Author:
Bobbie Johnson
Date Of Creation:
5 April 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 3: Changing Your Diet
- Method 2 of 3: Physical activity and lifestyle changes
- Method 3 of 3: Medicines
- Tips
- Warnings
Elevated triglyceride levels can lead to an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease. If you need to quickly lower your triglyceride levels, the following lifestyle changes and medications can help you achieve positive results.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Changing Your Diet
 1 Eliminate sweets from your diet. Refined sugar can cause triglyceride spikes, so one of the fastest ways to lower triglyceride levels is to cut back on sweets.This is due to the fact that most often sugar contains empty calories, which are converted into triglycerides, and subsequently into body fat.
1 Eliminate sweets from your diet. Refined sugar can cause triglyceride spikes, so one of the fastest ways to lower triglyceride levels is to cut back on sweets.This is due to the fact that most often sugar contains empty calories, which are converted into triglycerides, and subsequently into body fat. - Limit sugar to 5-10% of your daily calorie intake. This means that women can consume 100 calories of sweets per day, while men can consume up to 150 calories.
- Avoid foods like sweet desserts and concentrated fruit juices.
 2 Reduce refined carbs. In some people, white rice and white flour baked goods and semolina can increase triglyceride levels. If your doctor suspects that the cause of the increase in triglycerides is related to the use of the above foods, then make changes to your diet by limiting the use of such foods. This will significantly reduce triglyceride levels.
2 Reduce refined carbs. In some people, white rice and white flour baked goods and semolina can increase triglyceride levels. If your doctor suspects that the cause of the increase in triglycerides is related to the use of the above foods, then make changes to your diet by limiting the use of such foods. This will significantly reduce triglyceride levels. - Choose whole grain breads and pasta instead of refined carbohydrate foods.
- Reduce your intake of foods high in carbohydrates. Include more protein in your diet. Proteins have a lower "glycemic index" compared to carbohydrates, which means they are digested and absorbed more slowly. This in turn helps lower blood sugar and lipid levels (including triglyceride levels). Also include healthy fats in your diet as they help stabilize blood sugar and lower triglyceride levels.
 3 Eliminate alcohol from your diet. Alcohol can significantly increase triglyceride levels, especially in alcohol-sensitive people. It is highly recommended that you eliminate alcohol from your diet while you are trying to lower your triglyceride levels.
3 Eliminate alcohol from your diet. Alcohol can significantly increase triglyceride levels, especially in alcohol-sensitive people. It is highly recommended that you eliminate alcohol from your diet while you are trying to lower your triglyceride levels. - Once your triglycerides have returned to normal levels, you can gradually introduce alcoholic beverages into your diet. However, do not drink too much or too often, as this may again not have the best effect on triglyceride levels.
 4 Include foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids in your diet. Omega-3 fatty acids are considered "good" fats, so consuming them regularly can help the body reduce triglyceride levels.
4 Include foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids in your diet. Omega-3 fatty acids are considered "good" fats, so consuming them regularly can help the body reduce triglyceride levels. - Include about two servings of oily fish per week in your diet. If you do this regularly, you will likely notice a drop in triglyceride levels soon.
- Fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids: salmon, mackerel, sardines, tuna and trout.
- Other sources of omega-3 fatty acids include ground flaxseed, flaxseed oil, soy, legumes, walnuts, and dark green leafy vegetables. Include these foods in your daily diet.
- You can take omega-3 supplements as it improves your omega-6 to omega-3 ratio.
 5 Include plant-based foods in your diet. Especially if you prefer plant-based protein (over red meat), you will soon find that your cholesterol and triglyceride levels have dropped significantly.
5 Include plant-based foods in your diet. Especially if you prefer plant-based protein (over red meat), you will soon find that your cholesterol and triglyceride levels have dropped significantly. - Protein-rich foods: Dried beans, peas, and soy foods.
- You can also substitute chicken for red meat as it is the best alternative for lowering triglycerides.
 6 Include fiber-rich foods in your diet. Fiber promotes digestion and absorption of food, so foods high in fiber can significantly lower triglycerides and cholesterol levels.
