Author:
Morris Wright
Date Of Creation:
27 April 2021
Update Date:
26 June 2024

Content
- To step
- Method 1 of 3: Basic earnings per share calculation
- Method 2 of 3: Calculating the weighted earnings per share
- Method 3 of 3: Apply earnings per share
- Tips
Earnings per share (EPS) is a commonly used term in the financial world. Earnings per share represent the portion of a company's earnings attributable to one share. Therefore, by multiplying EPS by the number of shares a company owns, you can calculate the net profit. The EPS is a calculation that many people pay attention to who track the stock market.
To step
Method 1 of 3: Basic earnings per share calculation
 Find the company's net profit from last year. This information can be found on most financial web pages or on the corporate website. Using the company's net profit as the primary number in the calculation is the most fundamental way to determine EPS.
Find the company's net profit from last year. This information can be found on most financial web pages or on the corporate website. Using the company's net profit as the primary number in the calculation is the most fundamental way to determine EPS. - For example, let's say you want to calculate Microsoft's EPS based on net profit. Soon, on Microsoft's website, you'll find that net income in 2012 was nearly $ 17 billion.
- Note that you have the net profit of a quarter not to be confused with the annual net profit. Quarterly net profit is calculated every three months, while annual net profit is calculated every twelve months. By using the net profit of three months instead of twelve, your outcome will be about four times lower.
 Find out how many shares are outstanding. How many shares does a company have on the stock exchange? This information can be collected through a financial website by searching the information of the respective company.
Find out how many shares are outstanding. How many shares does a company have on the stock exchange? This information can be collected through a financial website by searching the information of the respective company. - Let's continue Microsoft's example. In 2012, Microsoft had 8.33 billion shares outstanding.
 Divide the net profit by the number of shares outstanding. Using Microsoft's data as an example, we divide $ 17 billion by 8.33 billion and get a baseline outcome of an EPS of $ 2.
Divide the net profit by the number of shares outstanding. Using Microsoft's data as an example, we divide $ 17 billion by 8.33 billion and get a baseline outcome of an EPS of $ 2. - Let's give another basic example. A company that sells bocce balls has a net profit of $ 4 million and 575,000 shares outstanding. We divide $ 4 million by 575,000 and get EPS of $ 6.95.
Method 2 of 3: Calculating the weighted earnings per share
 Adjust the basic EPS calculation a bit to get the weighted EPS calculation. Weighted EPS is a more accurate calculation because it also takes into account dividends paid to shareholders. This formula is a bit more complex than the basic calculation, which means that it is used less often even though it is more accurate.
Adjust the basic EPS calculation a bit to get the weighted EPS calculation. Weighted EPS is a more accurate calculation because it also takes into account dividends paid to shareholders. This formula is a bit more complex than the basic calculation, which means that it is used less often even though it is more accurate.  Find the dividend on preferred stock. A dividend is an amount of money from the profit that is usually paid to shareholders every quarter.
Find the dividend on preferred stock. A dividend is an amount of money from the profit that is usually paid to shareholders every quarter. - To give another example, let's take Apple as the company for which we are going to make the calculation. In 2012, Apple announced that it would pay out $ 2.5 billion in dividends on a quarterly basis, starting in the third quarter. That means that about $ 5 billion in dividends will be paid out in one year.
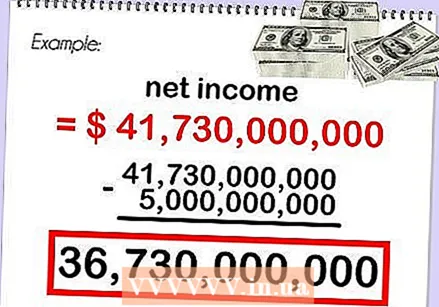 Take the company's net profit and subtract the preferred stock dividend. Using Apple as an example, we quickly find that Apple had net profit of $ 41.73 billion in 2012. Take off $ 5 billion to get to $ 36.73 billion.
Take the company's net profit and subtract the preferred stock dividend. Using Apple as an example, we quickly find that Apple had net profit of $ 41.73 billion in 2012. Take off $ 5 billion to get to $ 36.73 billion.  Divide the difference by the average number of shares outstanding. Apple's net profit less its dividend in 2012 was $ 36.73 billion. Divide this amount by the number of shares outstanding, 934.82 million, to get the weighted EPS of $ 39.29.
Divide the difference by the average number of shares outstanding. Apple's net profit less its dividend in 2012 was $ 36.73 billion. Divide this amount by the number of shares outstanding, 934.82 million, to get the weighted EPS of $ 39.29.
Method 3 of 3: Apply earnings per share
 Use EPS as an expression of a company's profitability. EPS shows (potential) investors the profitability of a company. A higher EPS generally indicates a more robust company, given the profit. However, the WPA should not be considered alone. There is no set level of earnings per share, requiring a company's stock to be bought if it is above it, or sold if it is below it. It's important to look at a company's EPS in relation to other companies.
Use EPS as an expression of a company's profitability. EPS shows (potential) investors the profitability of a company. A higher EPS generally indicates a more robust company, given the profit. However, the WPA should not be considered alone. There is no set level of earnings per share, requiring a company's stock to be bought if it is above it, or sold if it is below it. It's important to look at a company's EPS in relation to other companies.  Know that EPS is probably the single most important factor in determining the share price. It says more when you look at EPS rather than net profit, because EPS puts a company's earnings into perspective: a huge company making $ 1 million in net profit isn't nearly as impressive as a very small company is. Makes $ 1 million net profit. EPS is also integrated into the price-earnings ratio, or the Price to Earnings ratio (P / E).
Know that EPS is probably the single most important factor in determining the share price. It says more when you look at EPS rather than net profit, because EPS puts a company's earnings into perspective: a huge company making $ 1 million in net profit isn't nearly as impressive as a very small company is. Makes $ 1 million net profit. EPS is also integrated into the price-earnings ratio, or the Price to Earnings ratio (P / E).  Keep in mind that calculating EPS is not enough to make an informed decision about whether to invest or not. The WPA shows how well a company is doing compared to another company or compared to the industry average, but it doesn't give a single glance as to whether or not it is a good idea to buy stock in a company. To make an informed decision as to whether you can invest in a company, you should at least consider the following points:
Keep in mind that calculating EPS is not enough to make an informed decision about whether to invest or not. The WPA shows how well a company is doing compared to another company or compared to the industry average, but it doesn't give a single glance as to whether or not it is a good idea to buy stock in a company. To make an informed decision as to whether you can invest in a company, you should at least consider the following points: - The stock market value
- The share price
- Dividend and redemption of own shares
- The long-term financial outlook
- Sufficient liquidity
Tips
- When determining whether or not to invest in a business, EPS is often used instead of the company's total net profit. This term is used so much because it is an easier way to portray the actual profitability of a business.
- Pay attention to the number of shares outstanding when making these calculations. The more shares involved, the more diluted the EPS result will be.
- Almost all the information you need for these calculations can be found online. To find this information, you will need to visit a financial website and look up the company's profit and loss (and other) accounts.
- Be careful when calculating the regular WPA or the weighted WPA. In some cases these two numbers are barely different, but it is still important to know whether you are using the base calculation for a more general estimate, or the weighted calculation, which takes into account the fact that numbers change over time.



