Author:
Eric Farmer
Date Of Creation:
3 March 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 3: Calculating kilowatt-hours from the power of the device
- Method 2 of 3: Calculating Kilowatt Hours from Current and Voltage
- Method 3 of 3: Using a wattmeter
- Tips
Most household appliances have a label (label) on which you can find information about the power consumption and which is applied to the back or bottom of the appliance. This label indicates the maximum value of the consumed electricity. To calculate the total energy consumption, convert this value to kilowatt-hours (kWh).
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Calculating kilowatt-hours from the power of the device
 1 Find its wattage on the product label. Most electrical appliances have an energy label on the back or bottom. On such a label, find the power consumption value, which is indicated as "W" or "W". Typically, the label indicates the maximum power consumption of the device, which is significantly higher than the average power consumption. This section describes the process of calculating an approximate kWh value that is greater than the actual power consumption.
1 Find its wattage on the product label. Most electrical appliances have an energy label on the back or bottom. On such a label, find the power consumption value, which is indicated as "W" or "W". Typically, the label indicates the maximum power consumption of the device, which is significantly higher than the average power consumption. This section describes the process of calculating an approximate kWh value that is greater than the actual power consumption. - Some devices provide a range of power consumption, for example, "200-300 W". In this case, select the average for calculations; in our example, this value is 250 watts.
 2 Multiply the power consumption by the number of hours you use the appliance each day. Watts are a measure of power without reference to time. By multiplying the unit of measure of power by the unit of measure of time, you can estimate the amount of electricity consumed and calculate the amount you have to pay.
2 Multiply the power consumption by the number of hours you use the appliance each day. Watts are a measure of power without reference to time. By multiplying the unit of measure of power by the unit of measure of time, you can estimate the amount of electricity consumed and calculate the amount you have to pay. - For example, a large 250 W window fan runs 5 hours a day. Thus, the fan consumes (250 W) x (5 h) = 1250 W ∙ h of electricity every day.
- For air conditioners and heaters, make separate calculations for each season.
- The refrigerator only consumes about 8 hours of electricity per day (if you never turn it off).
 3 Divide the result by 1000. Since 1 kW = 1000 W, this step converts the unit from Wh to kWh.
3 Divide the result by 1000. Since 1 kW = 1000 W, this step converts the unit from Wh to kWh. - In our example, you calculated that the fan consumes 1250 Wh daily. (1250 W ∙ h) ÷ (1000 W) = 1.25 kW ∙ h per day.
 4 Multiply your result by the specified number of days. At this point, you have calculated the amount of electricity (in kWh) consumed by the device every day. Multiply the daily value by the number of days in a month or a year to find your monthly or yearly electricity consumption.
4 Multiply your result by the specified number of days. At this point, you have calculated the amount of electricity (in kWh) consumed by the device every day. Multiply the daily value by the number of days in a month or a year to find your monthly or yearly electricity consumption. - In our example, for a month (30 days), the fan will consume (1.25 kWh per day) x (30 days) = 37.5 kWh of electricity.
- In our example, for a year (365 days), the fan will consume (1.25 kWh per day) x (365 days) = 456.25 kWh of electricity.
 5 Multiply the resulting value by the cost of one kilowatt-hour. The electricity payment form indicates the cost of one kilowatt-hour.Multiply this cost by the calculated amount of electricity consumed to determine the amount you have to pay.
5 Multiply the resulting value by the cost of one kilowatt-hour. The electricity payment form indicates the cost of one kilowatt-hour.Multiply this cost by the calculated amount of electricity consumed to determine the amount you have to pay. - For example, if 1 kWh costs 5 rubles, then you will have to pay for the electricity consumed by the fan (5 rubles per kWh) x (456.25 kWh per year) = 2281.25 rubles (per year).
- Remember that calculations based on the power label of the appliance give the maximum value for the cost of the electricity consumed - in fact, you will pay less.
- If you work with different regions (areas) of the country, find the cost of 1 kWh of electricity in each region. We recommend that residents of Russia open this site.
Method 2 of 3: Calculating Kilowatt Hours from Current and Voltage
 1 Find the amperage on the product label. Some devices do not indicate the power value on the labels. In this case, find the current value, which is designated as "A".
1 Find the amperage on the product label. Some devices do not indicate the power value on the labels. In this case, find the current value, which is designated as "A". - Laptop and phone chargers are marked with two current values. Use the value that is labeled "Input" or "Input".
 2 Determine the voltage for your area. In Russia and most other countries, the standard mains voltage is 230 V (220-240 V). In some countries (for example, in the USA) this value is 120 V.
2 Determine the voltage for your area. In Russia and most other countries, the standard mains voltage is 230 V (220-240 V). In some countries (for example, in the USA) this value is 120 V. - In the United States, large electrical appliances, such as washing machines, can be plugged into a special 240V electrical supply. To find the voltage of an electrical appliance, look for its energy label (the label shows the recommended voltage, but it can be assumed that the voltage in the electrical network to which the appliance is connected , complies with this recommendation).
