Author:
Tamara Smith
Date Of Creation:
28 January 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- To step
- Method 1 of 3: Calculate the average
- Method 2 of 3: Finding the variance in your sample
- Method 3 of 3: Calculate the standard deviation
The standard deviation tells you the spread of the numbers in your sample. To find the standard deviation for your sample or data set, you must first make some calculations. You must determine the mean and variance of your data before you can calculate the standard deviation. The variance is a measure of the spread of your values around the mean. You determine the standard deviation by calculating the square root of the variance. This article tells you how to calculate the mean, variance and standard deviation.
To step
Method 1 of 3: Calculate the average
 Look at your data collection. This is an important step in any statistical calculation, even if it is a simple value such as the mean or median.
Look at your data collection. This is an important step in any statistical calculation, even if it is a simple value such as the mean or median. - Know how many numbers your sample contains.
- Are the numbers far apart? Or are the differences between the numbers small, for example only a few decimal places?
- Know what type of data you are looking at. What do the numbers in your sample mean? These can be test figures, heart rate values, height, weight, and so on.
- For example, a test grade data set consists of the numbers 10, 8, 10, 8, 8, and 4.
 Collect all your data. You need every number in your sample to calculate the mean.
Collect all your data. You need every number in your sample to calculate the mean. - The mean is the mean value of all numbers.
- You calculate the mean by adding up all the numbers in your sample and then dividing this value by the number of numbers in your sample (n).
- The data set with test grades (10, 8, 10, 8, 8, and 4) consists of 6 numbers. Therefore: n = 6.
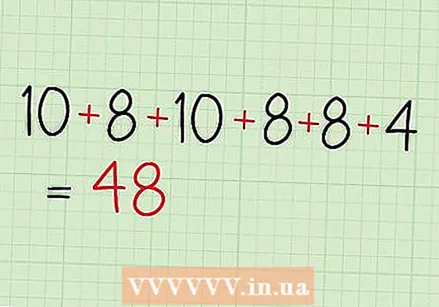 Add up the numbers in your sample. This is the first step in calculating the arithmetic mean, or mean.
Add up the numbers in your sample. This is the first step in calculating the arithmetic mean, or mean. - For example, use the data set with test grades: 10, 8, 10, 8, 8, and 4.
- 10 + 8 + 10 + 8 + 8 + 4 = 48. This is the sum of all numbers in the data set or sample.
- Add the numbers a second time to check the answer.
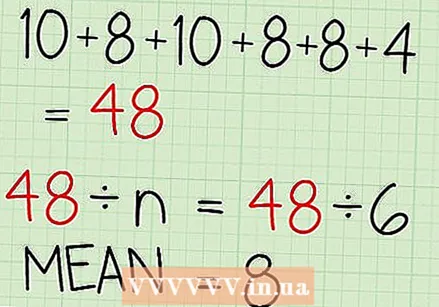 Divide the sum by the number of numbers in your sample (n). This calculates the average of all data.
Divide the sum by the number of numbers in your sample (n). This calculates the average of all data. - The data set with test grades (10, 8, 10, 8, 8, and 4) consists of six numbers. Therefore: n = 6.
- The sum of all test scores in the example was 48. So you have to divide 48 by n to calculate the mean.
- 48 / 6 = 8
- The average test mark in the sample is 8.
Method 2 of 3: Finding the variance in your sample
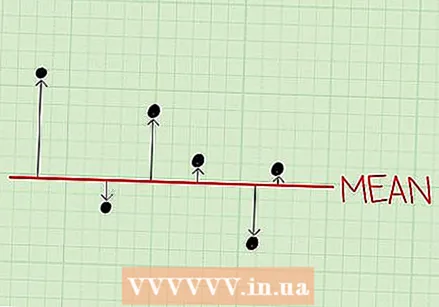 Determine the variance. The variance is a number that indicates the spread of your values around the mean.
Determine the variance. The variance is a number that indicates the spread of your values around the mean. - This number will give you an idea of the degree to which the values differ from each other.
