Author:
Randy Alexander
Date Of Creation:
28 April 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
Sugar maple (scientific name Acer saccharumIt grows abundantly in the northeastern part of the North American continent: the northeastern United States (extending south to Tennessee) and the southeastern regions of Canada. Sugar maple has very strong wood and supplies maple syrup, two items that make a significant contribution to the local economy. The sugar maple is known as the iconic tree of New York State, and its image printed on the Canadian flag is proof of the plant's economic importance. You can identify a sugar maple tree by the features of its leaves, bark, branches and small fruits.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Identify the sugar maple tree based on its leaves
Observe carefully the color of the leaves. The maple leaf is dark green on the top and lighter green on the bottom. In autumn, the leaves change color from green to gorgeous yellow, orange or red.

Count the leaf lobes. Sugar maple leaves are divided into many parts including 5 lobes. There are 3 large main lobes in the middle of the leaves and 2 smaller lobes on the sides. Leaf lobes are prominent with pointed serrations and have shallow U-shaped notches between lobes.- Some stunted or underdeveloped leaves will have only 3-4 lobes. If you suspect a tree is a sugar maple but see a leaf with less than 5 lobes, look around and look for other leaves that could model better.
- You can distinguish the leaves of the silver maple (Acer saccharinum) with sugar maple leaves. The leaves of the silver maple have very deep grooves between the lobes, and the underside of the leaves is silver or white.

Examine the edges of the leaves. Sugar maple leaves have a U-shaped smooth edge between the sharp peaks. The leaves are also round at the base of the leaves.- Although many other maple species also have smooth leaf margins, the extremely popular one is the red-leaf maple (Acer rubrum) have pointed tips and serrated leaf margins between lobes. This can be a very useful distinguishing feature.
- The leaf stalk of a maple tree, the part that connects the leaves to the branch, is equal in length (or slightly shorter) to the length of the leaf blade.

Check the leaf growth pattern on the branches. Find leaves that are perpendicular to pairs on the branch. This is called opposite leaf pattern. The leaves will grow in "pairs" of 2 leaves, always symmetrical on each branch and branch.- Only a single leaf grows from each leaf stalk.
Measure the leaf size. The mature leaves of the sugar maple are about equal length in width (about 8 cm to 13 cm).
- If you're going to check leaves in the woods and don't have a ruler, you can measure the length of a knuckle and use it as a relative gauge in place. For example, the length from the tip of the thumb to the first joint is usually about 2.5 cm.
Find the three main veins on the leaf. Each lobe has a vein that runs the entire length of the lobe, but two smaller lateral lobes have no veins on it. These veins are prominent on the undersides of leaves, and smooth on the upper surfaces of leaves.
- On the underside of the leaves, the veins can be a little "rough."
Method 2 of 3: Identify the maple tree based on the bark and branches
Observe that the bark is brown and grooved. The bark of the sugar maple tree changes color with the age of the tree. Young trees have gray-brown bark. As the tree matures, the bark is darker brown. Another feature is that the bark has grooves that run vertically and close together.
- The bark is described as “grooved” with deep cracks between the bark fragments.
- Sugar maple is often confused with Norwegian maple (Acer platanoides) in Europe and West Asia. The easiest way to differentiate these two species of maple is from the bark: The bark of a young Norwegian maple tree has a thin layer. Gradually, the Norwegian maple will develop longitudinal grooves, but they are not as deep and as pronounced as the grooves of the sugar maple, and the edges of the bark fragments do not prune much either.
Examine the edge of the bark. The edges of each piece of the maple bark will gradually rise up as the tree gets older, and pieces of bark will peel off from top to bottom as the tree reaches maturity.
- The mature sugar maple tree looks "rough" in the distance due to the peeling of the bark.
Examine the tip of the branch. Branches are small, thin branches that grow from the larger branches and are where leaves come from. Look for branches that are thin, shiny, and reddish-brown. The small shoots at the tip of the branch are covered in small brown scales.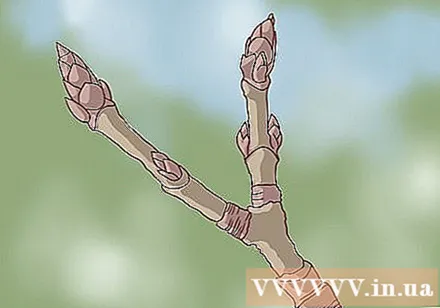
- During the winter months, conical buds will grow opposite along the length of the branch, and a larger shoot will grow upright on the tip of the branch.
- The leaf buds on the branches are also helpful for distinguishing the sugar maple and the Norwegian maple. The leaf buds of the Norwegian maple are larger than the leaf buds of the maple. The buds of the Norwegian maple leaf are covered in larger scales and are purple in color, forming a rounded tip.
Method 3 of 3: Identify maple tree based on its fruit
Pick a small fruit from the tree. The sugar maple fruit is green and turns brown when ripe in the fall. The fruit has two "horseshoe" leaves, meaning that each fruit has two opposite leaves on either side. The flowers of the sugar maple plant form a bifurcated fruit shaped like wings.
- This pair of "wings" connect together at the fruit and form an angle of 60 -90 degrees.
Measure the fruit size. Sugar maple fruit about 2.5 cm long, including "wings".These two wings grow parallel to each other. The term for this fruit is "wing."
- These berries are sometimes called "seeds." However, its correct name should be fruit, as the seed will be inside the pulp.
Identify the double particle structure. Each sugar maple between the two horseshoe leaves will have a double structure. There are two distinct pods, each about the size of a small pea, that appears to be tied together in the middle of each fruit. advertisement
Advice
- Sugar maple can reach a height of about 20 - 33 m.
- The width of the canopy depends on the environment. In a large space, the branch can swoop down near the ground and the canopy is about 18-24 m in diameter. However, trees that grow in cramped land and in the shade will rise higher and have narrower foliage.