Author:
Christy White
Date Of Creation:
5 May 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- To step
- Method 1 of 3: Estimate kilowatt hours using the information on the label
- Method 2 of 3: Determine kilowatt hours from the amperage and voltage
- Method 3 of 3: Using a power meter
- Tips
Most household appliances have an electrical rating label on the back or bottom. This label specifies the maximum power of the device. To estimate the total energy consumption of the appliance, you will have to convert this to kilowatt hours, or kWh.
To step
Method 1 of 3: Estimate kilowatt hours using the information on the label
 Look for the worry on the device's label. Most high-power devices have an energy label on the back or bottom. There you will find the power, often stated in Watts ("W"). This is usually it maximum power under which the device operates, which can be much higher than the actual average power. The steps below provide a rough estimate of the number of kWh derived from this number, but the actual kWh consumption is usually lower.
Look for the worry on the device's label. Most high-power devices have an energy label on the back or bottom. There you will find the power, often stated in Watts ("W"). This is usually it maximum power under which the device operates, which can be much higher than the actual average power. The steps below provide a rough estimate of the number of kWh derived from this number, but the actual kWh consumption is usually lower. - Some devices indicate a power range, such as "200-300W". It may be more accurate to choose the average of this range (250W in this example).
 Multiply the power by the number of hours of use per day. Power measures power, or energy consumption over time. By multiplying by a unit of time, you get an answer in terms of energy, which is important for your energy bill.
Multiply the power by the number of hours of use per day. Power measures power, or energy consumption over time. By multiplying by a unit of time, you get an answer in terms of energy, which is important for your energy bill. - Example: A large 250-watt window fan runs on average for 5 hours a day. The number of watt hours per day is equal to (250 watts) x (5 hours / day) =1250 watt-hours per day.
- For air conditioning and heating you make separate calculations per season.
- A refrigerator only draws power about ⅓ of the time, or about 8 hours a day when the refrigerator is always on.
 Divide the result by 1000. A kilowatt equals 1000 watts, so this step converts your answer from watt-hours to kilowatt-hours.
Divide the result by 1000. A kilowatt equals 1000 watts, so this step converts your answer from watt-hours to kilowatt-hours. - Example: You have calculated that the fan uses 1250 watt-hours of energy per day. (1250 watt-hours / day) ÷ (1000 watts / 1 kilowatt) =1.25 kilowatt hours per day.
 Multiply your answer by the number of days you measure. Now you know how many kilowatt hours (kWh) the appliance uses every day. To calculate the number of kWh per month or per year, simply multiply by the number of days in that period.
Multiply your answer by the number of days you measure. Now you know how many kilowatt hours (kWh) the appliance uses every day. To calculate the number of kWh per month or per year, simply multiply by the number of days in that period. - Example: Over the course of a 30-day month, your fan will consume (1.25 kWh / day) x (30 days / month) =37.5 kWh per month.
- Example: If the fan runs every day for a year, it consumes (1.25 kWh / day) x (365 days / year) =456.25 kWh per year.
 Multiply this by the price for electricity per kWh. Your electricity bill indicates the costs per kilowatt hour. Multiply this number by the number of kWh for the amount you are expected to pay.
Multiply this by the price for electricity per kWh. Your electricity bill indicates the costs per kilowatt hour. Multiply this number by the number of kWh for the amount you are expected to pay. - Example: If energy costs 17 cents / kWh, running the fan will (0.17 euro / kWh) x (456.25 kWh / year) =€ 77.56 per year going to cost (rounded to cents).
- Remember that an estimate based on the power displayed is a maximum. In reality, your bill may be much lower.
- If you want to know what this would cost in a different environment than where you live, search online for an overview of the electricity costs. For locations in the US, you can start with the EIA website.
Method 2 of 3: Determine kilowatt hours from the amperage and voltage
 Find the amperage (amps) for your device. Some appliance labels do not indicate wattage. In such a case, look for the value for ampere or "A".
Find the amperage (amps) for your device. Some appliance labels do not indicate wattage. In such a case, look for the value for ampere or "A". - The laptop and phone chargers may display two amperage values. In that case, take the value Input.
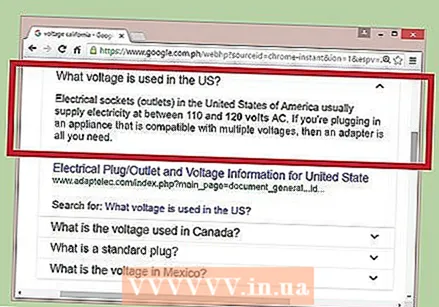 Find the voltage in your area. In the United States and a few other countries, the standard household voltage is 120V. In the EU and most other countries in the rest of the world, the voltage falls between 220V and 240V.
Find the voltage in your area. In the United States and a few other countries, the standard household voltage is 120V. In the EU and most other countries in the rest of the world, the voltage falls between 220V and 240V. - In the US, some large appliances such as washing machines can be connected to dedicated 240V circuits. Check the voltage on the device label to find out. (The label will not give you more than the recommended voltage, but you can assume that a professionally installed appliance meets this recommendation.)
