Author:
Laura McKinney
Date Of Creation:
6 August 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
One of the most important factors a woman can conceive is the menstrual cycle. The length of time you have sex with your partner during the conception days of the menstrual cycle and when it falls apart can greatly increase your chances of getting pregnant. Before you can identify the most fertile days, also known as the time of conception, you need to have a better understanding of the menstrual cycle and proper monitoring.
Steps
Part 1 of 2: Understanding the Menstrual Cycle
Identify the key phases of your menstrual cycle. The menstrual cycle has several phases, but that doesn't mean you can conceive the entire cycle or cycle. In fact, there is a perception that a woman can conceive during the entire menstrual cycle. But really you can only get pregnant on the days that are most fertile, before and during ovulation. Eggs are released when they are ripe and are released from the ovaries, and travel down the fallopian tube so that sperm can be fertilized. The stages in a menstrual cycle are: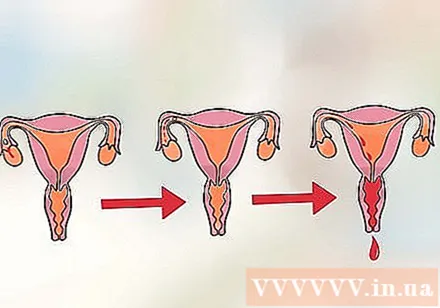
- Menstrual blood, the start of the menstrual cycle. It comes when the body pushes the endometrium out of the body through the vagina. Thus causes menstrual bleeding during the cycle, and usually lasts 3 to 7 days. It also marks the first day of ovarian follicle development stage, stimulates the ovarian follicle to grow, and in this follicle contains eggs. This phase ends when ovulation. Ovarian follicle development usually lasts 13-14 days, but can also last 11-21 days.
- Ovulation stage occurs when the concentration of the corpus luteum-stimulating hormone increases with a high concentration. It will stimulate ovulation. This stage is quite short, usually lasts only 16-32 hours, and ends when the body is ovulating.
- Luteum stage starts after ovulation and continues until the start of the next cycle. It helps prepare the uterus in case the egg is fertilized and implanted into the uterine wall. This phase usually starts about 14 days in the cycle and lasts about 14 days.

Be aware of the stage of fertility or when to conceive. This is the time in your menstrual cycle when you are most likely to get pregnant during sex. For most women, conception takes about six days.- Keep in mind that having sex during the fertile stage doesn't guarantee you will conceive. But your chances of conception are greatly increased if you have sex during the 5 days before ovulation and 24 hours after ovulation. Healthy, fertile couples usually have a 20-37% chance of getting pregnant based on how long they are conceived.
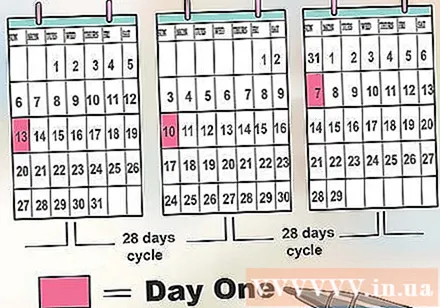
Determine whether your menstrual cycle is regular or not. Every woman's cycle will be different and can vary or vary based on external factors such as stress. The best way to determine whether your cycle is even or not where your period will come at almost the same day each month is to chart your period for three or four months to see how long it lasts.- Mark on the calendar the first day of the cycle. Mark it as Day One. Then count each day until the next cycle visits. Remember that the average cycle is 28 days; however, your cycle can range from 21 to 35 days.
- Perform in three to four months. Note if your cycle is equally long each month.
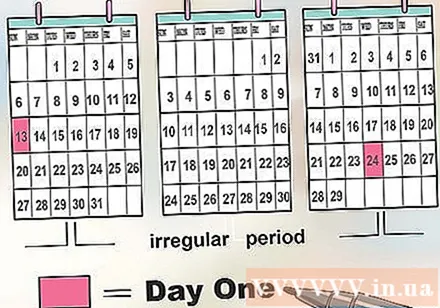
Determine whether your menstrual blood is regular or not. If after three to four months of monitoring your menstrual cycle and you don't notice your period appearing, then you may have irregular menstrual periods. This phenomenon occurs in many women and can be caused by many factors such as excessive weight loss, excessive physical activity, stress, or some serious biological problem. Talk to your doctor if you have irregular periods to find out about any underlying health conditions. Women with irregular menstrual cycles can still track conception time, but it will take more time and effort than women with regular cycles.- Talk to your doctor if your cycle has not come within 90 days or more and you are not pregnant at all. If your cycle is irregular after having been regular, or you have a period in the middle of your period, talk to your doctor to make sure you don't have a hormone disorder, reproductive organ infection, or health problems another strong.
