Author:
Charles Brown
Date Of Creation:
6 February 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- To step
- Method 1 of 2: Fix a blocked ear at home
- Method 2 of 2: Get medical attention
- Tips
- Warnings
- Necessities
The Eustachian tube connects the ears to the back of the nose. It can become blocked by a cold or allergy. Severe cases should be treated by an ENT specialist. But a mild case can be managed at home with home remedies, over-the-counter remedies, or prescription medications.
To step
Method 1 of 2: Fix a blocked ear at home
 Recognize the symptoms. Whether due to a cold, allergy or infection, if the Eustachian tube swells it becomes blocked and no more air can enter. This changes the pressure and sometimes fluid can build up in the ear. When that happens, you will experience the following symptoms:
Recognize the symptoms. Whether due to a cold, allergy or infection, if the Eustachian tube swells it becomes blocked and no more air can enter. This changes the pressure and sometimes fluid can build up in the ear. When that happens, you will experience the following symptoms: - Ear pain, or a "full" feeling in the ear
- Whispering or clicking noises or sensations that do not seem to come from outside
- Children sometimes describe it as a "tickling" feeling
- Difficulty hearing properly
- Dizziness and trouble keeping balance
- Symptoms can worsen if you change altitude quickly - such as when you're flying, riding an elevator, or riding in the mountains
 Wiggle your jaw. This simple trick is called the Edmonds technique. Just stick your jaw forward and wiggle it front to back and side to side. If the ear blockage is only mild, this maneuver can reopen the Eustachian tube and return the air pressure to normal.
Wiggle your jaw. This simple trick is called the Edmonds technique. Just stick your jaw forward and wiggle it front to back and side to side. If the ear blockage is only mild, this maneuver can reopen the Eustachian tube and return the air pressure to normal.  Do the Valsalva maneuver. This maneuver, in which you force air through the blocked ear canal to restore air flow, must be performed very carefully. When you blow through the blocked ear canal, the air pressure in your body is affected. The sudden flow of air can cause a rapid change in your blood pressure and heart rate.
Do the Valsalva maneuver. This maneuver, in which you force air through the blocked ear canal to restore air flow, must be performed very carefully. When you blow through the blocked ear canal, the air pressure in your body is affected. The sudden flow of air can cause a rapid change in your blood pressure and heart rate. - Take a deep breath and hold your breath, with your mouth closed and your nose pinched.
- Now try to blow out air through your closed nostrils.
- If the maneuver is successful, you will hear a popping sound in your ears and the symptoms will be gone.
 Try the Toynbee technique. Like the Valsalva maneuver, the Toynbee technique is designed to open the Eustachian tube. But instead of letting the patient change the pressure by breathing, the pressure is adjusted by swallowing. To perform this technique, do the following:
Try the Toynbee technique. Like the Valsalva maneuver, the Toynbee technique is designed to open the Eustachian tube. But instead of letting the patient change the pressure by breathing, the pressure is adjusted by swallowing. To perform this technique, do the following: - Pinch your nose.
- Take a sip of water.
- Swallow.
- Repeat this process until you feel your ears pop and open.
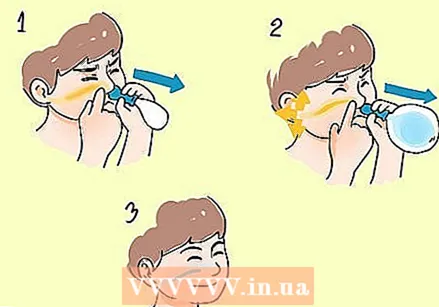 Blow up a balloon with your nose. It may feel crazy and look weird, but this, also called the Otovent technique, allows you to effectively restore the pressure in your ears. Buy an "Otovent Balloon" on the Internet. It is a normal balloon, but the nozzle fits exactly in your nose.If you have another nozzle that fits exactly in the opening of the balloon and fits in your nose, you can also make an Otovent balloon yourself.
Blow up a balloon with your nose. It may feel crazy and look weird, but this, also called the Otovent technique, allows you to effectively restore the pressure in your ears. Buy an "Otovent Balloon" on the Internet. It is a normal balloon, but the nozzle fits exactly in your nose.If you have another nozzle that fits exactly in the opening of the balloon and fits in your nose, you can also make an Otovent balloon yourself. - Put the nozzle in one nostril and press your other nostril closed with your finger.
- Try to inflate the balloon through one nostril until it is the size of a fist.
- Repeat the process with your other nostril. Repeat until you hear a popping sound and air can flow back into the Eustachian tube.
