Author:
Tamara Smith
Date Of Creation:
23 January 2021
Update Date:
2 July 2024
Content
- To step
- Part 1 of 3: The preparation
- Part 2 of 3: Giving a subcutaneous injection
- Part 3 of 3: Giving an intramuscular injection
- Tips
- Warnings
If you have to inject your medicines yourself at home, proper training is necessary to prevent injuries and infections. With the right care and sufficient attention to detail, it is not difficult at all to give an injection. Start at Step 1 to learn how to give subcutaneous and intramuscular injections.
To step
Part 1 of 3: The preparation
 Determine what kind of injection you are going to give. Read the instructions that you received from the doctor, nurse or pharmacist. If the medication contains instructions, read them. If you have any questions or concerns about how and when to give the injection, talk to your doctor (or other medical professional) before proceeding. There are two common injections you can legally give at home: subcutaneous and intramuscular injections. If you do not know what type of injection to give, consult your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist before continuing.
Determine what kind of injection you are going to give. Read the instructions that you received from the doctor, nurse or pharmacist. If the medication contains instructions, read them. If you have any questions or concerns about how and when to give the injection, talk to your doctor (or other medical professional) before proceeding. There are two common injections you can legally give at home: subcutaneous and intramuscular injections. If you do not know what type of injection to give, consult your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist before continuing. - Subcutaneous injections are administered into the fat layer directly under the skin. Examples are insulin for diabetic patients and blood thinners.
- Intramuscular injections are injected directly into the muscle tissue. Examples include vaccinations, hormones, and antibiotics.
 Wash your hands thoroughly. This will help prevent infections.
Wash your hands thoroughly. This will help prevent infections.  Prepare the medication and needle. Make sure the needle is sterile, unused, and suitable for the type of injection you will be giving. Note that intramuscular and subcutaneous injections require different needles.
Prepare the medication and needle. Make sure the needle is sterile, unused, and suitable for the type of injection you will be giving. Note that intramuscular and subcutaneous injections require different needles. - Some medications are ready for immediate use, but others require you to fill the needle with medication from an ampoule. In the latter case, sterilize the top of the ampoule with alcohol and remove the needle from the package. Read the instructions to determine how much liquid you need.
- To fill the syringe, you draw in as much air as the required liquid. Turn the ampoule upside down, insert the needle, and inject all the air from the syringe into the ampoule. Withdraw the plunger to withdraw the liquid from the ampoule.
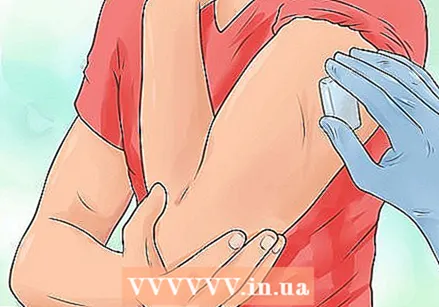 Make the patient feel comfortable. Consider numbing the area with ice before giving the injection, especially if it is a child. Have him / her sit in a comfortable position and expose the area where the injection is to be administered.
Make the patient feel comfortable. Consider numbing the area with ice before giving the injection, especially if it is a child. Have him / her sit in a comfortable position and expose the area where the injection is to be administered.
Part 2 of 3: Giving a subcutaneous injection
 Based on the doctor's instructions, determine where to give the injection. Choose an area with a lot of meat, such as the upper arm.
Based on the doctor's instructions, determine where to give the injection. Choose an area with a lot of meat, such as the upper arm. - Alternating between injection sites can prevent bruising. You can switch arms and places to make it less painful.
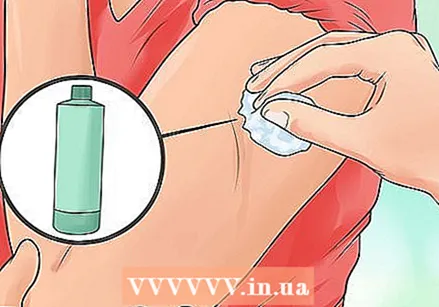 Clean the skin on and around the injection site with rubbing alcohol. Let the alcohol dry thoroughly before giving the injection. This shouldn't take more than a minute or two.
