Author:
Roger Morrison
Date Of Creation:
4 September 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- To step
- Part 1 of 5: Preparations
- Part 2 of 5: Sowing
- Part 3 of 5: Growing in a pot
- Part 4 of 5: Daily and long-term care
- Part 5 of 5: Harvest and storage
- Warnings
- Necessities
Red kidney beans are fairly easy to grow, but you will want to make sure that the roots do not fill up with water or get damaged in any way during the season. Like other bean varieties, red kidney beans can grow as shrubs or tendrils, so you will need to choose the type that best suits the space you have.
To step
Part 1 of 5: Preparations
 Instead of seedlings, use seeds. Most red kidney bean plants do not survive transplanting, so it is better to buy seeds instead of seedlings.
Instead of seedlings, use seeds. Most red kidney bean plants do not survive transplanting, so it is better to buy seeds instead of seedlings.  Choose a suitable location. Red kidney beans need a lot of sun to thrive, so sow them where they get at least 6 hours of direct sunlight a day, if not more.
Choose a suitable location. Red kidney beans need a lot of sun to thrive, so sow them where they get at least 6 hours of direct sunlight a day, if not more. - If possible, find a piece of land that is naturally loose. Loose soil provides better drainage, which is crucial if you want to grow a healthy kidney bean plant. If you notice that water does not flow through or forms puddles after a rain shower, choose a different location.
- Rotate annually. Do not plant red kidney beans in soil where you have previously grown legumes in the past 3 years.
 Improve the soil. The bottom should be reasonably light and loose so that the water can run through. If the soil is too heavy, you will need to improve it with enough organic matter to balance it out. The soil pH should also be close to neutral.
Improve the soil. The bottom should be reasonably light and loose so that the water can run through. If the soil is too heavy, you will need to improve it with enough organic matter to balance it out. The soil pH should also be close to neutral. - Good soil improvers are manure and compost. Both options will generally loosen up the soil while providing adequate nutrition for the young plant.
- Improve the soil by mixing these additional components with a trowel or small garden rake a few weeks before you start planting.
- The soil pH should be between 6 and 7.
- You can also add a powdered inoculant to the soil. This is a type of natural and healthy bacterial culture that makes it easier for the beans to absorb nitrogen during the earliest and most crucial stage of growth.
 Install a trawl. While many popular red kidney bean varieties are shrub beans, there are a number of stick bean varieties as well. Climbing beans grow vertically, so you will need to place a stick or a trawl for maximum yield.
Install a trawl. While many popular red kidney bean varieties are shrub beans, there are a number of stick bean varieties as well. Climbing beans grow vertically, so you will need to place a stick or a trawl for maximum yield.
Part 2 of 5: Sowing
 Wait until the last frost has passed. Red kidney beans need enough heat and humidity to thrive. Plant them in the spring when you are sure the last frost has passed.
Wait until the last frost has passed. Red kidney beans need enough heat and humidity to thrive. Plant them in the spring when you are sure the last frost has passed. - The temperature of the ground should be between 21 and 27 degrees Celsius. If possible, prevent the ground temperature from dropping below 16 degrees.
- The ideal air temperature should be between 18 and 27 degrees Celsius for most of the growing season.
- If there is still an unexpected night frost after the red kidney bean plants sprout, cover the seedlings with gauze or canvas to protect them from the freezing cold.
 Plant the seeds deep enough. Red kidney bean seeds should be planted at a depth of 2.5 to 4 cm.
Plant the seeds deep enough. Red kidney bean seeds should be planted at a depth of 2.5 to 4 cm. - Many gardeners prefer to plant the seeds an inch apart from each other. After your seedlings reach a height of about three inches, thin them out so they have more room, removing the weakest plants where possible and leaving the strongest.
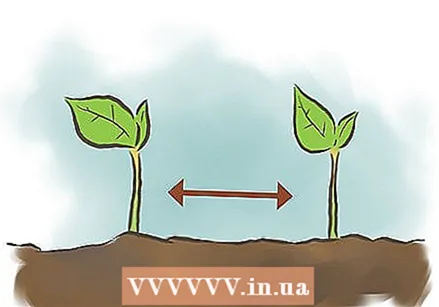 Give the seeds enough space. For most varieties you will need to plant the seeds about 8 to 10 cm apart.
