Author:
Bobbie Johnson
Date Of Creation:
10 April 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Part 1 of 3: Choosing Mulching Materials
- Part 2 of 3: Timing your mulching
- Part 3 of 3: Mulching Process
- What do you need
- Warnings
The use of organic mulch in the garden or garden beds allows you to better retain moisture in the soil, protect plant roots, improve the quality of the soil itself, protect it from temperature extremes and prevent weed growth. Inorganic, or decorative, mulch is less effective at controlling weeds and protecting plant roots, but it can add a little more color and texture to your yard and flower beds. First of all, you need to decide on the choice of specific mulching materials, and then mulch correctly in order for this method of plant health to bring the expected results.
Steps
Part 1 of 3: Choosing Mulching Materials
 1 Choose organic mulch to replenish the soil with nutrients. Organic mulching materials include sawdust, straw, grass cuttings, cut foliage and compost. When such mulch is overheated, the soil is naturally enriched with nutrients. Organic mulch also helps retain moisture in the soil, prevents weeds from growing and helps protect plant roots from extreme temperature extremes. However, organic mulch will not protect your plants from pests.
1 Choose organic mulch to replenish the soil with nutrients. Organic mulching materials include sawdust, straw, grass cuttings, cut foliage and compost. When such mulch is overheated, the soil is naturally enriched with nutrients. Organic mulch also helps retain moisture in the soil, prevents weeds from growing and helps protect plant roots from extreme temperature extremes. However, organic mulch will not protect your plants from pests. - You can purchase organic mulching materials at a garden supply store or online store of your choice.
- Organic mulch needs to be replaced or renewed annually.
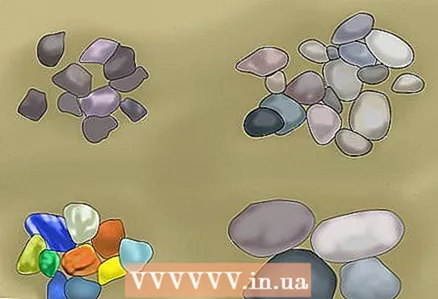 2 Opt for inorganic mulching materials for decorative purposes. Inorganic mulching materials include gravel, stone, glass, and river pebbles. Inorganic mulch can interfere with weed germination, help retain moisture in the soil, and regulate soil temperature, but is often less effective than organic mulching materials. However, unlike organic mulch, inorganic mulch comes in a wide variety of colors and textures that can be used to decorate outdoor areas. Just choose the stones or gravel that best suit the aesthetic of your yard.
2 Opt for inorganic mulching materials for decorative purposes. Inorganic mulching materials include gravel, stone, glass, and river pebbles. Inorganic mulch can interfere with weed germination, help retain moisture in the soil, and regulate soil temperature, but is often less effective than organic mulching materials. However, unlike organic mulch, inorganic mulch comes in a wide variety of colors and textures that can be used to decorate outdoor areas. Just choose the stones or gravel that best suit the aesthetic of your yard. - For example, you can purchase an inorganic mulch to match the exterior of your home.
- If you are aiming for a modern, well-groomed decor, you will probably want all the inorganic mulch pebbles to be the same size and shape.
- Please note that the use of stones and gravel in high temperature conditions can cause plants to overheat and damage them.
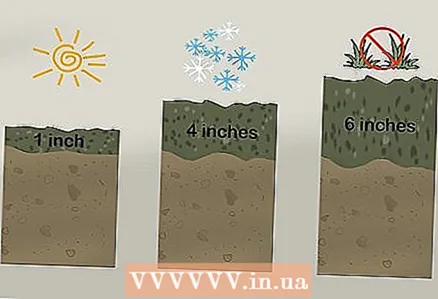 3 Purchase enough mulch to cover an appropriate area of soil. In the summertime, the soil in the flower beds or beds should be covered with a 2.5–5 cm layer of mulch. To calculate the exact amount of mulch you will need to buy, you can use an online calculator such as this one.