Clean the skin on and around the injection site with rubbing alcohol. Let the alcohol dry thoroughly before giving the injection. This shouldn't take more than a minute or two. 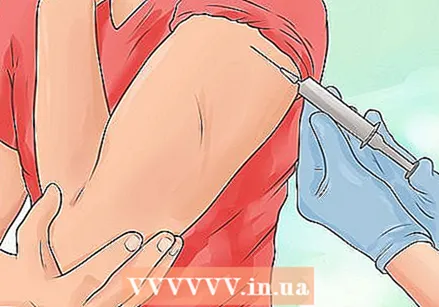 Insert the needle quickly and gently at a 45 degree angle. Hold the patient's arm with your free hand and quickly insert the needle - don't build up any tension or start a dramatic countdown. By doing it quickly, the patient will not have time to cramp, and you will ensure that it is done easily and quickly.
Insert the needle quickly and gently at a 45 degree angle. Hold the patient's arm with your free hand and quickly insert the needle - don't build up any tension or start a dramatic countdown. By doing it quickly, the patient will not have time to cramp, and you will ensure that it is done easily and quickly. - Pull back on the plunger slightly to check for blood in the syringe. If there is blood in it, gently remove the needle and try to give the injection in a different site. If there is no blood in it, then move on.
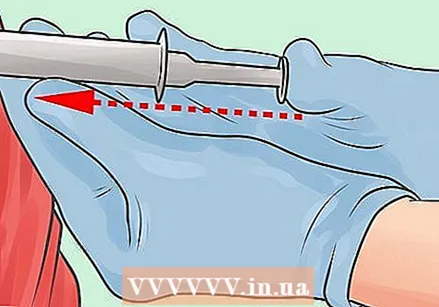 Inject the medicine. Push the plunger all the way down until all of the liquid has been injected.
Inject the medicine. Push the plunger all the way down until all of the liquid has been injected. 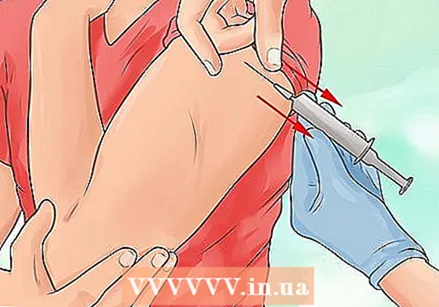 Remove the needle. Press the skin above the injection site and remove the needle gently and quickly at the same angle that you inserted the needle. If you did it right, the whole process shouldn't have taken longer than five to ten seconds.
Remove the needle. Press the skin above the injection site and remove the needle gently and quickly at the same angle that you inserted the needle. If you did it right, the whole process shouldn't have taken longer than five to ten seconds.
Part 3 of 3: Giving an intramuscular injection
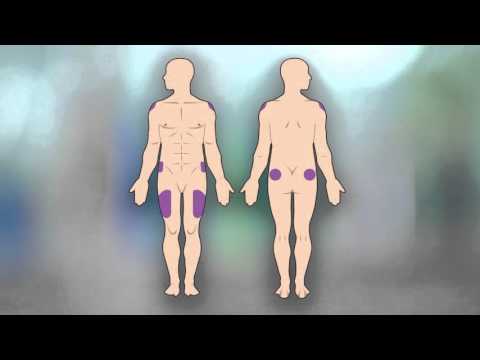
 Determine the injection site. Frequently used areas include the buttocks and thighs.
Determine the injection site. Frequently used areas include the buttocks and thighs. - Alternate injection sites to avoid bruising and irritation.