Give the seeds enough space. For most varieties you will need to plant the seeds about 8 to 10 cm apart. - More specifically, pole or vine varieties do well at a distance of 10 cm from each other, while dense shrubs grow best when the distance between them is 20 cm.
- The seeds should emerge within 10 to 14 days.
Part 3 of 5: Growing in a pot
 Choose a large pot. While potted and planter gardens do not provide the best conditions for red kidney beans, these plants can grow in pots provided they are properly cared for. For each plant you need a pot with a diameter of 30 cm.
Choose a large pot. While potted and planter gardens do not provide the best conditions for red kidney beans, these plants can grow in pots provided they are properly cared for. For each plant you need a pot with a diameter of 30 cm. - If you choose to grow red kidney beans in pots, it is better to choose a shrub than a stick bean. Bush beans tend to do better when space is limited.
- The main reason red kidney beans are not usually grown in pots is simply that the yield of an average plant is not enough for one person. You usually need 6-10 plants if you want to provide yourself with enough beans on a regular basis. However, don't plant more than one plant per pot, so you will need 6 pots if you plan to produce enough for yourself.
 Add additional gravel to the pot. Before adding soil to the pot, spread a layer of gravel over the bottom to improve drainage. Otherwise, the roots of the red kidney bean plants in a pot can quickly become saturated with water.
Add additional gravel to the pot. Before adding soil to the pot, spread a layer of gravel over the bottom to improve drainage. Otherwise, the roots of the red kidney bean plants in a pot can quickly become saturated with water. 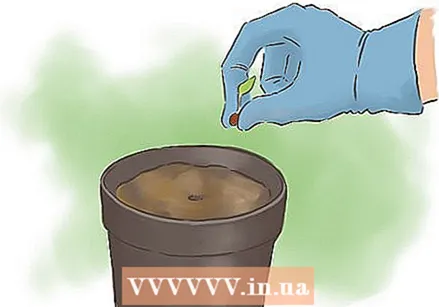 Plant the seeds deep enough. Just like in a regular garden, you will need to plant the seed of the red kidney beans 2.5 to 4 cm deep. Sow it in the center of the pot.
Plant the seeds deep enough. Just like in a regular garden, you will need to plant the seed of the red kidney beans 2.5 to 4 cm deep. Sow it in the center of the pot.
Part 4 of 5: Daily and long-term care
 Water only where the soil has dried out. The soil should never get too wet because the roots of the plant can easily absorb and damage too much water. Therefore, only water the plant when it is very dry in the area.
Water only where the soil has dried out. The soil should never get too wet because the roots of the plant can easily absorb and damage too much water. Therefore, only water the plant when it is very dry in the area. - Rather than dampening the soil in an effort to keep it wet all the time, it is better to water only when the soil has dried out to within an inch (2.5 cm) of the soil. You can test this by gently pushing your finger into the soil until you come across wet soil.
 Avoid fertilizers with extra nitrogen. While fertilizers with extra nitrogen will make your red kidney bean plants look lush and leafy, these types of agents do more harm than good, as they stimulate the plant to send all the energy to the leaves instead of the fruits. High doses of nitrogen will produce an impressive leafy plant, but not many edible beans.
Avoid fertilizers with extra nitrogen. While fertilizers with extra nitrogen will make your red kidney bean plants look lush and leafy, these types of agents do more harm than good, as they stimulate the plant to send all the energy to the leaves instead of the fruits. High doses of nitrogen will produce an impressive leafy plant, but not many edible beans. - After the plant has started growing, red kidney beans actually make their own nitrogen in the roots. Nitrogen-rich fertilizers will inevitably contribute to the plant getting too much nitrogen.
- If your plants need more nutrition, use small amounts of organic fertilizer that doesn't contain as much nitrogen.
 Be careful removing weeds. The roots of the plant are very shallow, so when digging out weeds you will need to do it carefully to avoid accidentally disturbing or damaging the roots of the plant.
Be careful removing weeds. The roots of the plant are very shallow, so when digging out weeds you will need to do it carefully to avoid accidentally disturbing or damaging the roots of the plant. - Never cut weeds around a kidney bean plant with a hoe or shovel. It is better to pull the weeds out of the ground with your hands.