6 Include fiber-rich foods in your diet. Fiber promotes digestion and absorption of food, so foods high in fiber can significantly lower triglycerides and cholesterol levels. - Fiber, absorbing water in the intestine, becomes a gel-like mass, to which fats "attach" well. It helps reduce the level of fats (including triglycerides) that are absorbed by the body. In addition, fiber has a beneficial effect on the digestive system as a whole.
- Include more cereals in your diet to get enough fiber. Also, eat legumes, fruits, and vegetables.
- Fiber also gives you a feeling of fullness so you don't eat too much.
- Drink more water if you are increasing your fiber intake. Otherwise, you may experience moderate to severe intestinal upset.
 7 Keep track of what fats you eat, and how much. Saturated and trans fats are especially bad, so avoiding them can significantly lower triglyceride levels.
7 Keep track of what fats you eat, and how much. Saturated and trans fats are especially bad, so avoiding them can significantly lower triglyceride levels. - Most of these "bad" fats are found in packaged foods and fast food. Animal products, as well as foods made with hydrogenated vegetable oil, butter, fat, lard and margarine, can be sources of "bad" fats.
- Give preference to mono- and polyunsaturated fats. Your body needs to get some fat on a daily basis, and these sources are considered healthy and do not affect triglyceride levels. Sources of "good" fats include olive oil, rapeseed oil, rice bran, walnut oil, and flaxseed oil.
 8 Limit your fructose intake. Fructose is a natural sugar found in most fruits, as well as honey and some table sugar. Eating less than 50-100 grams of fructose per day will help lower triglyceride levels faster.
8 Limit your fructose intake. Fructose is a natural sugar found in most fruits, as well as honey and some table sugar. Eating less than 50-100 grams of fructose per day will help lower triglyceride levels faster. - Low fructose fruits: apricots, citrus fruits, melons, strawberries, avocados, and tomatoes if you want to eat some kind of fruit, then give preference to one of the above.
- High fructose fruits: mangoes, bananas, grapes, pears, apples, watermelon, pineapples, and blackberries Eliminate these fruits from your diet, or at least significantly reduce their intake.
Method 2 of 3: Physical activity and lifestyle changes
 1 Monitor your calorie intake. Pay close attention to how many calories you consume daily and consider if you can reduce that amount (consult your doctor about this).
1 Monitor your calorie intake. Pay close attention to how many calories you consume daily and consider if you can reduce that amount (consult your doctor about this). - This is especially useful if you are overweight or obese. Being overweight can cause high triglyceride levels.
- Women should consume 1200 calories per day, men 1800 calories per day (value may vary depending on physical activity and other factors). If you desperately need to lose weight or reduce your calorie intake, your doctor may recommend a lower calorie diet. However, do not start following any diet without first consulting your doctor.
- Also, avoid snacking before bed.
 2 Eat small meals. Try to eat more often, but little by little. This is better than two or three large meals a day.
2 Eat small meals. Try to eat more often, but little by little. This is better than two or three large meals a day.  3 Go in for sports. Moderate exercise is essential if you want to lower your cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
3 Go in for sports. Moderate exercise is essential if you want to lower your cholesterol and triglyceride levels. - Don't set a rigorous training regimen. You may think that vigorous exercise can help you reduce triglyceride levels faster, but in reality you are not. Setting the bar too high is more likely to set yourself up for failure. Start with 10 minute sessions and add 1-2 minutes each week until you reach 30-40 minutes.
- Diversify your activities. You can walk, cycle, or exercise with the course on DVD. Get creative. Thanks to this, you will not be bored and you will study with great enthusiasm. It will also help you find a form of exercise that you enjoy!
 4 Stop smoking. Quitting smoking is an important step in reducing your risk of heart disease. Plus, it helps lower triglyceride levels.
4 Stop smoking. Quitting smoking is an important step in reducing your risk of heart disease. Plus, it helps lower triglyceride levels. - Smoking is a risk factor for heart disease, including increased blood clotting, damage to arteries, and a decrease in the body's ability to control blood lipids (including triglycerides).
- Quitting smoking significantly improves overall health. Find a program in your city (or region) that will help you quit smoking, or contact a therapist for advice.
