Author:
Clyde Lopez
Date Of Creation:
26 June 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Part 1 of 2: What is latitude and longitude
- Part 2 of 2: Finding Latitude and Longitude Coordinates on a Map
Latitude and longitude are needed to determine the position on the globe. Knowing how to read latitude and longitude from the map, you will be able to determine the geographical coordinates of any point on the map. While online maps allow you to determine latitude and longitude with a simple click of a button, it is sometimes useful to know how to do this on a paper map. In order to calculate latitude and longitude correctly, you must first figure out what it is. After you grasp the basics, you can learn how to determine latitude and longitude marks on a map and determine the coordinates of any point.
Steps
Part 1 of 2: What is latitude and longitude
 1 Become familiar with the concept of latitude. Latitude is a measure of the distance north or south of the equator, which is an imaginary horizontal line equidistant from the poles. The entire Earth is divided by 180 latitudinal lines located on either side of the equator, which are called parallels. Parallels run parallel to the equator and are usually horizontal on a map. 90 of them are north of the equator, another 90 are south.
1 Become familiar with the concept of latitude. Latitude is a measure of the distance north or south of the equator, which is an imaginary horizontal line equidistant from the poles. The entire Earth is divided by 180 latitudinal lines located on either side of the equator, which are called parallels. Parallels run parallel to the equator and are usually horizontal on a map. 90 of them are north of the equator, another 90 are south. 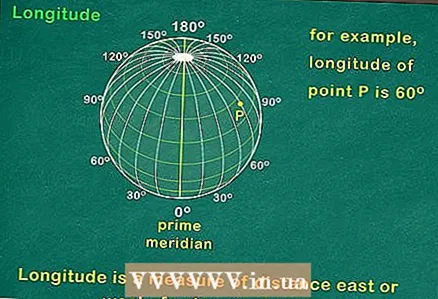 2 Find out the definition of longitude. Longitude is a measure of the distance east or west of an imaginary line running across the surface of the globe from the North Pole to the South Pole, called the Prime Meridian. Longitude lines are a series of lines running from the North Pole to the South Pole, which are called meridians; they are usually vertical on maps. At all points through which one meridian passes, noon occurs at the same time. There are 360 meridians on Earth, of which 180 are located east of the prime meridian, and 180 are located to the west.
2 Find out the definition of longitude. Longitude is a measure of the distance east or west of an imaginary line running across the surface of the globe from the North Pole to the South Pole, called the Prime Meridian. Longitude lines are a series of lines running from the North Pole to the South Pole, which are called meridians; they are usually vertical on maps. At all points through which one meridian passes, noon occurs at the same time. There are 360 meridians on Earth, of which 180 are located east of the prime meridian, and 180 are located to the west. - The meridian on the opposite side of the earth relative to the prime meridian is called the antimeridian.
 3 Learn the units of measure for latitude and longitude. Latitude and longitude are usually measured in degrees (°), minutes (′), and seconds (″). The total distance from one parallel to another or from one meridian to another is 1 °. To make more accurate measurements, each degree can be divided by 60 minutes, and each minute by 60 seconds (so there are 3600 seconds in a degree).
3 Learn the units of measure for latitude and longitude. Latitude and longitude are usually measured in degrees (°), minutes (′), and seconds (″). The total distance from one parallel to another or from one meridian to another is 1 °. To make more accurate measurements, each degree can be divided by 60 minutes, and each minute by 60 seconds (so there are 3600 seconds in a degree). - Latitude and longitude are measured in degrees, not absolute length units (such as kilometers), because the Earth is shaped like a ball. While the distance between degrees of latitude is constant (60 nautical miles or 111.12 km), the distance between degrees of longitude decreases as you get closer to the poles due to the shape of the Earth.
 4 Measure latitude and longitude from the zero point. When measuring latitude, the equator is considered as the starting line, which has a latitude of 0 °. Similarly, the prime meridian is the starting line for measuring longitude, having a longitude of 0 °. Any latitude or longitude value is expressed by how far a given point is from the starting line and in which direction it is from it.
4 Measure latitude and longitude from the zero point. When measuring latitude, the equator is considered as the starting line, which has a latitude of 0 °. Similarly, the prime meridian is the starting line for measuring longitude, having a longitude of 0 °. Any latitude or longitude value is expressed by how far a given point is from the starting line and in which direction it is from it. - For example, the latitude of the North Pole is 90 ° N. NS. (latitude north), which means it is 90 ° north of the equator.
- Antimeridian has a longitude of 180 °, it can be designated both west and east longitude.
- The Great Sphinx at Giza, Egypt, is located at 29 ° 58′31 ″ N. NS. and 31 ° 8'15 ″ in. (east longitude). This means that it is slightly south of 30 ° north of the equator in latitude, and about 31 ° east of the prime meridian in longitude.
