Author:
Christy White
Date Of Creation:
10 May 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- To step
- Part 1 of 2: Write the problem as a regular sub-problem
- Part 2 of 2: Solving the long division
- Tips
- Warning
Dividing by a decimal number may seem difficult at first glance. After all, no one taught you the "0.7" tables. The secret is to change the division problem to a format that uses only integers. Once you rewrite the problem in this way, it will become common long division.
To step
Part 1 of 2: Write the problem as a regular sub-problem
 Write down the partial problem. Use a pencil in case you want to make changes to your work.
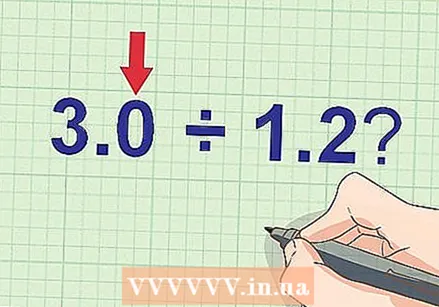
Write down the partial problem. Use a pencil in case you want to make changes to your work. - Example: What's 3 ÷ 1,2?
 Write the whole number as a decimal. Write a decimal point after the whole number, then write zeros after the decimal point. Do this until both numbers have the same number of digits to the right of the decimal point. This does not change the value of the integer.
Write the whole number as a decimal. Write a decimal point after the whole number, then write zeros after the decimal point. Do this until both numbers have the same number of digits to the right of the decimal point. This does not change the value of the integer. - Example: In the problem 3 ÷ 1.2, the integer is 3. Since 1.2 has a decimal, we rewrite 3 as 3.0, making it also a decimal number. Now the problem is 3,0 ÷ 1,2.
- Warning: Do not put zeros to the left of the decimal point! 3 is the same as 3.0 or 3.00, but not same as 30 or 300.
 Move the comma to the right until you have created whole numbers. In subproblems you can move the comma, but only if you move them by the same amount for each number. With this you turn numbers in the problem into integers.
Move the comma to the right until you have created whole numbers. In subproblems you can move the comma, but only if you move them by the same amount for each number. With this you turn numbers in the problem into integers. - Example: To convert 3.0 ÷ 1.2 to whole numbers, move the decimal point one place to the right. 3.0 then becomes 30 and 1.2 becomes 12. Now the problem is 30 ÷ 12.
 Write the problem as long division. Place the dividend (usually the larger number) below the long division symbol. You write the divisor outside it. Now you have a normal long division with integers. If you don't remember how to do long division, read the next section.
Write the problem as long division. Place the dividend (usually the larger number) below the long division symbol. You write the divisor outside it. Now you have a normal long division with integers. If you don't remember how to do long division, read the next section.
Part 2 of 2: Solving the long division
 Determine the first digit of the answer. Start by working out this problem as you normally would, by comparing the divisor with the first digit of the dividend. Calculate the number of times the divisor goes into this number, and write this number above that number.
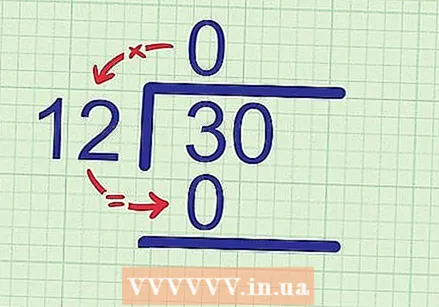
Determine the first digit of the answer. Start by working out this problem as you normally would, by comparing the divisor with the first digit of the dividend. Calculate the number of times the divisor goes into this number, and write this number above that number. - Example: We try to fit 12 in 30. Compare 12 with the first digit of the dividend, 3. Since 12 is greater than 3, it fits 0 times. Make a note 0 above 3 on the answer line.
 Multiply that number by the divisor. Write the product (the answer to the multiplication problem) under the dividend. Write it directly below the first digit of the dividend, as this is the digit you just viewed.
Multiply that number by the divisor. Write the product (the answer to the multiplication problem) under the dividend. Write it directly below the first digit of the dividend, as this is the digit you just viewed. - Example: Since 0 x 12 = 0, you write down 0 below 3.
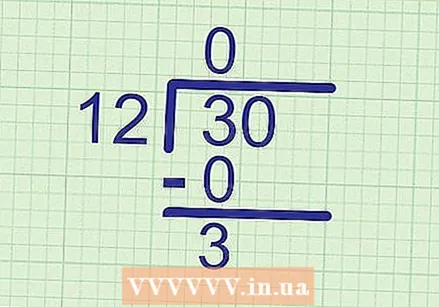 Subtract what's left. Subtract the product you just calculated from the number immediately above it. Write the answer below it, on a new line.
Subtract what's left. Subtract the product you just calculated from the number immediately above it. Write the answer below it, on a new line. - Example: 3 - 0 = 3, so you write down 3 directly below 0.
 Bring down the next digit. Bring the next digit of the dividend down next to the number you just wrote down.