Method 3 of 3: Medicines
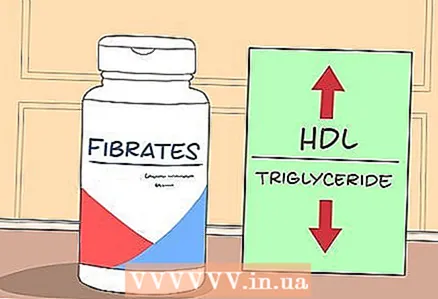 1 Take fibrates. Typically, doctors prescribe gemfibrozil and fenofibrate.
1 Take fibrates. Typically, doctors prescribe gemfibrozil and fenofibrate. - Fibrates are organic compounds from the group of carboxylic acids that have an amphipathic effect, that is, they attract both water molecules and fat molecules.
- These drugs raise HDL levels and lower triglyceride levels. It does this by reducing the liver's production of triglyceride-carrying particles.
- Note that fibrates can cause digestive upset and liver dysfunction, as well as contribute to the formation of gallstones. They are also dangerous if used with blood thinners. Fibrates can also cause muscle damage when taken with statins.
 2 Take nicotinic acid. Nicotinic acid is a form of niacin.
2 Take nicotinic acid. Nicotinic acid is a form of niacin. - Nicotinic acid is also a carboxylic acid.
- Like fibrates, niacin reduces the liver's ability to produce triglyceride-carrying particles called very low density lipoproteins.
- Nicotinic acid raises HDL ("good") cholesterol levels much better than other drugs of this type.
- Check with your doctor before taking these drugs as they can interact with other drugs and cause dangerous side effects.
- Possible side effects of niacin are: shortness of breath, severe abdominal pain, jaundice, and dizziness. Although they are rare, it is very important to be aware of the possible side effects.
 3 Learn about prescription omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids can lower triglyceride levels, and high doses of prescription omega-3s can lower triglyceride levels even faster.
3 Learn about prescription omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids can lower triglyceride levels, and high doses of prescription omega-3s can lower triglyceride levels even faster. - Prescription omega-3s are usually available as fish oil pills.
- Take high doses of omega-3s as directed and under your doctor's supervision as they may interact with other medications. Too much omega-3s cause excessive blood thinning and lower blood pressure. They can also raise blood sugar levels and impair liver function. In addition, high doses of omega-3s can lead to mental health problems.
 4 Learn about statins. The most commonly used statin is atorvastatin. Other popular statins are fluvastatin, lovastatin, pitavastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin, and simvastatin.
4 Learn about statins. The most commonly used statin is atorvastatin. Other popular statins are fluvastatin, lovastatin, pitavastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin, and simvastatin. - These drugs lower cholesterol levels by blocking an enzyme known as HMG-CoA reductase. This enzyme plays a key role in the production of cholesterol.
- The main goal of a statin is to lower LDL cholesterol. The drug can also reduce triglycerides, but it is less effective than many other drugs designed for this purpose.
- Side effects are extremely rare, but they are quite severe. The main side effect is muscle damage, especially if statins are used in conjunction with fibrates. In addition, statins can cause liver problems and increase the risk of diabetes.
- Beware of the symptoms of excess omega-3 intake. These may include oily skin / acne, greasy hair, and general weakness.
Tips
- Before making any significant changes to your lifestyle, you must be aware of the implications. High triglyceride levels are one of the main risk factors for heart disease (including heart attacks, strokes and atherosclerosis, that is, a decrease in the elasticity of the vascular walls).
- Triglycerides also affect metabolic syndrome.Metabolic Syndrome Symptoms: High blood pressure, high triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, increased waist circumference, and / or high blood sugar. Metabolic syndrome is a lifestyle disorder that increases the risk of heart disease, diabetes, fatty liver and certain cancers. Thus, these are a few more reasons why you need to monitor your triglyceride levels.
- The more positive changes you make to your lifestyle, including healthy eating and exercise (in addition to the medication prescribed by your doctor), the more likely you are to feel happy and live a healthy and fulfilling life. Sometimes the hardest part is taking the first step, but once you see progress, you will surely have additional motivation!
Warnings
- Always check with your doctor before making dietary and exercise changes. Sudden changes, even beneficial ones, can negatively affect overall health.