- You can also prevent weeds from spreading by spreading a 1 to 2 inch (2.5 to 5 cm) layer of mulch around the plant after it emerges. In addition, mulch also offers other benefits, such as keeping the soil around the plant warm and moist, and preventing pods from rotting when they hit the ground.
 Keep an eye out for pests and diseases. Some pests in your garden target red kidney beans, and the plant is also susceptible to a variety of diseases. If you are having problems with this, you may still have to resort to a pesticide or fungicide.
Keep an eye out for pests and diseases. Some pests in your garden target red kidney beans, and the plant is also susceptible to a variety of diseases. If you are having problems with this, you may still have to resort to a pesticide or fungicide. - Beetles, snails, caterpillars and leafhoppers love the leaves of the plant. You can easily remove these if you check the plants regularly. Pick them off the plant when you see them. If this is not an option, look for a pesticide that is specifically aimed at these insects.
- Aphids can also attack your plant, but these can be removed by hand. Treat the plant with a suitable pesticide as soon as you see them, as these pests can spread the mosaic virus.
- Rust is a reddish-brown fungus that can be identified by the spots on the leaves of a bean plant, and should be treated with a fungicide as soon as you notice it.
- Mildew can also attack your plant. It looks like a fine white powder. You will need to treat the plants with a fungicide as soon as possible and reduce the amount of water you give. Humid conditions produce mildew, so make sure the plants only get water from the soil and not the leaves.
- If squirrels, deer and rabbits threaten your harvest, you can install screens or fencing.
Part 5 of 5: Harvest and storage
 Harvest all beans at the end of the season. Bush beans should be harvested at the end of the growing season. You can harvest French beans several times during the season, but you can usually expect the largest harvest at the end of the growing season.
Harvest all beans at the end of the season. Bush beans should be harvested at the end of the growing season. You can harvest French beans several times during the season, but you can usually expect the largest harvest at the end of the growing season. - Depending on the variety you choose, red kidney beans are ready to harvest after 90 to 150 days.
- Climbing beans produce a regular crop every month or two months.
- Adult pods are dry to the touch, and the beans in the pods are very hard.
- Check the beans of a pod before harvesting the rest of the pods. You can check if the beans are ready by gently biting one of the beans. If your teeth can make a dent in a bean, you will have to let the rest dry for a longer period of time before you can harvest and shell them.
 If necessary, remove the plants from the ground earlier. If low temperatures or other conditions threaten your harvest, you can harvest the red kidney bean plants earlier and let the beans dry for a while afterwards.
If necessary, remove the plants from the ground earlier. If low temperatures or other conditions threaten your harvest, you can harvest the red kidney bean plants earlier and let the beans dry for a while afterwards. - High humidity can also make it difficult to dry the plant's beans. In this case you will also have to dry them inside the last piece.
- Remove the plants and hang them upside down from the roots for several days to weeks, until the pods look dry and the beans have hardened. Make sure that most of the leaves have died before removing the plants from the ground.
- Store the beans indoors in a warm location with adequate air circulation during drying.
 Break the pods in half. After you pick the pods from the plant, you will have to break them in half to get the beans out. Once you have allowed the beans to mature properly, the beans should be hard and dry right away.
Break the pods in half. After you pick the pods from the plant, you will have to break them in half to get the beans out. Once you have allowed the beans to mature properly, the beans should be hard and dry right away. - You can shell a small harvest by hand, but if you have a large harvest, you may prefer to do this in batches. Place the pods in a pillowcase or similar bag. Now carefully step on the pods in the pillowcase to open them. When you're done, pick out the beans by hand.
 Keep the beans in a dark place. Put the harvest of red kidney beans in a jar and store them in a dry, dark place until ready to use.
Keep the beans in a dark place. Put the harvest of red kidney beans in a jar and store them in a dry, dark place until ready to use. - Dried beans can be stored for up to a year under the right conditions.
- For best results, store the beans in airtight bottles or bags.
Warnings
- Raw red kidney beans and their sprouts are poisonous. You should only eat red kidney beans after they have been soaked and boiled for at least 10 minutes.
Necessities
- Red kidney bean seeds
- Manure or compost
- Inoculant in powder form
- Treillage (possibly)
- Trowel
- Pot with a diameter of 30 cm (optional)
- Gravel (possibly)
- Watering can
- Pesticide or fungicide (if needed)
- Fence or net (if necessary)