Author:
Gregory Harris
Date Of Creation:
7 August 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
Shock occurs when the body does not receive enough blood flow or oxygen, which can lead to permanent organ damage or death. Shock can result from injury, heatstroke, blood loss, allergic reactions, and more. Read on to learn how to identify and manage both shock and anaphylactic shock that results from an allergic reaction.
Steps
Method 1 of 2: Treating Shock
 1 Definition of symptoms. Before giving any help, it is very important to know what you are dealing with. Common signs and symptoms of shock:
1 Definition of symptoms. Before giving any help, it is very important to know what you are dealing with. Common signs and symptoms of shock: - Paleness, coldness, clammy skin. The skin will be grayish and the lips and nails will be blue.
- Rapid breathing and palpitations.
- The person experiences disorientation and dizziness.
- Nausea and vomiting may occur.
- A person may experience weakness and emptiness in the eyes.
 2 Call the emergency number. It is very important that during the first aid, the ambulance is already on the way, as shock is a very serious condition that requires hospitalization. Stay in touch with the emergency dispatcher in case the victim's condition worsens. This way, you will be able to receive the necessary guidance and provide proper first aid.
2 Call the emergency number. It is very important that during the first aid, the ambulance is already on the way, as shock is a very serious condition that requires hospitalization. Stay in touch with the emergency dispatcher in case the victim's condition worsens. This way, you will be able to receive the necessary guidance and provide proper first aid.  3 Let the person lie on the ground. Be very careful, as any sudden movement can harm a person. If the person is not in pain, place his or her feet on a pillow to lift them about 30 cm above the head.
3 Let the person lie on the ground. Be very careful, as any sudden movement can harm a person. If the person is not in pain, place his or her feet on a pillow to lift them about 30 cm above the head. - Do not move the victim's head.
- Do not move a person unless the area is dangerous, for example, if you find a person lying on the highway at the scene of an accident.
- It is necessary that the person lies on a flat surface and does not move.
 4 Check to see if the victim is breathing. Observe the person's chest to see if it rises and falls. Also place your cheek next to his / her mouth to check if he / she is breathing. If the person is not breathing, give him / her artificial respiration.
4 Check to see if the victim is breathing. Observe the person's chest to see if it rises and falls. Also place your cheek next to his / her mouth to check if he / she is breathing. If the person is not breathing, give him / her artificial respiration. - If the victim is a child, perform artificial respiration for children. If the victim is an infant, artificial respiration for the infant.
- Check your breathing every 5 minutes before an ambulance arrives.
 5 Make the victim feel comfortable. Loosen collar, open or cut tight clothing. Unbuckle the belt, undo the laces on your boots, and remove jewelry from the wrists and neck that are blocking free breathing and blood circulation. Cover the person with a sheet.
5 Make the victim feel comfortable. Loosen collar, open or cut tight clothing. Unbuckle the belt, undo the laces on your boots, and remove jewelry from the wrists and neck that are blocking free breathing and blood circulation. Cover the person with a sheet. - Do not give food or water to the victim.
- Encourage and comfort the victim. Make sure he remains calm until the ambulance arrives.
 6 Examine it for vomiting or bleeding from the mouth. If you notice traces of bleeding or vomiting from your mouth or nose, turn his / her head to the side to prevent it from choking. Place pillows under it.
6 Examine it for vomiting or bleeding from the mouth. If you notice traces of bleeding or vomiting from your mouth or nose, turn his / her head to the side to prevent it from choking. Place pillows under it.  7 Pay attention to injury and blood loss. If the victim is injured, you may need to stop bleeding from the wound or give first aid to a broken bone. For additional instructions, contact the ambulance dispatcher by phone.
7 Pay attention to injury and blood loss. If the victim is injured, you may need to stop bleeding from the wound or give first aid to a broken bone. For additional instructions, contact the ambulance dispatcher by phone.
Method 2 of 2: Treating anaphylactic shock
 1 Definition of symptoms. Anaphylactic juice usually occurs a few seconds or minutes after contact with an allergen (nuts, soy, wheat and other foods; bee sting; other causes). The symptoms of anaphylactic shock are:
1 Definition of symptoms. Anaphylactic juice usually occurs a few seconds or minutes after contact with an allergen (nuts, soy, wheat and other foods; bee sting; other causes). The symptoms of anaphylactic shock are: - The man's skin turned red, blotchy and began to itch.
- The person experiences intense warmth.
- The person feels as if he has a lump in his throat and it is difficult for him to breathe.
- There was swelling of the throat, tongue and face.
- The victim feels nausea, diarrhea, or weakness.
- The pulse is weak and rapid.
 2 Call an ambulance. Anaphylactic shock can be fatal if not treated in time. Stay with the dispatcher on the line for further instructions on how to assist the victim.
2 Call an ambulance. Anaphylactic shock can be fatal if not treated in time. Stay with the dispatcher on the line for further instructions on how to assist the victim. 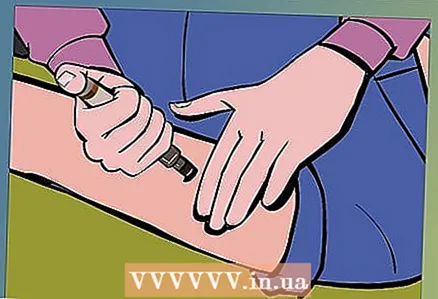 3 Inject adrenaline. Ask the person if he / she has an adrenaline syringe. It is needed to slow down the allergic reaction. It is often carried by people who are allergic to food or bee stings. The injection is usually in the thigh.
3 Inject adrenaline. Ask the person if he / she has an adrenaline syringe. It is needed to slow down the allergic reaction. It is often carried by people who are allergic to food or bee stings. The injection is usually in the thigh.  4 The victim should lie on the floor. Loosen his / her clothing and place the victim on the ground. Cover the victim with a sheet and reassure him / her that you know what you are doing.
4 The victim should lie on the floor. Loosen his / her clothing and place the victim on the ground. Cover the victim with a sheet and reassure him / her that you know what you are doing. 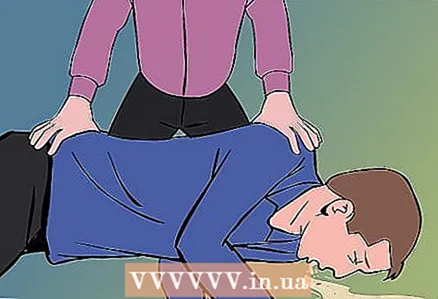 5 Examine it for bleeding or vomiting from the mouth. If vomiting or bleeding is present, turn the victim's head to the side so that he / she does not choke.
5 Examine it for bleeding or vomiting from the mouth. If vomiting or bleeding is present, turn the victim's head to the side so that he / she does not choke.  6 Check breathing and perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation if necessary. If the victim is not breathing, start giving him / her heart massage before ambulance arrives.
6 Check breathing and perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation if necessary. If the victim is not breathing, start giving him / her heart massage before ambulance arrives.
Tips
- Remember to reassure the victim that you know what to do.
- Call an ambulance as soon as possible.
- If necessary, offer the victim a wet towel to moisten the lips.
Warnings
- Don't try to do more than you can. This can lead to even more harm. If you do not know how to properly help the victim, look for someone who does.