- Samples with a low variance contain values that deviate little from the mean.
- High variance samples contain values that deviate much from the mean.
- The variance is often used to compare the dispersion of values in two data sets.
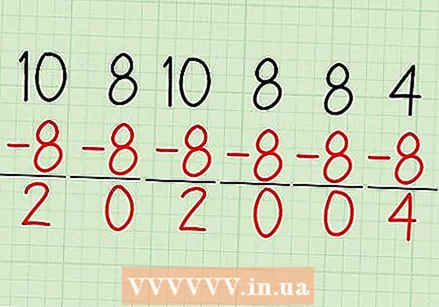 Subtract the mean from each of the numbers in your sample. You now get a series of values that indicate how much each number in the sample differs from the mean.
Subtract the mean from each of the numbers in your sample. You now get a series of values that indicate how much each number in the sample differs from the mean. - For example, in our sample of test grades (10, 8, 10, 8, 8, and 4), the mean or arithmetic mean was 8.
- 10 - 8 = 2; 8 - 8 = 0, 10 - 8 = 2, 8 - 8 = 0, 8 - 8 = 0 and 4 - 8 = -4.
- Repeat the calculations to check each answer. It is very important that all numbers are correct because you will need them for the next step.
 Square all the numbers you calculated in the previous step. You need all of these values to determine the variance of your sample.
Square all the numbers you calculated in the previous step. You need all of these values to determine the variance of your sample. - Think back to how we subtracted the mean (8) of each of the numbers in the sample (10, 8, 10, 8, 8, and 4) in our sample and we got the following results: 2, 0, 2, 0 , 0 and -4.
- In the following calculation to determine the variance, do the following: 2, 0, 2, 0, 0 and (-4) = 4, 0, 4, 0, 0 and 16.
- Please check your answers before moving on to the next step.
 Add the squared numbers together. This is the sum of the squares.
Add the squared numbers together. This is the sum of the squares. - In our example with test figures, we calculated the following squares: 4, 0, 4, 0, 0 and 16.
- Remember, in the example, we started with test grades by subtracting the mean of each of the numbers and then squaring the results: (10-8) + (8-8) + (10-2) + (8- 8) + (8-8) + (4-8)
- 4 + 0 + 4 + 0 + 0 + 16 = 24.
- The sum of the squares is 24.
 Divide the sum of the squares by (n-1). Remember that n is the number of numbers in the sample. By performing this step you determine the variance.
Divide the sum of the squares by (n-1). Remember that n is the number of numbers in the sample. By performing this step you determine the variance. - Our sample with test grades (10, 8, 10, 8, 8 and 4) consists of 6 numbers. Therefore: n = 6.
- n - 1 = 5.
- The sum of the squares for this sample was 24.
- 24 / 5 = 4,8.
- The variance of this sample is therefore 4.8.
Method 3 of 3: Calculate the standard deviation
 Record the variance. You need this value to calculate the standard deviation of your sample.
Record the variance. You need this value to calculate the standard deviation of your sample. - Remember, the variance is the degree to which the values deviate from the mean.
- The standard deviation is a similar value that indicates the spread of the numbers in your sample.
- In our example with test figures, the variance was 4.8.
 Calculate the square root of the variance. The result of this is the standard deviation.
Calculate the square root of the variance. The result of this is the standard deviation. - Typically, at least 68% of all values are within one standard deviation of the mean.
- Remember, in our sample of test scores, the variance was 4.8.
- √4.8 = 2.19. The standard deviation of our sample of test scores is therefore 2.19.
- 5 of the 6 numbers (83%) in our sample of test grades (10, 8, 10, 8, 8, and 4) are within one standard deviation (2.19) of the mean (8).
 Calculate the mean, variance, and standard deviation again. This way you can check your answer.
Calculate the mean, variance, and standard deviation again. This way you can check your answer. - It is important that you write out all the steps when you perform the calculations by heart or with a calculator.
- If you get a different result the second time, check your calculation.
- If you can't find your mistake, start over a third time to compare your calculations.



