Author:
Eugene Taylor
Date Of Creation:
9 August 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
A portable generator can provide backup power when the normal power source, usually the utility grid, fails. It does not need to supply power to all the equipment in the house, only the essential applications such as lighting, TV, refrigerator, etc. Stoves, air conditioners and dryers, among others, consume more power than an average sized portable generator can provide.
To step
Method 1 of 2: Wiring the system
 Determine the essential uses in the home. A generator with a rated power of about 3500 watts that runs on gasoline can be used for lighting, TV, fans and a refrigerator or freezer. The nominal power is usually displayed on the generator housing, which can be supplied continuously on one full tank for an average of 12 hours.
Determine the essential uses in the home. A generator with a rated power of about 3500 watts that runs on gasoline can be used for lighting, TV, fans and a refrigerator or freezer. The nominal power is usually displayed on the generator housing, which can be supplied continuously on one full tank for an average of 12 hours.  List the electrical applications and appliances you want to use, then review their "wattage," or power requirements. For example, an average microwave oven uses 1500 watts, while an entire lighting circuit with CFC lamps may only require 150 watts. Refrigerators consume about 1200-1500 watts, but have a starting capacitor that temporarily increases their wattage when the compressor starts. Televisions consume less than 1000 watts, depending on type and size. A small room fan can use about 500 watts and so on.
List the electrical applications and appliances you want to use, then review their "wattage," or power requirements. For example, an average microwave oven uses 1500 watts, while an entire lighting circuit with CFC lamps may only require 150 watts. Refrigerators consume about 1200-1500 watts, but have a starting capacitor that temporarily increases their wattage when the compressor starts. Televisions consume less than 1000 watts, depending on type and size. A small room fan can use about 500 watts and so on.  Choose a wiring system. Various wiring systems can be used to connect a generator to a home. The two most commonly used systems are discussed here. Contact the Ministry of Social Affairs and Employment, the Ministry of Infrastructure and Water Management or the electricity company to find out which system is or is not allowed in your region. Many people are not qualified to advise you on this and the laws can be very different in different countries, regions and cities.
Choose a wiring system. Various wiring systems can be used to connect a generator to a home. The two most commonly used systems are discussed here. Contact the Ministry of Social Affairs and Employment, the Ministry of Infrastructure and Water Management or the electricity company to find out which system is or is not allowed in your region. Many people are not qualified to advise you on this and the laws can be very different in different countries, regions and cities. - Consider an interlock system. These are quite easy to install yourself and are also the cheapest option. However, they are prohibited in many areas and can pose security risks. They must be installed absolutely correctly. Safe installation means, among other things, that you have several free connections in your fuse box or that you install a new fuse box, which must be done professionally. It is also very important that you choose a system that is approved for your type of fuse box (must be made by the same company).
- Consider a manual switch. The equipment is a bit more expensive and must be installed professionally, but it is the only option that is guaranteed to be legal and therefore the safest option. It prevents you from accidentally electrocuting someone else or yourself.
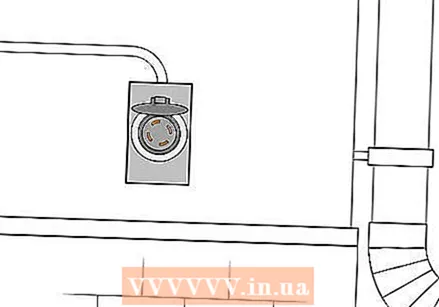 Install an inlet box. This is installed on the outside of the house and has a recessed male connection (probes that protrude, instead of having holes for inserting a plug). It is connected to the system you have installed in the house. The installation must be done by an expert, both to keep you safe and to ensure that your installation meets all requirements. If you don't get the installation done by a professional, your insurance may not cover your home, the council may impose a heavy fine on you, and seriously injure yourself or others (at an in-hospital-if-you- lucky way).
Install an inlet box. This is installed on the outside of the house and has a recessed male connection (probes that protrude, instead of having holes for inserting a plug). It is connected to the system you have installed in the house. The installation must be done by an expert, both to keep you safe and to ensure that your installation meets all requirements. If you don't get the installation done by a professional, your insurance may not cover your home, the council may impose a heavy fine on you, and seriously injure yourself or others (at an in-hospital-if-you- lucky way).  Keep your family safe! There is a lot of advice and instructions on the internet that are not safe and that seriously increase the risk of injury, electrocution and fire. Always consult a specialist before doing anything that could endanger you and your family. Some general things you not must do are:
Keep your family safe! There is a lot of advice and instructions on the internet that are not safe and that seriously increase the risk of injury, electrocution and fire. Always consult a specialist before doing anything that could endanger you and your family. Some general things you not must do are: - Do not connect your generator directly to the fuse box without an approved switch.
