Content
Edema occurs when excess fluid builds up in the body's tissues and causes swelling. Although edema usually occurs in the hands, feet or lower legs, any part of the body can develop swelling. You may experience temporary edema due to injury or pregnancy, but it may last longer if the cause is a serious underlying medical condition. The edema is often painful and uncomfortable, but there are ways to reduce swelling without medication. However, if the edema does not go away or if the pain persists, make an appointment with your doctor to see you.
Steps
Method 1 of 4: Reduce fluid accumulation
Every hour walk a few minutes. Avoid sitting or standing in one place for long periods of time, as this can cause fluid to accumulate in the body and cause more swelling. Get up and stretch your legs and go for a 3-4 minute walk, at least once every hour if possible. As long as you move regularly, the swelling should ease and the pain should be less.
- Avoid crossing your legs while sitting, as this position interferes with blood circulation and causes more edema.
Other solution: If you're on an airplane or train and can't get up, try stretching your leg muscles and changing your sitting position often.
Massage the swollen area towards the heart. Place your hand next to the swelling just far from the heart. Try to push as hard on the swollen area as much as you can, as long as it doesn't hurt. Move your hand over the swollen area and rub in the direction of the heart so that body fluids can circulate normally.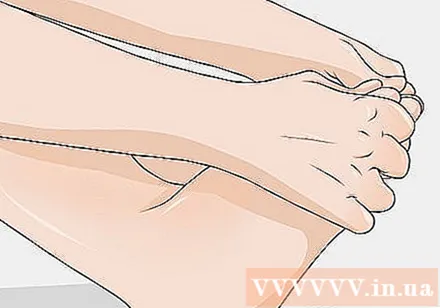
- For example, if there is swelling in your feet, massage from your toes toward your ankles.

Raise the swollen area 30 minutes above the heart level at a time. Lie on your back if possible to make it easier to lift the swollen area higher than your heart. Place the affected area on a pillow or cushion to allow blood and fluid to drain. If possible, you should place the area up to the edema for 30 minutes, 3-4 times a day.- If you have swelling in your hands or arms, raise your hand over your head for 1-2 minutes at a time to help drain the fluid. Raise your hand once every hour to reduce ongoing swelling.
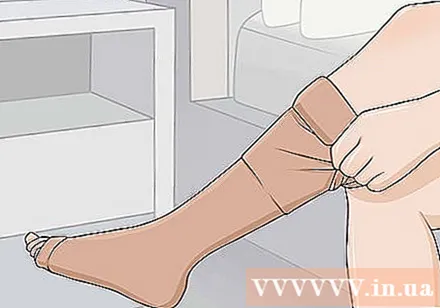
Wear pressure clothing if you want to prevent further swelling. Choose a product such as a sleeve, sock, or pressure glove that is designed to put moderate pressure on body parts. Wear it as soon as you wake up in the morning and continue wearing it as long as you can bear it, which can be hours or days.You can wear pressure clothing every day to help control and prevent edema.- Avoid using tight-fitting products, as they can irritate the skin.
- Pressure clothing puts even pressure on the swollen area to prevent fluid build up.
Method 2 of 4: Pain control
Use a cold compress if you experience swelling due to injury. You can use a damp cloth or an ice pack to make a cold compress. Apply gauze to swollen area and press down firmly to reduce swelling. Continue pressing against the skin for about 20 minutes whenever you feel pain or want to reduce swelling immediately. You can apply a cold compress once every hour.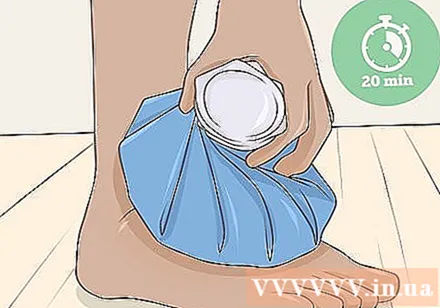
- Avoid applying cold compresses to your skin for more than 20 minutes, as this can cause cold burns.
- Cold compresses help reduce inflammation so you should not feel much pain.
Wear loose clothing to reduce the pressure on the swollen area. Avoid wearing tight clothing that gets close to the skin, as they can squeeze into the area and cause pain. Choose clothes that fit comfortably and don't limit your range, such as loose sports t-shirts. If your feet are swollen, choose wider shoes and tie looser laces to reduce the risk of pain.
- Tight clothing that rubs on edema for long periods of time can cause skin irritation.
Soak the swelling in Epsom salt for pain relief. Turn on warm running water into the tub and mix 2 cups (200 g) of Epsom salt in the water. Wait for the Epsom salt to dissolve completely before entering the tub. Soak the affected area for 15-20 minutes to relieve the pain or soreness.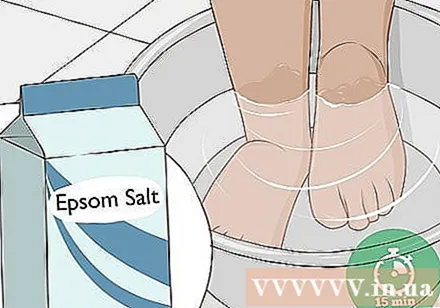
- You can buy Epsom salt online or at a pharmacy.
- Epsom salts break down into magnesium and sulfate that can be absorbed through the skin and help relieve pain.
Take magnesium supplements to control fluid retention and pain. Choose a supplement with 200–400 mg of magnesium for the best effect. Take a supplement every day in the morning to relieve pain and limit fluid retention, thereby reducing the size of the swollen area.
- Always consult your doctor before taking a new supplement to make sure it doesn't interact with medications you are taking.
