Author:
Mark Sanchez
Date Of Creation:
6 January 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
This article looks at a standard quadratic equation of the form:
ax + bx + c = 0
The article deduces a formula for the roots of a quadratic equation by complementing to a full square; numeric values instead of a, b, c will not be substituted.
Steps
 1 Write an equation.
1 Write an equation.
ax + bx + c = 0 2 Divide both sides of the equation by but.
2 Divide both sides of the equation by but.
x + (b / a) x + c / a = 0 3 Subtract s / a from both sides of the equation.
3 Subtract s / a from both sides of the equation.
x + (b / a) x = -c / a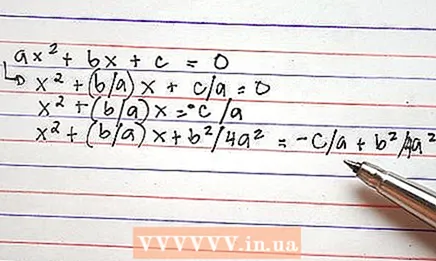 4 Divide the coefficient at NS (b / a) by 2, and then square the result. Add the result to both sides of the equation.
4 Divide the coefficient at NS (b / a) by 2, and then square the result. Add the result to both sides of the equation.
(b / 2a)
b / 4a
x + (b / a) x + b / 4a = -c / a + b / 4a 5 Simplify the expression by factoring the left side and adding the terms on the right side (find a common denominator first).
5 Simplify the expression by factoring the left side and adding the terms on the right side (find a common denominator first).
(x + b / 2a) (x + b / 2a) = (-4ac / 4a) + (b / 4a)
(x + b / 2a) = (b - 4ac) / 4a 6 Take the square root of each side of the equation.
6 Take the square root of each side of the equation.
√ ((x + b / 2a)) = ± √ ((b - 4ac) / 4a)
x + b / 2a = ± √ (b - 4ac) / 2a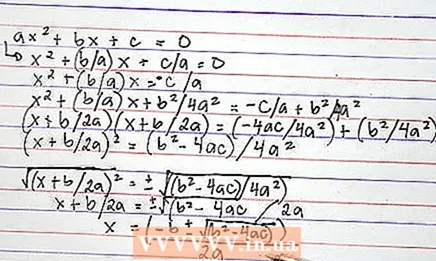 7 Subtract b / 2a from both sides and you get the quadratic formula.
7 Subtract b / 2a from both sides and you get the quadratic formula.
x = (-b ± √ (b - 4ac)) / 2a
Tips
- Note: This method is also called full square's complement.
What do you need
- Pencil and paper