3 Purchase enough mulch to cover an appropriate area of soil. In the summertime, the soil in the flower beds or beds should be covered with a 2.5–5 cm layer of mulch. To calculate the exact amount of mulch you will need to buy, you can use an online calculator such as this one. - Mulch is usually sold in bags with volume and fraction size.
- If you plan to use mulch for weed control, lay it on the soil in a layer of 5-10 cm.
- If you insulate fruit plants for the winter, they should be protected with a layer of mulch of 10-15 cm.
- Remember that overuse of mulch can suffocate the roots of cultivated plants and kill the plants.
Part 2 of 3: Timing your mulching
 1 For best results, lay your organic mulch in early summer. Mulching can be done at any other time, but late spring and early autumn are often the best times to mulch. During this period, the soil becomes already warm enough and the plants wake up from their winter sleep.
1 For best results, lay your organic mulch in early summer. Mulching can be done at any other time, but late spring and early autumn are often the best times to mulch. During this period, the soil becomes already warm enough and the plants wake up from their winter sleep. - If you are going to mulch the soil for weed control, it is better to do it as soon as possible, rather than waiting for the optimal moment.
 2 To shelter plants for the winter, mulch in late autumn. It is a common misconception that winter mulching prevents the ground from freezing at low temperatures. This is not true, but due to mulch, the freezing process is smoother and reduces the number of sudden temperature changes with freezing and thawing, which has a better effect on plants. To protect the plants for the winter, surround them with a 10-15 cm layer of mulch.
2 To shelter plants for the winter, mulch in late autumn. It is a common misconception that winter mulching prevents the ground from freezing at low temperatures. This is not true, but due to mulch, the freezing process is smoother and reduces the number of sudden temperature changes with freezing and thawing, which has a better effect on plants. To protect the plants for the winter, surround them with a 10-15 cm layer of mulch. - For winter mulching, you can use both organic and inorganic types of mulching materials.
 3 Mulch newly planted trees and bushes. Organic mulches such as compost or manure are best for newly planted shrubs, trees and flowers as they nourish the soil with essential trace minerals and protect the plants from weeds. Inorganic mulch does not have this beneficial effect on newly planted plants.
3 Mulch newly planted trees and bushes. Organic mulches such as compost or manure are best for newly planted shrubs, trees and flowers as they nourish the soil with essential trace minerals and protect the plants from weeds. Inorganic mulch does not have this beneficial effect on newly planted plants. - Organic sawdust mulch can compete for nitrogen with newly planted plants, so if you plan to use sawdust, apply nitrogen fertilizer to the soil first.
Part 3 of 3: Mulching Process
 1 Weed the weeds. Use a garden shovel to dig up any weeds. Uproot the weeds deep enough, otherwise they may regrow from the remnants of the roots. This step is important to prevent weeds from growing under the mulch.
1 Weed the weeds. Use a garden shovel to dig up any weeds. Uproot the weeds deep enough, otherwise they may regrow from the remnants of the roots. This step is important to prevent weeds from growing under the mulch. - Alternatively, if you have time, you can use a chemical herbicide that will kill the weeds on its own.
- Selective herbicides only harm broadleaf weeds and grasses. General herbicides kill any plants they come into contact with.
- Before using the herbicide, take all the precautions recommended in the instructions and carefully follow the directions for using the product.
 2 Create an edge for the mulched area. Use a conventional or lawn edging shovel and carefully dig in the area you want to mulch. This will create a smooth, continuous mulching boundary around the flower beds or trees, so that the mulch will not scatter beyond the area delineated for it (for example, onto the lawn).
2 Create an edge for the mulched area. Use a conventional or lawn edging shovel and carefully dig in the area you want to mulch. This will create a smooth, continuous mulching boundary around the flower beds or trees, so that the mulch will not scatter beyond the area delineated for it (for example, onto the lawn). - Do not throw the excavated soil into the area to be mulched, otherwise you can provoke the germination of grass through the mulch.