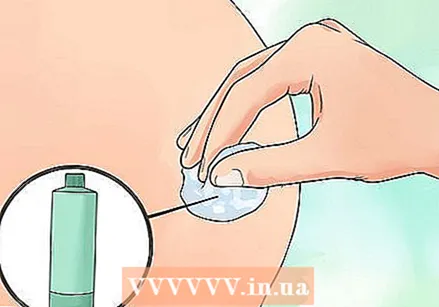 Clean the skin on and around the injection site with rubbing alcohol. Let the alcohol dry thoroughly before giving the injection.
Clean the skin on and around the injection site with rubbing alcohol. Let the alcohol dry thoroughly before giving the injection. 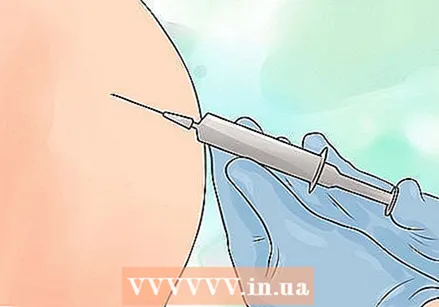 Insert the needle through the skin into the muscle tissue at a 90 degree angle. Hold the area with your free hand, and quickly insert the needle - don't add tension.
Insert the needle through the skin into the muscle tissue at a 90 degree angle. Hold the area with your free hand, and quickly insert the needle - don't add tension. 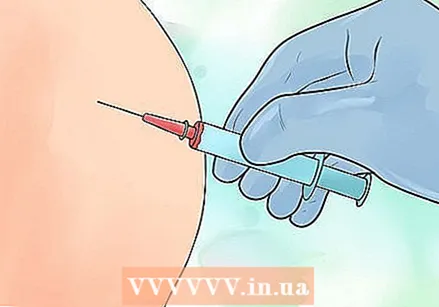 Pull back on the plunger slightly to check for blood in the syringe. If there is blood in it, gently remove the needle and try to give the injection in a different site. If there is no blood in it, then move on.
Pull back on the plunger slightly to check for blood in the syringe. If there is blood in it, gently remove the needle and try to give the injection in a different site. If there is no blood in it, then move on. 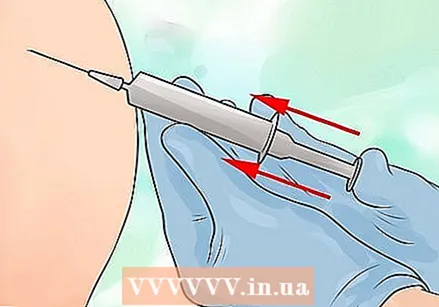 Gently inject the drug. Push the plunger all the way down until all of the liquid has been injected. Don't press too hard; apply the medicine gently to limit the pain.
Gently inject the drug. Push the plunger all the way down until all of the liquid has been injected. Don't press too hard; apply the medicine gently to limit the pain. 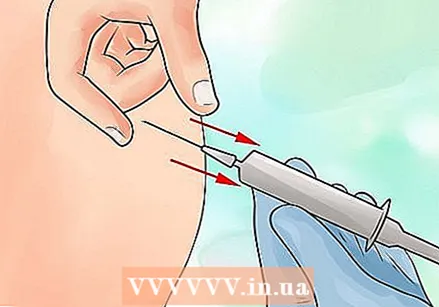 Remove the needle at the same angle that you inserted it. Cover the injection site with gauze and check regularly to see if it still looks clean.
Remove the needle at the same angle that you inserted it. Cover the injection site with gauze and check regularly to see if it still looks clean.
Tips
- If the patient is a child, distract him / her by singing a song, turning on the TV, or asking questions.
- Always instruct the patient to look away and relax the affected part of the body. This reduces the chance that the injection will hurt.
- Alternate injection sites to avoid bruising and irritation.
Warnings
- Contact a medical professional if bruises appear at the injection site that do not seem to go away, or if a fever or cough develops after the injection, and / or if you have questions about how to give the injection.
- Seek immediate help if the following symptoms occur immediately after an injection: shortness of breath, swelling of the mouth or face, and / or a rash or itching at the injection site. .