 3 Multiply the amperage by the voltage. This will calculate the wattage value.
3 Multiply the amperage by the voltage. This will calculate the wattage value. - For example, the microwave oven label states that the current is 3.55 A and the voltage is 220 V. The power of this oven is 3.55 A x 220 V ≈ 780 W.
 4 Multiply the power consumption by the number of hours you use the appliance each day. Power characterizes the amount of energy consumed by the device during its operation. Multiply the power consumption by the average number of hours the appliance is on each day.
4 Multiply the power consumption by the number of hours you use the appliance each day. Power characterizes the amount of energy consumed by the device during its operation. Multiply the power consumption by the average number of hours the appliance is on each day. - In our example, the microwave is on for 30 minutes daily. 1430 W x 0.5 hour / day = 715 W ∙ h per day.
 5 Divide the result by 1000. This step converts units of measurement from Wh to kWh.
5 Divide the result by 1000. This step converts units of measurement from Wh to kWh. - In our example: 715 W ∙ h (per day) ÷ 1000 W = 0.715 kW ∙ h per day.
 6 Multiply your result by the specified number of days. For example, to find the monthly electricity consumption, multiply the daily value by the number of days in one month.
6 Multiply your result by the specified number of days. For example, to find the monthly electricity consumption, multiply the daily value by the number of days in one month. - In our example: 0.715 kWh (per day) x 31 days = 22.165 kWh.
Method 3 of 3: Using a wattmeter
 1 Buy a wattmeter. This device measures the actual power consumed by electrical appliances. This method results in more accurate results than using the values indicated on the instrument label.
1 Buy a wattmeter. This device measures the actual power consumed by electrical appliances. This method results in more accurate results than using the values indicated on the instrument label. - If you are familiar with electrician tools, use a multimeter instead of a wattmeter. This will require access to the wiring of the instrument when it is connected to the mains. If you are unsure of what to do, do not disassemble the appliance.
 2 The wattmeter is connected between the electrical outlet and the appliance. Plug the wattmeter into an outlet, and connect the electrical appliance to the wattmeter.
2 The wattmeter is connected between the electrical outlet and the appliance. Plug the wattmeter into an outlet, and connect the electrical appliance to the wattmeter.  3 Measure the power value in kilowatt-hours. Set the watt-hour meter to display the power consumption in kilowatt-hours. By connecting the device to a working wattmeter, the device will measure the total amount of electricity consumed (in kilowatt-hours).
3 Measure the power value in kilowatt-hours. Set the watt-hour meter to display the power consumption in kilowatt-hours. By connecting the device to a working wattmeter, the device will measure the total amount of electricity consumed (in kilowatt-hours). - If your wattmeter model measures power only in watts, use the method described in the first section of this article to calculate the power in kilowatt-hours.
- Read the instruction manual of the wattmeter if you do not know how to set it up.
 4 Use the appliance as usual. By connecting the device to a working wattmeter for a long time, you will get more accurate results.
4 Use the appliance as usual. By connecting the device to a working wattmeter for a long time, you will get more accurate results. 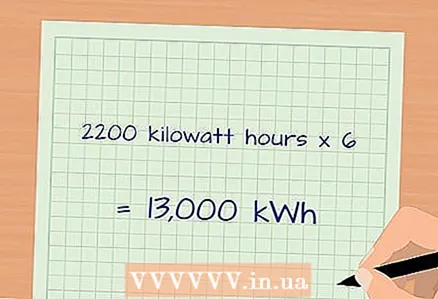 5 Find the monthly or yearly power consumption (in kilowatt-hours). The indicator of the wattmeter displays the value of kilowatt-hours, measured from the moment the electrical appliance was connected to a working wattmeter. Multiply this value by a certain number to find out the amount of electricity consumed over a longer period of time.
5 Find the monthly or yearly power consumption (in kilowatt-hours). The indicator of the wattmeter displays the value of kilowatt-hours, measured from the moment the electrical appliance was connected to a working wattmeter. Multiply this value by a certain number to find out the amount of electricity consumed over a longer period of time. - For example, a wattmeter works for 5 days, but you need to calculate the monthly (30 days) power consumption. In this case, divide 30 by 5 and get 6, and then multiply 6 by the value displayed on the wattmeter indicator.
Tips
- If there is no power value on the label of an electrical appliance, read the instructions for use of this appliance. Moreover, on some labels the power value in kilowatt-hours is already indicated and denoted as "kWh / year" (kWh per year), "kWh / annum" (kWh annually) or "kWh / 60minutes" (kWh h in 60 minutes). These calculations are based on averages and are more accurate than those described in this article.
- Some electrical appliances can be configured to consume different wattage. In this case, the label indicates either the power at each setting or the maximum power value.