Bring down the next digit. Bring the next digit of the dividend down next to the number you just wrote down. - Example: The dividend is 30. We've already looked at the 3, so the 0 is the next digit to drop. Bring it down next to the 3 to get there 30 to make of it.
 See if the divisor fits in the new number. Now repeat the first step of this section to find the second digit of your answer. This time, compare the divisor with the number you just wrote down on the lowest line.
See if the divisor fits in the new number. Now repeat the first step of this section to find the second digit of your answer. This time, compare the divisor with the number you just wrote down on the lowest line. - Example: " How often does 12 in 30 go? The closest answer to that is 2, because 12 x 2 = 24. Make a note 2 in the second place of the answer.
- If you're not sure what the answer is, try a few multiplications until you find the largest number that fits. For example, if it looks like 3 is about right, multiply 12 x 3 and you get 36. This is too large, because the number must fit within 30. Try the following, 12 x 2 = 24. This fits, so 2 is the correct answer.
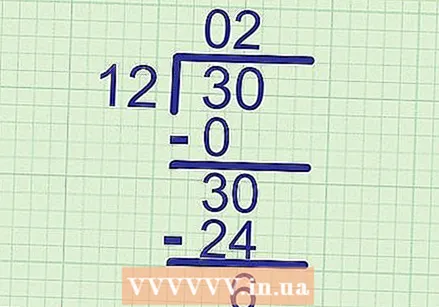 Repeat the steps above to find the next number. This is the same long division as above (and also a normal long division):
Repeat the steps above to find the next number. This is the same long division as above (and also a normal long division): - Multiply the new number on your answer line by the divisor: 2 x 12 = 24.
- Write the product on a new line below your dividend: Write 24 directly below 30.
- Subtract the bottom number from the number above it: 30-24 = 6, so write 6 on a new line below.
 Continue until you get to the end of the answer. If there is another digit to the left of the dividend, bring it down and keep solving the problem in the same way. When you reach the end of the answer, go to the next step.
Continue until you get to the end of the answer. If there is another digit to the left of the dividend, bring it down and keep solving the problem in the same way. When you reach the end of the answer, go to the next step. - Example: We have 2 as the last digit of the answer. Go to the next step.
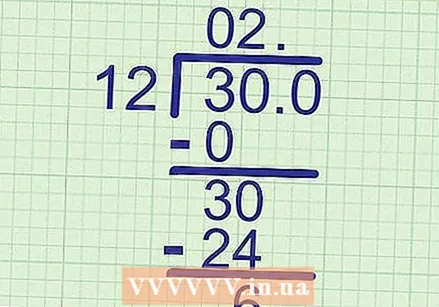 Add a decimal to expand the dividend, if necessary. If the numbers are divisible, the last subtraction returns "0". That means you are done and an integer is the answer to the problem. But if you've reached the end of the answer while there is still something to divide, then you need to expand the dividend with a comma followed by a 0. Remember, this doesn't change the value of the number.
Add a decimal to expand the dividend, if necessary. If the numbers are divisible, the last subtraction returns "0". That means you are done and an integer is the answer to the problem. But if you've reached the end of the answer while there is still something to divide, then you need to expand the dividend with a comma followed by a 0. Remember, this doesn't change the value of the number. - Example: We have reached the end of the answer, but our last subtraction answer is "6." Add a zero to the "30" below the long division. Also write a comma in the same place on the answer line, but do not write anything after it.
 Repeat the same steps to find the next digit. The only difference here is that you have to put the decimal point (the comma) in the same place in the answer. Once you've done that, finding the remaining digits of the answer proceeds exactly the same.
Repeat the same steps to find the next digit. The only difference here is that you have to put the decimal point (the comma) in the same place in the answer. Once you've done that, finding the remaining digits of the answer proceeds exactly the same. - Example: Bring the new 0 down to the last line to make "60". Because 12 goes into 60 exactly 5 times, you write 5 as the last digit on the answer line. Don't forget that we have placed a comma in the answer, so 2,5 is the definitive answer to our problem.
Tips
- You can also write this as remainder (so the answer to 3 ÷ 1.2 becomes "2 remainder 6"). But now that you're working with decimals, your teacher probably expects you to solve the decimal part of the answer as well.
- If you do the long division correctly, you will always end up with a decimal point in the correct position (or no comma if the numbers are divisible). Don't try to guess where the decimal point will go; it is often different from where the decimal point is in the numbers you started with.
- If it's a long long division, you can stop at some point and round the answer to a number that is the closest. For example, to solve for 17 ÷ 4.20, calculate to the answer 4., 047 ... and round the answer to "approximately 4.05."
- Don't forget the calculation rules for sharing:
- The dividend is the number that is divided.
- The divisor is the number by which you divide.
- The quotient is the solution to the calculation problem.
- All together: Divisor ÷ Divisor = Quotient.
Warning
- Remember, 30 ÷ 12 will give exactly the same answer as 3 ÷ 1.2. Do not try to "correct" your answer afterwards by scrolling the comma.