Author:
Louise Ward
Date Of Creation:
9 February 2021
Update Date:
28 June 2024

Content
Privacy concerns on the internet are no longer limited to child pornography, terrorism and hackers: indeed, if you do not know how to hide your personal information, you become a prime target for identity thieves and other illegal acts. Some even worry about how they can be kept safe from their government (and that makes sense too!). If you want to keep yourself safe in this digital age, by taking some of the following basic precautions that will help you conceal your (anonymity) identity.
Steps
Learn The Basics of Anonymity
Websites often track visitors for advertising purposes and links to social media. Every time you visit a website it records your IP address (the address of your computer on the internet), what page are you from, the browser you are using, your operating system. , how long you are on a certain page, and what links you clicked on.

Popular search engines keep a record of your search history. Your search engine queries are associated with your IP address (and your account if you are logged in). These are combined and analyzed to more accurately target your advertising and provide more relevant search results.
Social networks also track your every move. If your computer is logged into any social network (Facebook, Twitter ...), these networks will be able to track your browser history if the pages you visit have plugins (plug-ins ) for social media ("Like", Retweet, etc. buttons).
Your internet service provider (ISP) can analyze network traffic to see what you do on the network. This is most commonly used to determine if customers are using the network to download torrent files that contain copyrighted content.
Complete anonymity is not possible. No matter how much you hide your tracks, there will always be “some” information that can be used to profile and identify you. The goal of using anonymity tools is to reduce the amount of your existing personal information, but because of the nature of the internet, you can never truly anonymize.
When you go online, you have to choose between convenience and anonymity. It's not that easy to stay anonymous online as it requires a significant amount of your conscious effort. Your connections will be much slower when browsing web pages, and you'll have to go through more perimeters before you go online. So if anonymity is important to you, be prepared and accept some trade-offs to get there.- The next section will talk about how to keep your personal information from being tied to your IP address, but not guaranteeing your anonymity. To increase your anonymity online, see also the last two sections of this article.
Part 1 of 3: Protecting Your Personal Information

Use a discardable email (secondary email) to subscribe to websites. Make sure that this email address does not contain personal information, and is not tied to any accounts that store your personal information.- Click here for details on how to create an extra email address.
Using search engines protects user privacy. Major search engines like Google, Bing and Yahoo! all track your searches and associate them with your IP address. Use an alternative search engine instead but don't track your searches, like DuckDuckGo or StartPage.
Use a password manager to keep your passwords strong enough. If you are on the internet for more than a week, chances are you have a few passwords to keep in mind. It is very easy to use the same password, or if it is different, just make small changes, for many different sites for simplicity of use, but this is a serious security risk. If a website with your password and email gets hacked, every site that you use the same password and email combination is at the same risk. Therefore, a password manager remembers passwords for every page you visit and allows you to generate strong and random passwords for each site.
- Click here for detailed instructions on how to install a password manager.
- With a password manager, you don't need to worry about creating an easy-to-remember password. Instead, you can create strong passwords that are almost impossible to crack. "Kz2Jh @ ds3a $ gs * F% 7" is a stronger password than "MyDogName1983".
Part 2 of 3: Browsing the Web with Basic Anonymity
Let's learn a few basic terms. When it comes to online anonymity, things get technical very quickly. Before diving into it, it can be helpful to have some basic understanding of some of the most used terms.
- Flow In networking terms, traffic is the transmission of data from one computer to another.
- Server - This is a remote computer that contains files and establishes connections. All web pages will be stored on servers that you access through the use of a certain browser.
- Encode This is the act of protecting data sent over a network using a randomly generated set of codes. When the data is encrypted, it is mixed up according to a unique code that only your computer and the server have. This ensures that if the data is intercepted it cannot be decoded.
- Proxy (Proxy) - A proxy server is a server that is configured to collect and resend network traffic. In essence, a proxy server will allow you to connect to it, and then it will send your requests to web pages. It then takes the data from the web pages and sends it back to you. This is beneficial in that it hides your IP address from the websites you visit.
- VPN - A VPN is a virtual private network. This is an encrypted connection between you and the server. It is often used in enterprise environments so that remote employees can securely access enterprise resources. A VPN can be described as a "tunnel" through the Internet to connect you directly to a server.
Use a web-based proxy. There are thousands of proxies out there, and this number changes every day. These are the websites that route traffic through a proxy server. They only affect traffic going through that website; then open another tab in your browser and anything you send will be sent anonymously.
- When using a web-based credential, avoid sites where using it requires your secure login credentials (used to access Facebook, banking, etc.) by never trusting. pages like that.
- Most proxies cannot display certain content, such as videos.
Connect to a proxy server. A proxy is a server that forwards your internet traffic. This is beneficial in that it conceals your personal IP address from Web sites when you connect through a proxy. The downside is that you have to be confident that the proxy server won't do anything harmful to your traffic.
- There are a variety of proxy services available online, both free and paid. Free hosts usually support advertising.
- Once you have found a proxy server you want to connect to, you will need to configure your browser to connect to the server. This will only affect traffic generated from your browser (eg an instant messaging program will not be forwarded through the proxy unless it is configured to do so).
- As with web-based proxies, you should avoid logging into anything that requires confidential information, you simply cannot trust a proxy that they will not disclose the data. your.
- Do not connect to any "open" proxies. These proxies are actually left open by someone else, and are often malicious or illegal.