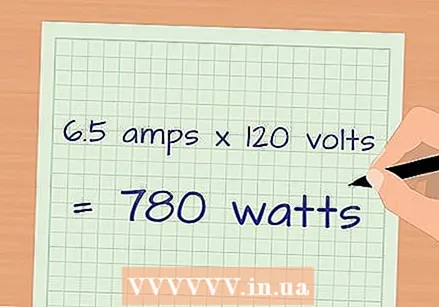 Multiply the amperage by the voltage. By multiplying the amperage by the voltage, you get an answer in watts, or electrical power.
Multiply the amperage by the voltage. By multiplying the amperage by the voltage, you get an answer in watts, or electrical power. - Example: The label of a microwave oven reads 3.4 A and is connected to a 230 V wall socket. The appliance consumes 3.4 A x 120 V ≈ 780 W..
 Multiply this by the usage per day. The wattage gives you an indication of the extent to which energy is consumed when the device is on. Multiply the wattage by the number of hours the appliance is on during a typical day.
Multiply this by the usage per day. The wattage gives you an indication of the extent to which energy is consumed when the device is on. Multiply the wattage by the number of hours the appliance is on during a typical day. - Example: If the microwave has been in use for half an hour every day, this is 780 watts x 0.5 hours / day =390 watt-hours per day.
 Divide this by 1000. In this way you convert watt-hours to kilowatt-hours.
Divide this by 1000. In this way you convert watt-hours to kilowatt-hours. - Example: 390 watt hours / day ÷ 1000 watts / kilowatts =0.39 kilowatt hours per day.
 Multiply to find the number of kilowatt hours over a longer period. For example, if you want to know how many kilowatt-hours will be billed in a 31-day period, multiply your answer by 31 days.
Multiply to find the number of kilowatt hours over a longer period. For example, if you want to know how many kilowatt-hours will be billed in a 31-day period, multiply your answer by 31 days. - Example: 0.39 kilowatt hours / day x 31 days =12.09 kilowatt hours.
Method 3 of 3: Using a power meter
 Buy a power meter online. Also called a wattage meter or kilowatt meter, this measures the actual power consumed by a device. This is usually more accurate than using the information on the device label.
Buy a power meter online. Also called a wattage meter or kilowatt meter, this measures the actual power consumed by a device. This is usually more accurate than using the information on the device label. - If you are familiar with tools for electricians, you can also use a multimeter. This does require access to the device's wiring while it is connected. It can't be said often enough, but never take anything apart unless you know what you're doing.
 Connect the meter between the wall outlet and the device. Plug the power meter into the wall socket. Connect the device to the power meter.
Connect the meter between the wall outlet and the device. Plug the power meter into the wall socket. Connect the device to the power meter.  Measure the kilowatt hour. Set your meter to show the number of kilowatt hours. As long as the meter remains plugged in, it calculates the total kilowatt hours of the connected device.
Measure the kilowatt hour. Set your meter to show the number of kilowatt hours. As long as the meter remains plugged in, it calculates the total kilowatt hours of the connected device. - If your meter can only measure wattages, you can use the above method to calculate the number of kilowatt hours based on this reading.
- Read the manual of the meter if you are unsure how to change its settings.
 Use the device as usual. The longer you leave the meter plugged in, the more accurate the calculation will be.
Use the device as usual. The longer you leave the meter plugged in, the more accurate the calculation will be. 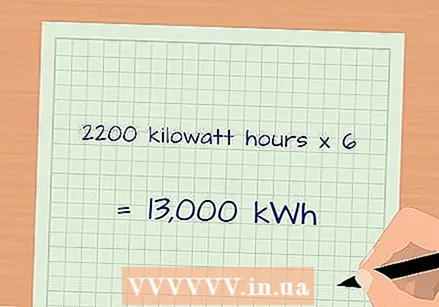 Determine the monthly or annual consumption in kilowatt hours. The number of kilowatt hours as indicated on the meter is a running total from the time the device is connected. You can multiply this number to estimate the number of kWh over a longer period of time.
Determine the monthly or annual consumption in kilowatt hours. The number of kilowatt hours as indicated on the meter is a running total from the time the device is connected. You can multiply this number to estimate the number of kWh over a longer period of time. - For example, suppose the meter has been running for 5 days and you want to know the estimate for 30 days. 30 divided by 5 is 6, so multiply the number of kWh as shown by 6.
Tips
- If the label does not say wattage, refer to the device user manual. Many modern labels do all the work for you, including listing yellow energy labels in the US and blue / white labels in the EU. Find the number of kilowatt hours as indicated as "kWh / year", "kWh / annum" (year), or "kWh / 60minutes". These are based on typical household usage and often more accurate than the calculations below.
- Some devices have multiple power settings. The labels may show separate information for each setting, or just the maximum.