 Swallow with your nose closed. This is also called the Lowery maneuver, and it is more difficult than it looks. Before you swallow, you need to build up pressure in your body by pushing as if you had to defecate. When you hold your breath and close your nose, it feels like you want to squeeze air out of all your openings. Some people find it difficult to swallow under these conditions due to the increased pressure on the body. But be patient and hold on. If you practice enough, your ears might pop open.
Swallow with your nose closed. This is also called the Lowery maneuver, and it is more difficult than it looks. Before you swallow, you need to build up pressure in your body by pushing as if you had to defecate. When you hold your breath and close your nose, it feels like you want to squeeze air out of all your openings. Some people find it difficult to swallow under these conditions due to the increased pressure on the body. But be patient and hold on. If you practice enough, your ears might pop open. 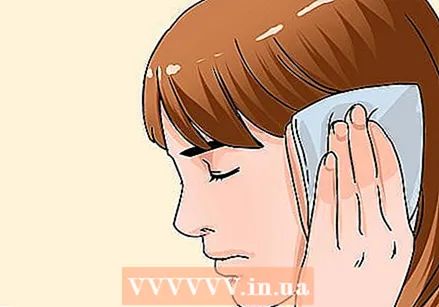 Put something warm on your ear. This can soothe the pain and clear the constipation. The heat from a warm compress can clear the blockage and open the Eustachian tube. If you are using a pitcher, put a cloth between the pitcher and your skin so you don't burn yourself.
Put something warm on your ear. This can soothe the pain and clear the constipation. The heat from a warm compress can clear the blockage and open the Eustachian tube. If you are using a pitcher, put a cloth between the pitcher and your skin so you don't burn yourself.  Use a nasal spray for a stuffy nose. Ear drops will not clear the blockage because the ear is closed. However, because the nose and ears are connected by tubes, a nasal spray can be effective in clearing a blocked Eustachian tube. Hold the nasal spray bottle so that it is pointing through your nostril and towards the back of your throat, almost perpendicular to your face. As you administer the spray, sniff hard enough to move the liquid towards the back of your throat, but not so hard that you swallow it or get it in your mouth.
Use a nasal spray for a stuffy nose. Ear drops will not clear the blockage because the ear is closed. However, because the nose and ears are connected by tubes, a nasal spray can be effective in clearing a blocked Eustachian tube. Hold the nasal spray bottle so that it is pointing through your nostril and towards the back of your throat, almost perpendicular to your face. As you administer the spray, sniff hard enough to move the liquid towards the back of your throat, but not so hard that you swallow it or get it in your mouth. - After using the nasal spray, try one of the pressure equalizing techniques. Maybe it works more effectively now.
 Take an antihistamine if the problem is caused by an allergy. While an antihistamine does not normally help open a blocked Eustachian tube, it can clear up an allergy blockage. Consult with your doctor whether this is a good option for you.
Take an antihistamine if the problem is caused by an allergy. While an antihistamine does not normally help open a blocked Eustachian tube, it can clear up an allergy blockage. Consult with your doctor whether this is a good option for you. - Note that antihistamines are usually not recommended for people with ear infections.
Method 2 of 2: Get medical attention
 Ask your doctor to prescribe a nasal spray. While you can try a regular drug store nasal spray first, a prescription may work better. If you have an allergy, ask your doctor about a steroid or antihistamine nasal spray.
Ask your doctor to prescribe a nasal spray. While you can try a regular drug store nasal spray first, a prescription may work better. If you have an allergy, ask your doctor about a steroid or antihistamine nasal spray.  Take antibiotics if you have an ear infection. Although a blocked Eustachian tube is usually short and harmless, it can lead to a painful ear infection. If your blocked ear seems to be developing in that direction, contact your doctor to ask for antibiotics. Your doctor may not prescribe it until you have a fever of 39ºC or higher, or if it lasts longer than 48 hours.
Take antibiotics if you have an ear infection. Although a blocked Eustachian tube is usually short and harmless, it can lead to a painful ear infection. If your blocked ear seems to be developing in that direction, contact your doctor to ask for antibiotics. Your doctor may not prescribe it until you have a fever of 39ºC or higher, or if it lasts longer than 48 hours. - For the dosage, follow the instructions in the package insert. Finish the entire course of antibiotics, even if the symptoms seem to pass before you are done.