- You can also create a mulching boundary by installing curb stones around the area.
 3 Remove old mulch from the soil, or sprinkle a similar type of mulch on top of it. Use a shovel to scoop the old mulch off the top of the soil in your garden bed or flower bed. Place it in the wheelbarrow and throw it away. You will know you have removed enough old material when you see dark soil with plant roots.
3 Remove old mulch from the soil, or sprinkle a similar type of mulch on top of it. Use a shovel to scoop the old mulch off the top of the soil in your garden bed or flower bed. Place it in the wheelbarrow and throw it away. You will know you have removed enough old material when you see dark soil with plant roots. - Old mulch can be poured into a compost heap and allowed to decompose further.
- If you are only going to add fresh mulch of a similar type, you can simply sprinkle the new mulch on top of the old mulch, after leveling it with a rake.
 4 Spread small piles of mulch on the ground of the flower garden or garden with a shovel. Pour fresh mulch into the wheelbarrow first to make it easier for you to transport it. Then use a shovel to sprinkle small piles of mulch where you want to add it. Once you've prepared 3-4 small piles, move on to the next step.
4 Spread small piles of mulch on the ground of the flower garden or garden with a shovel. Pour fresh mulch into the wheelbarrow first to make it easier for you to transport it. Then use a shovel to sprinkle small piles of mulch where you want to add it. Once you've prepared 3-4 small piles, move on to the next step. - If you sprinkle the entire volume of mulch in one place, the layer may become too thick, which will suffocate the roots of your plants.
 5 Use a rake to smooth the mulch layer. Using a rake, spread the previously prepared mulch piles evenly over the surface of the ground. If you are doing spring or summer mulching, create a 2.5–5 cm layer of mulch throughout the mulch area. If you are using coarse inorganic mulching material, it can be spread by hand without using a rake. Add more mulch with a shovel as needed.
5 Use a rake to smooth the mulch layer. Using a rake, spread the previously prepared mulch piles evenly over the surface of the ground. If you are doing spring or summer mulching, create a 2.5–5 cm layer of mulch throughout the mulch area. If you are using coarse inorganic mulching material, it can be spread by hand without using a rake. Add more mulch with a shovel as needed. - If you are doing winter mulching or mulching the ground to keep weeds out, you can create a layer 10 cm thick.
- Leave an empty space of about 2.5 cm between tree trunks or plant stems and mulch.
 6 Drizzle over organic mulch. Watering your organic mulch with a garden hose will keep it hydrated and keep it from scattering in the wind. Be careful not to overmoisten the mulch, otherwise water will start to collect in puddles right on it, and this will adversely affect your plants.
6 Drizzle over organic mulch. Watering your organic mulch with a garden hose will keep it hydrated and keep it from scattering in the wind. Be careful not to overmoisten the mulch, otherwise water will start to collect in puddles right on it, and this will adversely affect your plants.  7 Replace organic mulch annually. Organic mulching materials degrade over time, losing most of their beneficial properties. For this reason, it is necessary to remove the layer of old organic mulch from the soil at about the same time every year and replace it with a new one.
7 Replace organic mulch annually. Organic mulching materials degrade over time, losing most of their beneficial properties. For this reason, it is necessary to remove the layer of old organic mulch from the soil at about the same time every year and replace it with a new one. - Sawdust usually lasts longer than other organic mulches, but turns gray over time.
 8 Replace inorganic mulching materials when they lose their appearance. Inorganic mulch lasts much longer than organic mulch and does not need to be replaced frequently. If the gravel or pebbles become dirty, they can simply be hosed to clean them instead of replacing them.
8 Replace inorganic mulching materials when they lose their appearance. Inorganic mulch lasts much longer than organic mulch and does not need to be replaced frequently. If the gravel or pebbles become dirty, they can simply be hosed to clean them instead of replacing them.
What do you need
- Shovel
- Wheelbarrow
- garden hose
- Lawn edge shovel (optional)
Warnings
- Organic cocoa husk mulch is toxic to dogs.