Part 2 of 2: Timing Conception
Based on the time of the cycle to determine when to conceive. If your cycle is regular, you can determine when to conceive based on the number of menstrual days you normally have. Your conception date will be the previous six days and include ovulation. But your most fertile day will be three days before your period and ovulation included. Determine the most fertile time based on the duration of the cycle by subtracting the total number of days from the cycle from 14 days: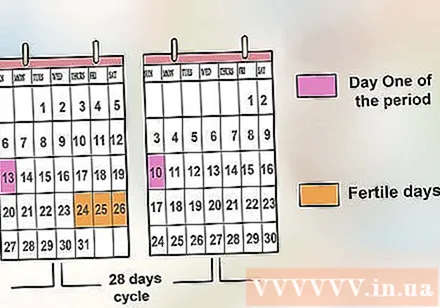
- 28-day cycle: If your cycle is usually 28 days, the date of ovulation will be the 14th day of your cycle. So the most fertile days would be the 12th, 13th, and 14th.
- 35-day cycle: If you have a longer menstrual cycle, your eggs will ovulate on the 21st and your most fertile days will be 19, 20, and 21.
- 21-day cycle: If you have a shorter menstrual cycle, eggs will ovulate on day 7 and your most fertile days are 5, 6, and 7.
- If your menstrual cycle is regular, but doesn't fall into one, you can use an online conception date calculator to determine when to conceive. All you need to do and determine the first date of your past cycle.
Check your body temperature or use an ovulation prediction kit if you have irregular periods. If you often have irregular periods, or if you feel your cycle might stop, you can use other methods to determine when an egg will ovulate: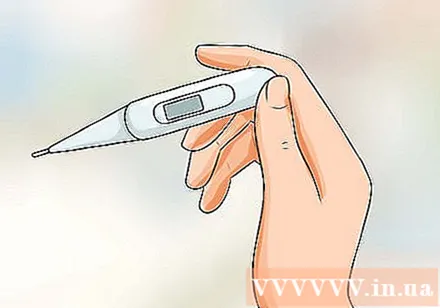
- Monitor body temperature. During ovulation, your body temperature will increase. Notice if your body has a “change in temperature” by taking your temperature at the same time every morning. Most women experience a half a degree change in body temperature between 24-48 hours after ovulation. You can use an ordinary thermometer or buy a special thermometer.
- Use an ovulation prediction kit. You can find an ovulation prediction kit at the pharmacy. Although it is more expensive to use when you need to monitor your body temperature, it is also a more accurate way to determine when to ovulate. This kit will check your urine to determine the luteinizing hormone (LH) level in your urine. You need to urinate on the test strip to determine when lutein levels are rising. This is a sign that either of the preceding ovaries is about to release an egg, or that you are about to ovulate.
- Watch for changes in the uterine fluid. During the pre-ovulation cycle, your body produces large amounts of clear, fluid. This fluid will create a convenient way for the sperm to meet the egg. Just before you start ovulating, you may notice fluid on the bottom of your underwear or around your vagina. It will be transparent, stretchable, and smooth like raw egg whites. You can take a sample of the vaginal discharge by gently wiping a tissue with a clean finger or tissue from the vaginal opening. If you check the vaginal discharge a few times a day and don't see any fluid, then you are not in the middle of a cycle of pregnancy.
Have sex during conception. Most doctors will recommend having sex with your partner every day or even every day for 5 days before ovulation and until the day after ovulation. Although sperm can live up to five days in a woman's body, but the lifespan of an egg is only 12-24 hours, it is advisable to have sex before ovulation, on the same day of ovulation and the day after. maximizes your chances of conceiving.
- Focus on having sex during conception, or three to five days before ovulation. If you wait until you start ovulating to have sex, when the sperm enters your body, it may be too late for the sperm to fertilize the egg.
- If you are under 35 years old and have been sexually active during both ovulation and non-ovulation for 12 months, or if you are 35 years or older and have been sexually active both during ovulation and both During the non-ovulation period for six months, you should see your doctor to evaluate your fertility. You and your partner can do a fertility test to determine if there are other problems that are preventing you from getting pregnant.
What you need
- Calendar
- Thermometer
- Ovulation prediction kit