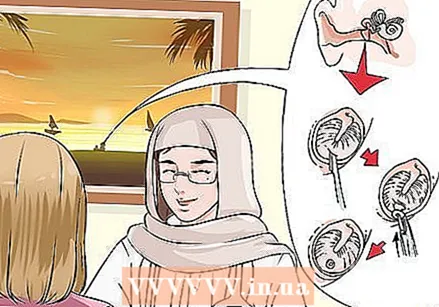 Talk to your doctor about myringotomy. In severe cases of blockage, your doctor may recommend surgical treatment to restore airflow to the middle ear. Two types of surgery are possible, and myringotomy is the fastest option. The doctor makes a small indentation in the eardrum and then sucks out fluid in the middle ear. It may seem unnatural, but that notch should be like this slowly possibly cured. If the cut is left open long enough, the swelling of the Eustachian tube will gradually subside. If it heals too quickly (within 3 days) fluid can build up in the middle ear again, causing the symptoms to persist.
Talk to your doctor about myringotomy. In severe cases of blockage, your doctor may recommend surgical treatment to restore airflow to the middle ear. Two types of surgery are possible, and myringotomy is the fastest option. The doctor makes a small indentation in the eardrum and then sucks out fluid in the middle ear. It may seem unnatural, but that notch should be like this slowly possibly cured. If the cut is left open long enough, the swelling of the Eustachian tube will gradually subside. If it heals too quickly (within 3 days) fluid can build up in the middle ear again, causing the symptoms to persist. 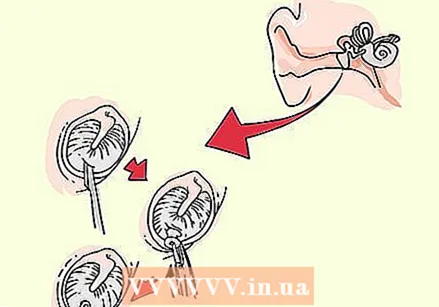 Consider having tubes inserted. This surgery is more likely to be successful, but it is a lengthy process. As with myringotomy, the doctor makes a cut in the eardrum and sucks the fluid out of the middle ear. The doctor then places a small tube in the eardrum to better ventilate the middle ear. While the eardrum heals, the tube is pushed out, but this can take as long as 6 to 12 months. This method is recommended for patients who have chronic Eustachian tube problems, so discuss the option with your doctor.
Consider having tubes inserted. This surgery is more likely to be successful, but it is a lengthy process. As with myringotomy, the doctor makes a cut in the eardrum and sucks the fluid out of the middle ear. The doctor then places a small tube in the eardrum to better ventilate the middle ear. While the eardrum heals, the tube is pushed out, but this can take as long as 6 to 12 months. This method is recommended for patients who have chronic Eustachian tube problems, so discuss the option with your doctor. - If you have tubes in your ears, you should always fully protect your ears from water. Use earplugs or cotton wool when you shower, and use special earplugs when you go swimming.
- If water runs through the tubes in the middle ear, you can get an ear infection.
 Treat the underlying cause. A blocked Eustachian tube is often the result of a condition that causes mucus and swelling of the tissue. The most common causes for mucus and swelling to form are colds, flu, sinus infections and allergies. Don't let these conditions get out of hand and cause problems with your ears. Treat the flu and cold as soon as you develop symptoms, and talk to your doctor if you often have sinus infections or allergies.
Treat the underlying cause. A blocked Eustachian tube is often the result of a condition that causes mucus and swelling of the tissue. The most common causes for mucus and swelling to form are colds, flu, sinus infections and allergies. Don't let these conditions get out of hand and cause problems with your ears. Treat the flu and cold as soon as you develop symptoms, and talk to your doctor if you often have sinus infections or allergies.
Tips
- If you know there is moisture in your ears, do not use wax removal products. They can cause infections, and there is no point in using them because they are moisture, not ear wax.
- Don't lie flat if you have an earache.
- Drink warm drinks such as tea rather than cold water.
- Try popping chewable papaya tablets in your mouth. Papain, the active substance in papaya, is a good expectorant. You can also try fenugreek.
- Use an extra pillow to keep your head higher. Then the liquid can come out more easily and it hurts less when you sleep.
- If your clogged ears hurt, you can take acetaminophen, ibuprofen, or aspirin to relieve the pain.
- Wear a hat to keep your ears warm. Then moisture can get out more easily while you are just doing other things.
Warnings
- Don't use nasal spray for more than a few days as it can cause more blockage than it clears. If the spray doesn't help, see your doctor.
- Do not rinse your ears with a nose cup or use ear candles. It has not been scientifically researched whether it is safe to open your ears with these products.
- Do not dive if you have problems with your Eustachian tube. This can be very painful because the pressure is then not balanced.
Necessities
- Nose spray
- Antihistamine
- Tubes