Sign up for a VPN network. A virtual private network encrypts traffic to and from your network, and increases your privacy. It also makes your traffic appear as if it were coming from the VPN server, much like a proxy server. Most VPNs charge a fee, and many are required to log your traffic as required by the local authorities.- Don't trust any VPN company that says they won't record anything of you, no VPN company risks being forced to shut it down just to protect a single customer from a government request. .

Using the Tor Browser. Tor is a network that acts as many different proxies, it forwards your traffic back and forth between different relay servers before reaching your destination or to your machine. Only traffic going through the Tor Browser will be anonymized, and browsing using the Tor Browser will be significantly slower than regular browsing.- Click here for more detailed information about using Tor.
Part 3 of 3: Browsing the Web with Strong Anonymity

Follow the steps in this section. If you want to browse the web really anonymously, there are a few things you need to set up before going online. It sounds a bit confusing, but following these steps is the only guaranteed way that you will look like anonymity online.- This method will help you to configure your own VPN on your own server located abroad. This is much safer than signing up for a VPN service, since it's hard to trust that a company will always keep your data safe.
Install Linux on a virtual machine on your home computer. Your computer has many services connected to the Internet, each of which can compromise your anonymity on your network without you even realizing it. Windows is not particularly secure, but neither is Mac OS X, but it's a little better. The first step to becoming anonymous is to install Linux on a virtual machine, just like a computer inside your computer.
- A virtual computer has a "wall" around it that prevents any data from getting over it to reach your existing computer. This is important because it keeps your existing computer's signature from showing up while browsing anonymously.
- Click here for detailed instructions on how to install the Linux operating system on a virtual machine. Installation is free, but it will take about an hour.
- TailsOS is one of the most popular privacy-oriented Linux distributions. It is very lightweight and completely encrypted.
Find a virtual private server (VPS) overseas. It will cost you a few dollars per month for this service but will help ensure that you browse the web anonymously. It is important that you register for a VPS in another country, so that traffic to and from the VPS cannot be tracked to your home IP address.
- You will use VPS to install VPN (Virtual Private Network) software on it. This will allow you to connect through your VPN and hide your real IP address.
- Choose a VPS service that allows you to pay with methods without exposing your identity, such as DarkCoin.
- Once you've registered for a VPS, you'll need to install its own operating system.Install one of the following Linux distributions that will allow easier VPN installation: Ubuntu, Fedora, CentOS, or Debian.
- Keep in mind that your VPS provider may still be under a warrant from a court to disclose your VPN information if your government suspects your VPN is acting illegally. And then there's really not much you can do to prevent it.
Install your own VPN virtual private network on VPS. A VPN is what your computer will connect to to access the internet. This will essentially act as if you are browsing from the VPS location, not your home, as well as encrypting all data to and from the VPS. This step is a bit more complicated than installing a virtual operating system. It is arguably the most important step, so if anonymity is important to you, make sure you complete it. These steps are specific to OpenVPN on Ubuntu, one of the more reliable free VPN solutions.