Part 2 of 2: Finding Latitude and Longitude Coordinates on a Map
 1 Find a map with lines of latitude and longitude. Not all maps show latitude and longitude. You will most likely find them on maps of large areas, such as maps in the atlas. Among maps of smaller areas, they are more likely to be on maps that are designed to display terrain particularly accurately, such as topographic maps. Keep in mind that in Russia topographic maps on a scale of 1: 50,000 and larger are classified.
1 Find a map with lines of latitude and longitude. Not all maps show latitude and longitude. You will most likely find them on maps of large areas, such as maps in the atlas. Among maps of smaller areas, they are more likely to be on maps that are designed to display terrain particularly accurately, such as topographic maps. Keep in mind that in Russia topographic maps on a scale of 1: 50,000 and larger are classified.  2 Find the object that interests you. Look at the map and find the point or area for which you want to know the coordinates. Mark a specific point that interests you with a pin or pencil.
2 Find the object that interests you. Look at the map and find the point or area for which you want to know the coordinates. Mark a specific point that interests you with a pin or pencil.  3 Find latitude and longitude marks on the map. Latitude is indicated on the map by a series of equally spaced horizontal lines from one side of the map to the other, and longitude is represented by a series of equally spaced vertical lines from top to bottom. Look at the numbers along the edges of the map - they show the coordinate (latitude or longitude) for each line.
3 Find latitude and longitude marks on the map. Latitude is indicated on the map by a series of equally spaced horizontal lines from one side of the map to the other, and longitude is represented by a series of equally spaced vertical lines from top to bottom. Look at the numbers along the edges of the map - they show the coordinate (latitude or longitude) for each line. - Latitudes are shown along the eastern and western edges of the map. Longitudes are shown along its northern and southern boundaries.
- Depending on the scale of the map you are using, the numbers along the edges of the map may not show whole degrees, but fractions. For example, they can show every minute, not every degree (for example, 32 ° 0 ′, 32 ° 1 ′, and so on).
- The map should also indicate the position of latitude and longitude relative to the equator and prime meridian, respectively (that is, latitude north or south, longitude west or east).
- Be careful not to confuse latitude and longitude lines with a kilometer grid, another type of grid that can also often be seen on maps, especially topographic ones. On Russian topographic maps, the labels for kilometer lines are two-digit numbers (without the degree symbol) located along the entire border of the map, and labels for latitude and longitude are available only at the corners of the map. In other countries, the designations may be different.
 4 Use a ruler to mark the latitude of the point of interest. Take a ruler and pencil and draw a horizontal line from the desired point to the west or east edge of the map (whichever is closer). Make sure the line you drew is parallel to the closest latitude line on the map.
4 Use a ruler to mark the latitude of the point of interest. Take a ruler and pencil and draw a horizontal line from the desired point to the west or east edge of the map (whichever is closer). Make sure the line you drew is parallel to the closest latitude line on the map.  5 Draw another line to mark the longitude of the point. From the same point, draw a straight vertical line along the ruler to the top or bottom of the map (whichever is closer). Make sure the line you drew is parallel to the nearest line of longitude.
5 Draw another line to mark the longitude of the point. From the same point, draw a straight vertical line along the ruler to the top or bottom of the map (whichever is closer). Make sure the line you drew is parallel to the nearest line of longitude.  6 Determine the latitude and longitude of the point of interest using the latitude and longitude labels. Depending on the scale of the map, you will be able to determine the coordinates of the point of interest to degrees, minutes or seconds. Look at the location where the latitude and longitude lines you drew intersect the edge of the map, and determine their coordinates by their position relative to the nearest lines on the map.
6 Determine the latitude and longitude of the point of interest using the latitude and longitude labels. Depending on the scale of the map, you will be able to determine the coordinates of the point of interest to degrees, minutes or seconds. Look at the location where the latitude and longitude lines you drew intersect the edge of the map, and determine their coordinates by their position relative to the nearest lines on the map. - If the map you are using shows seconds, find the second mark closest to where the line you drew crosses the edge of the map. For example, if the line is about 5 ″ above the 32 ° 20 ′ N line. sh., the desired point has a latitude of approximately 32 ° 20'5 ″ s. NS.
- If the map shows every minute but does not show the seconds, you can determine the latitude or longitude to within 6 seconds by dividing the space between the lines into tenths. If the line of longitude is 2/10 to the left of the line 120 ° 14 ′ E. so, its longitude is approximately 120 ° 14'12 ″ E. etc.
 7 Combine measurements and get coordinates. Geographic coordinates are where the lines of latitude and longitude intersect at one point. Look at the results you get for the latitude and longitude of the point you are looking for and combine them (eg 32 ° 20'5 "N, 120 ° 14'12" E).
7 Combine measurements and get coordinates. Geographic coordinates are where the lines of latitude and longitude intersect at one point. Look at the results you get for the latitude and longitude of the point you are looking for and combine them (eg 32 ° 20'5 "N, 120 ° 14'12" E).