- Magnesium helps the body relieve nerve pain, so it can help improve edema.
Warning: Avoid taking magnesium supplements if you have kidney or heart problems.
Try lavender essential oil as a natural anti-inflammatory. Mix 2-3 drops of lavender oil with 1 tablespoon (15 ml) of carrier oil, such as olive oil, avocado oil, or almond oil. Gently rub the oil into the swollen skin until it is absorbed into your body. Continue applying the oil 1-2 times a day to help reduce swelling and pain.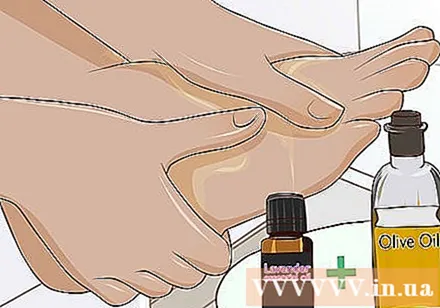
- Lavender oil is an antioxidant that has been shown to reduce and prevent edema.
- You can also try peppermint, eucalyptus, or chamomile oil.
Method 3 of 4: Adjusting diet and lifestyle
Switch to a low-salt diet to control fluid retention. Since salt causes fluid to build up in the body and increase the size of the swelling area, you should avoid eating processed foods and junk food. Instead, choose whole grains, salt-free snacks, fresh fruits and vegetables or fresh meat. Check the product's nutrition label and eat only the recommended serving sizes. If possible, choose low sodium products to avoid consuming too much salt.
- Instead of using salt to taste when cooking, you can choose other herbs and spices, even lemon juice to add flavor to your dishes.
- If you go out to eat, you can ask not to add salt to the food and put spices on the side.
Warning: Some medicines also contain sodium, so check the label before taking it. If it is a prescription drug, talk to your doctor about whether you can replace it with another medicine.
Drink water throughout the day to stay hydrated. Although the edema is caused by a buildup of fluid, the water will help clean the area and remove excess fluid. You should drink 8 glasses of water per day (240 ml each). Try to avoid drinks that contain caffeine or sugar, as these can make you more dehydrated.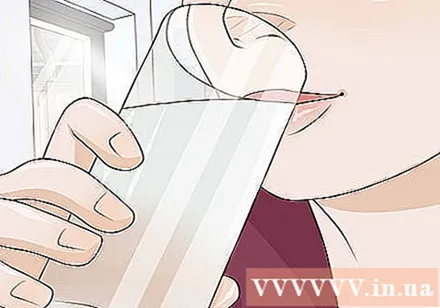
- Many sports drinks are also high in sodium, so you should avoid them as well.
Avoid drinking alcohol and smoking while having edema. Limit alcohol and all tobacco, as these stress your body and make you more dehydrated. Wait until the swelling stops or fully recover before drinking and smoking again; otherwise, you will experience more pain or swelling.
- Tobacco and alcohol use can interfere with the transfer of nutrients to the edematous area, making the condition worse.
Exercise gently every day to increase blood circulation. Try to exercise 4-5 days per week for at least 30 minutes a day. Try walking, slow running, swimming, or lifting weights, as these activities don't force your body too much. Once you get used to light exercise, you can try increasing the intensity of your exercise or weightlifting for further pain relief.
- Gentle activities help oxygen and nutrients reach the swollen area and help you recover faster.
- If you have a lot of headaches due to edema, consult your doctor about which exercises are best suited for you.
Protect and warm swollen areas to avoid damage. Apply a moisturizer or lotion to the affected area 2-3 times a day to keep your skin from drying out. Be careful during daily activities not to hurt or hurt the swelling. If possible, cover the swollen area with a cloth so you don't accidentally cut the skin or get scratched.
- If the skin is dry, you will be more vulnerable to injury and may take longer to heal.
Method 4 of 4: When to get medical attention
See your doctor if you have severe edema. Severe edema can be a symptom of a more serious underlying condition. If you have large swelling in any part of your body, arrange to see a doctor. Your doctor can help you determine the cause of your problem and treat it with the right methods. You should seek medical attention if:
- The skin is swollen, stretched, or shiny
- The skin remains sag for a long time after you apply the pressure
- Sudden swelling in your hands and face while pregnant
Call your doctor right away if you experience swelling in your legs and soreness. If you experience swelling and soreness in your legs after sitting for a long time, it may be due to a blood clot. This condition can be dangerous if left untreated. Call your doctor right away or go to the emergency room if you experience symptoms of a blood clot in your leg.
- Swollen legs may also be red and feel warm to the touch.
Warning: A blood clot in a blood vessel can fall off and travel into the lungs, causing a life-threatening condition called pulmonary embolism. Go to the emergency room or call emergency services if you experience sudden shortness of breath, chest pain when breathing, dizziness, heart palpitations or coughing up blood.
Seek emergency medical attention for pulmonary edema symptoms. Pulmonary edema is a form of edema with fluid that accumulates in the lungs. This is a dangerous condition that can lead to death, especially if it occurs suddenly. Call the emergency room or have someone drive you to the emergency room if you have symptoms of pulmonary edema, such as:
- Wheezing, difficulty breathing, or sudden heavy breathing
- Coughing up pink or foamy phlegm
- Sweating profusely
- The skin turns gray or blue
- Confusion, lightheadedness, or dizziness
Warning
- If the swelling persists for more than 2 weeks, you will need to contact your doctor to determine the potential cause of the edema.
- Always consult your doctor before starting any natural therapy or taking any supplements to make sure there are no negative reactions.
- If you experience severe headache, confusion, neck pain or blurred vision, this could be a sign of brain edema. You should seek help from your doctor and take medicine to reduce swelling.