- Log in to your VPS operating system. This process will vary depending on the VPS service you choose.
- Visit the OpenVPN website and download the appropriate software package. There are many different options available to you, so be sure to choose the correct version of your VPS operating system software. You can find the available downloads at
- Open the terminal on your VPS and type dpkg -i openvpnasdebpack.deb to install the OpenVPN software that you have downloaded. The command will be different if you are not using Ubuntu or Debian.
- Type passwd openvpn and set a new password when prompted. This will be the admin password for your OpenVPN software.
- Open a web browser on your VPS and enter the address shown in the terminal (terminal). This will open the OpenVPN dashboard. Login with the username and password you created. After logging in for the first time, the VPN is ready to go.
Open a web browser on your virtual computer. You will need to access the OpenVPN Connect Client to download the necessary configuration files for your connection program.
- Enter the same address as you used on the VPS to access the control panel, but without the part of the address.
- Log in to your OpenVPN admin account using “openvpn” as the username and password you created earlier.
- Upload the file or onto your virtual computer.
Upload the OpenVPN client to your virtual computer. Once the VPN is configured on your VPS, you need to set up the virtual machine to connect directly to it. The following instructions are for Ubuntu and Debian, so you may have to change the command to suit your operating system.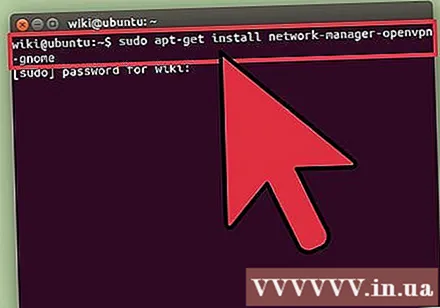
- Open a terminal and type sudo apt-get install network-manager-openvpn-gnome
- Wait for the package to download and install.
- Open Network Manager then click the "VPN" tab.
- Click the "Import" button then select the configuration file you downloaded.
- Review your settings. The Certificate and Key fields will be filled in automatically and your VPN address will appear in the Gateway field.
- Click the "IPV4 Settings" tab then select "Automatic (VPN) addresses only" from the Methods drop-down menu. This will ensure that all of your internet traffic is routed through the VPN.
Upload the Tor Browser Bundle to your virtual computer. Now that the VPS and VPN are configured, you can browse the web with quite a bit of anonymity. Your VPN will encrypt all traffic to and from your virtual machine. If you want to go one step further, using the Tor browser can add an extra layer of protection, but in return your browsing speed can be slower.
- You can download the Tor browser from
- Running Tor through a VPN will help hide the fact that you are using Tor from your ISP (they will only see your encrypted VPN traffic).
- Run the Tor installation program. The default settings of this program will provide comprehensive protection for most users.
- For more details on how to use Tor, click here.
Change VPS providers on a regular basis. If you are concerned about your anonymity, you will need to change VPS providers at least monthly. This also means you will have to reconfigure OpenVPN every time, but you will do it faster by repeating the process. Make sure you completely reinstall VPS before you switch to the new one.
Surf the web wisely. Once everything is configured, the strength of anonymity depends only on your surfing habits.
- Use alternative search engines like DuckDuckGo or StartPage.
- Avoid any sites that use Javascript. Javascript code can be used to reveal your IP address and reveal the identity of your traffic.
- Exit the Tor network when opening files you downloaded through Tor.
- Do not download torrent files while connected to the Tor network.
- Stay away from any sites that aren't using HTTPS (Look at the address bar of the open site to see if the page is using HTTP or HTTPS).
- Avoid installing browser plug-ins.