Author:
Louise Ward
Date Of Creation:
11 February 2021
Update Date:
12 May 2024

Content
- Since weight is a force, the scientists wrote this formula in another way F = mg.
- F = weight symbol, measured in Newtons, N.
- m = mass symbol, in kilograms, kg.
- g = denotes the acceleration of gravity, in units of m / s, ie meters per second squared.
- When you use unit is ''meters, the gravitational acceleration on the earth's surface will be 9.8 m / s. This is the value with the international standard units and you should use it.
- If you must use it feet then the value of gravity acceleration you need to use is 32.2 f / s, essentially the value does not change but only in feet instead of meters.

Determined mass of an object. Since we are looking for weight based on mass, we already know the value of mass. Mass is the amount of substance contained in an object, expressed in kilograms.

- The acceleration of gravity on the moon is different from the acceleration of gravity on the earth. Acceleration caused by gravity on the moon is worth about 1,622 m / s, which is about 1/6 of the corresponding value on earth. That is why the weight on your moon is only one-sixth of the weight on earth.
- The acceleration of gravity on the sun is also different from the acceleration of gravity on the moon and earth. In the sun, acceleration caused by gravity has a value of about 274.0 m / s, about 28 times that of acceleration caused by gravity on earth. So you would be 28 times heavier if you could survive in the sun.
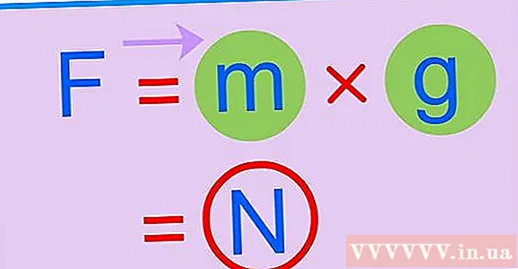
Plug the values into the formula. When had the value of m and g, you plug these values into the formula F = mg. The result of this calculation will be in units of Newtons, denoted by N. advertisement
Part 2 of 3: Example
Example 1."An object has a mass of 100 kilograms. What is the weight of the object on the earth?"
- I have the value of both m and g. Because we're looking for the weight of things on earth, so m equal to 100kg and g is 9.8 m / s.
- Putting the values into the formula gives: F = 100 kg x 9.8 m / s.
- Performing this calculation will get the final result. On the surface of the earth, an object with a mass of 100 kg would weigh about 980 Newtons. F = 980 N.

Example 2."An object has a mass of 40 kilograms. What is the weight of the object on the moon?"- I have the value of m and g. Inside, m equal to 40 kg, g is 1.6 m / s since we are examining things on the moon.
- Putting these two values into the formula, we have: F = 40 kg x 1.6 m / s.
- Perform the multiplication to get the final result. On the moon, an object with a mass of 40 kg would weigh about 64 Newtons. F = 64 N.
Listing 3."An object has a weight of 549 Newtons on the earth. What is the mass of the object?"
- This example is an inverse problem in which we have the value of F and g. We need to calculate m.
- Replace known values into the formula we have: 549 = m x 9.8 m / s.
- Instead of multiplying, we do the division. More specifically, we take F divide g. An object weighing 549 Newtons on earth has a mass of about 56 kilograms. m = 56 kg.
Part 3 of 3: Proofreading
Limit confusion between mass and weight. The most common mistake in this form of question is the confusion between mass and weight. Remember that mass is the amount of "substance" of an object, which is a constant value, regardless of the object's position. Weight, on the other hand, is the gravitational force acting on the amount of "substance" of an object and can change in different places. Here are some tips to help you distinguish these two:
- Mass is in units of grams or kilograms.In English, both volume (mass) and gram (gram) are text m. Weight is in units Newton. In English, weight (weight) and Newton (newton) have words w.
- For those of you who study in English or use English fluently, you can remember this sentence: You only have weight while you’re "wait"ing on Earth, but even"mass"tronauts have mass.
Using international metrology. Most physics problems use Newton units (N) for weight, meters per second squared (m / s) for gravity, and kilogram (kg) for mass. If you use other units, you can not apply the formulas outlined in this article if you have not yet converted the values to international measurement systems. Here are some common conversion values:
- 1 pound force = ~ 4,448 newtons
- 1 foot = ~ 0.3048 meters
Expands newton for unit testing. If you are working on a complex problem, check the units while solving the problem. Note that 1 newton equals 1 (kg * m) / s. If necessary, you can use this type of unit to suppress the unit in the calculation.
- Example: On the ground, An has a weight of 880 newton. What is the mass of An?
- Volume = (880 newtons) / (9.8 m / s)
- Volume = 90 newtons / (m / s)
- Weight = (90 kg * m / s) / (m / s)
- After annihilating the unit we have: mass = 90 kg
- Kg is the unit of mass, so we have calculated correctly.
Appendix: Weight in kgf
- Newton is the international system of measurement (SI-unit). However, in some documents and in some countries weight is also expressed in kilogram-force (kgf). This is not a standard unit, so it is generally less acceptable. However, using kgf is very convenient for comparing weight elsewhere with weights on earth.
- 1 kgf = 9,80665 N.
- Divide the Newton value by 9,80665, or include the number after the last comma when you know it.
- The weight of a 101 kg astronaut is 101.3 kgf at the North Pole point and 16.5 kgf while he is on the moon.
- What is International Measurement System (SI-unit)? SI-unit is the abbreviation of Systeme International d’Unites (translated into Vietnamese as International metrology system), is a system of regulations on measurement units in science.
Advice
- Distinguishing the difference between mass and weight is the most difficult part of this type of exercise, because normally we tend to use these two terms equivalent. In everyday life, we often use kilogram when it comes to weight instead of Newton or kgf. Even if your doctor wants to talk about your weight, they really want to talk about your mass.
- The acceleration of gravity g can also be written in units of N / kg. 1N / kg = 1 m / s. So changing the unit of the gravitational acceleration does not change its value.
- An astronaut with a 100kg glider would weigh 982.2 N at the North Pole and 162.0N while on the moon. If standing on a neutron star, this person would be even heavier, but he probably wouldn't be able to feel it.
- A scale is a mass measuring device (in kg) in which your weight is calculated based on the compression or expansion of the spring.
- The Newton unit is preferred over kgf because it makes it easier to calculate other values.
Warning
- The term 'atomic weight' (English is atomic weight) has nothing to do with the weight of the atom but to the mass (mass). This calling may not change, because 'atomic mass' has been used for another quantity.