account for the absolute fraction of the atomic mass, subtracting the number of protons (that is, the atomic number, which is equal to the number of protons) from the atomic mass gives the number of neutrons in the atom. The numbers after the decimal point refer to the very small mass of electrons in an atom. In our example: 190 (atomic weight) - 76 (number of protons) = 114 (number of neutrons). 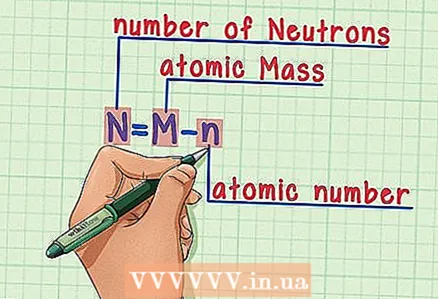 6 Remember the formula. To find the number of neutrons in the future, simply use this formula:
6 Remember the formula. To find the number of neutrons in the future, simply use this formula: - N = M - n
- N = number of neutrons
- M = atomic mass
- n = atomic number
- N = M - n
Method 2 of 2: Determining the Number of Neutrons in Isotopes
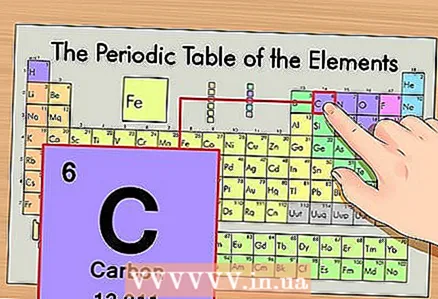 1 Find the element on the periodic table. As an example, we will consider the isotope of carbon 14C. Since the non-isotopic carbon 14C is just carbon C, find carbon on the periodic table (second period or second row from the top).
1 Find the element on the periodic table. As an example, we will consider the isotope of carbon 14C. Since the non-isotopic carbon 14C is just carbon C, find carbon on the periodic table (second period or second row from the top). 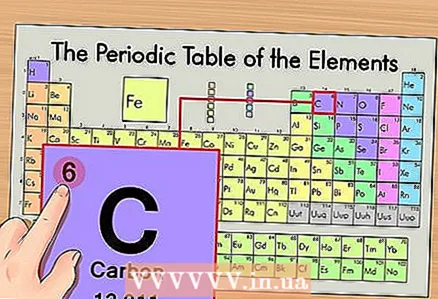 2 Find the atomic number of the element. This is, as a rule, the most noticeable number in the cell of an element and is usually located above its symbol (in the version of the periodic table that we use in our example, there are no other numbers). The atomic number is the number of protons in one atom of that element. Carbon is number 6, which means one carbon has six protons.
2 Find the atomic number of the element. This is, as a rule, the most noticeable number in the cell of an element and is usually located above its symbol (in the version of the periodic table that we use in our example, there are no other numbers). The atomic number is the number of protons in one atom of that element. Carbon is number 6, which means one carbon has six protons. 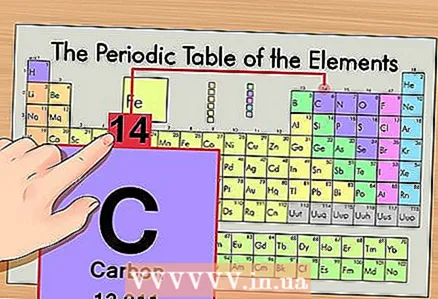 3 Find the atomic mass. In the case of isotopes, this is very easy to do, since they are named according to their atomic mass. In our case, carbon 14C has an atomic mass of 14. Now we know the atomic mass of the isotope; the subsequent calculation process is the same as for determining the number of neutrons in atoms (not isotopes).
3 Find the atomic mass. In the case of isotopes, this is very easy to do, since they are named according to their atomic mass. In our case, carbon 14C has an atomic mass of 14. Now we know the atomic mass of the isotope; the subsequent calculation process is the same as for determining the number of neutrons in atoms (not isotopes).  4 Subtract the atomic number from the atomic mass. Since protons and neutrons account for the absolute portion of the atomic mass, subtracting the number of protons (that is, the atomic number, which is equal to the number of protons) from the atomic mass gives the number of neutrons in the atom. In our example: 14 (atomic mass) - 6 (number of protons) = 8 (number of neutrons).
4 Subtract the atomic number from the atomic mass. Since protons and neutrons account for the absolute portion of the atomic mass, subtracting the number of protons (that is, the atomic number, which is equal to the number of protons) from the atomic mass gives the number of neutrons in the atom. In our example: 14 (atomic mass) - 6 (number of protons) = 8 (number of neutrons). 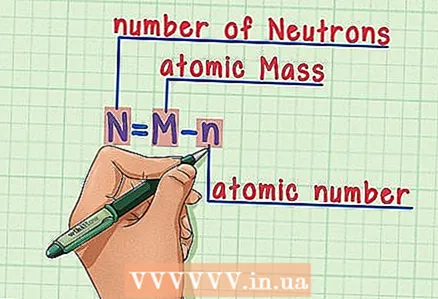 5 Remember the formula. To find the number of neutrons in the future, simply use this formula:
5 Remember the formula. To find the number of neutrons in the future, simply use this formula: - N = M - n
- N = number of neutrons
- M = atomic mass
- n = atomic number
- N = M - n
Tips
- Protons and neutrons make up almost the absolute mass of elements, while electrons and other particles make up an extremely insignificant mass (this mass tends to zero).Since one proton has about the same mass as one neutron, and the atomic number is the number of protons, you can simply subtract the number of protons from the total mass.
- Osmium - a metal in a solid state at room temperature, got its name from the Greek word "osme" - smell.
- If you are not sure what a number in the periodic table means, remember: the table is usually built around an atomic number (that is, the number of protons), which starts at 1 (hydrogen) and grows one unit from left to right, ending with 118 (Oganesson). This is because the number of protons in an atom determines the element itself, and such a number is the easiest way to organize the elements (for example, an atom with 2 protons is always helium, just like an atom with 79 protons is always gold).