- Do not plug your generator into a washing machine or dryer outlet.
 Have your installation inspected. This is especially important if you have no experience working with electricity. Make sure you and your family are safe and that, in the event of a fire, your insurance policy cannot deny your claim due to incorrect wiring.
Have your installation inspected. This is especially important if you have no experience working with electricity. Make sure you and your family are safe and that, in the event of a fire, your insurance policy cannot deny your claim due to incorrect wiring.
Method 2 of 2: Connect
 Move the generator away from your home. Place the generator as far away from the house as possible with the supplied cord. This is to prevent any fire from spreading to the house if something goes wrong with the generator and to prevent deadly carbon monoxide poisoning from the generator's exhaust fumes. This is a general safety warning and should not be ignored.
Move the generator away from your home. Place the generator as far away from the house as possible with the supplied cord. This is to prevent any fire from spreading to the house if something goes wrong with the generator and to prevent deadly carbon monoxide poisoning from the generator's exhaust fumes. This is a general safety warning and should not be ignored.  Connect your generator to the inlet box. Line up the holes on the end of the generator cord with the probes in the inlet box. Plug in the cord. You will probably have to turn the plug to complete the connection (usually about 15 degrees).
Connect your generator to the inlet box. Line up the holes on the end of the generator cord with the probes in the inlet box. Plug in the cord. You will probably have to turn the plug to complete the connection (usually about 15 degrees). 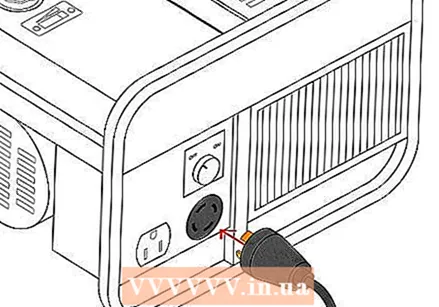 Plug the connection cord into your generator. Your generator should come with a cord to plug into the house. Plug these in, select the desired voltage (if possible) and twist, as you did with the other end of the cord.
Plug the connection cord into your generator. Your generator should come with a cord to plug into the house. Plug these in, select the desired voltage (if possible) and twist, as you did with the other end of the cord.  Check the engine. Check that the engine coupling is in the correct position and that the engine has sufficient oil. Depending on where you live, you may need to warm up the engine with the glow plug.
Check the engine. Check that the engine coupling is in the correct position and that the engine has sufficient oil. Depending on where you live, you may need to warm up the engine with the glow plug.  Start the engine. Start the engine of your generator according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Start the engine. Start the engine of your generator according to the manufacturer's instructions. 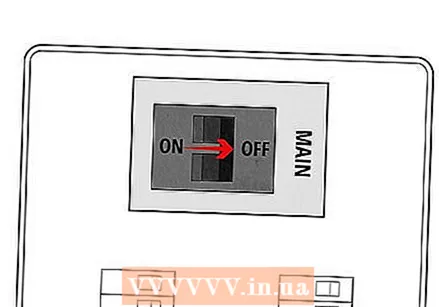 Switch between the systems. Go to your fuse box. Turn off utility power and turn on generator power.
Switch between the systems. Go to your fuse box. Turn off utility power and turn on generator power.  Convert the fuses. Switch the fuses of the system you have installed one by one (slowly).
Convert the fuses. Switch the fuses of the system you have installed one by one (slowly). 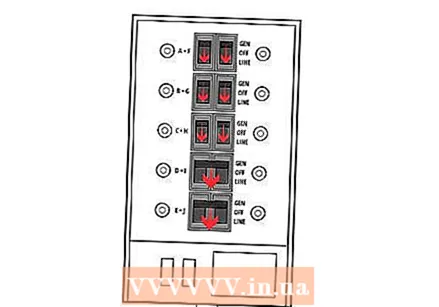 Return to utility power. To use the mains power again, follow the steps in reverse order.
Return to utility power. To use the mains power again, follow the steps in reverse order.
Tips
- Contact the local government for help and advice!
Warnings
- Working with electricity is very dangerous. If you are unsure of what to do, it is best to call an expert.