Author:
Helen Garcia
Date Of Creation:
16 April 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Part 1 of 2: How to Store Disposable Batteries
- Part 2 of 2: How to store rechargeable batteries
- Tips
- Warnings
- What do you need
- Additional articles
Batteries come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes and serve a wide variety of purposes. It is useful to store different types of batteries just in case, so that they are always at hand when needed. Proper storage prolongs the life of the batteries, keeps them safe and makes them easy to locate when needed.
Steps
Part 1 of 2: How to Store Disposable Batteries
 1 Keep batteries in their original packaging whenever possible. Keeping batteries unopened protects them from various environmental factors, including moisture. It will also help you avoid confusing new batteries with used ones and will prevent the battery input terminals from coming into contact with metal surfaces.
1 Keep batteries in their original packaging whenever possible. Keeping batteries unopened protects them from various environmental factors, including moisture. It will also help you avoid confusing new batteries with used ones and will prevent the battery input terminals from coming into contact with metal surfaces.  2 Sort batteries by manufacturer and date of manufacture. Batteries of different types and brands can react with each other, which can lead to battery leakage and other damage. When storing disposable (non-rechargeable) batteries, do not keep new and used batteries together. It is best to store them in separate boxes. If you are going to use one box, place each battery in a separate plastic bag.
2 Sort batteries by manufacturer and date of manufacture. Batteries of different types and brands can react with each other, which can lead to battery leakage and other damage. When storing disposable (non-rechargeable) batteries, do not keep new and used batteries together. It is best to store them in separate boxes. If you are going to use one box, place each battery in a separate plastic bag.  3 Check the charge on the rechargeable (rechargeable) batteries. Many rechargeable batteries deteriorate if stored in a discharged state. The optimal battery charge depends on the type of battery:
3 Check the charge on the rechargeable (rechargeable) batteries. Many rechargeable batteries deteriorate if stored in a discharged state. The optimal battery charge depends on the type of battery:
Lead acid
Store fully charged to prevent sulfation, which can reduce capacity. Li-ion
Best stored at 30-50% of maximum charge.
However, if you cannot recharge the battery for several months, store it fully charged. Nickel based (Ni-MH, NiZn, NiCd)
Can be stored in any condition.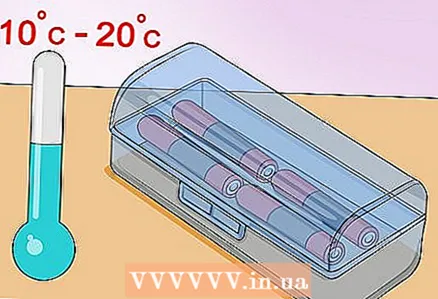 4 Store batteries at room temperature or colder. In most cases, any cool place that is not exposed to direct sunlight will do. Even at a relatively high temperature of 25ºC, a conventional battery loses only a few percent of its charge in a year.Storing batteries in the refrigerator (or other place at 1-15ºC) will not significantly reduce waste of charge, but this is not necessary unless you have other alternatives or need maximum efficiency. In most cases, there is no need to put batteries at risk and store them in the refrigerator, as they can get wet there. You will also have to wait for the batteries to warm up before using the batteries you removed from the refrigerator.
4 Store batteries at room temperature or colder. In most cases, any cool place that is not exposed to direct sunlight will do. Even at a relatively high temperature of 25ºC, a conventional battery loses only a few percent of its charge in a year.Storing batteries in the refrigerator (or other place at 1-15ºC) will not significantly reduce waste of charge, but this is not necessary unless you have other alternatives or need maximum efficiency. In most cases, there is no need to put batteries at risk and store them in the refrigerator, as they can get wet there. You will also have to wait for the batteries to warm up before using the batteries you removed from the refrigerator. - Do not put the battery in the refrigerator unless recommended by the manufacturer.
Standard nickel-based batteries lose their charge quickly at low temperatures. They recharge faster in colder temperatures (but not below 10 ° C for conventional chargers).
More recent low self-discharge (LSD) Ni-MH batteries are designed to hold a charge at room temperature.
- Do not put the battery in the refrigerator unless recommended by the manufacturer.
 5 Control the humidity in the air. Store batteries in an airtight container if there is high humidity or if there is a risk of condensation (eg in a refrigerator). Alkaline batteries can be stored in moderate humidity (35-65% RH). Most other types of batteries keep better in lower humidity.
5 Control the humidity in the air. Store batteries in an airtight container if there is high humidity or if there is a risk of condensation (eg in a refrigerator). Alkaline batteries can be stored in moderate humidity (35-65% RH). Most other types of batteries keep better in lower humidity.  6 Protect batteries from contact with conductors. On contact with metal, an electric current may flow through the batteries. In this case, they quickly discharge and warm up. To prevent battery discharge and reduce the risk of fire, take the following measures:
6 Protect batteries from contact with conductors. On contact with metal, an electric current may flow through the batteries. In this case, they quickly discharge and warm up. To prevent battery discharge and reduce the risk of fire, take the following measures: - Do not store batteries in metal containers. Use tightly sealed plastic boxes or special containers for storing batteries.
- Do not store coins or other metal objects with batteries.
- Place batteries so that the positive and negative poles are securely separated. If this is difficult to do, cover the battery terminals with insulating tape or plastic caps.
Part 2 of 2: How to store rechargeable batteries
 1 Recharge lead acid and lithium ion batteries periodically. If you store lead-acid batteries in a nearly discharged state, crystals may form in them (sulfation process), which will reduce their capacity. Inadequate charging of lithium-ion batteries can lead to restructuring of copper components and short-circuiting, which is unsafe. The optimal battery charge depends on the device used. If you do not have a manual for use, follow these guidelines:
1 Recharge lead acid and lithium ion batteries periodically. If you store lead-acid batteries in a nearly discharged state, crystals may form in them (sulfation process), which will reduce their capacity. Inadequate charging of lithium-ion batteries can lead to restructuring of copper components and short-circuiting, which is unsafe. The optimal battery charge depends on the device used. If you do not have a manual for use, follow these guidelines:
Lead acid batteries
Charge to maximum as soon as the battery voltage drops below 2.07 volts (12.42 volts for a 12 volt battery).
Usually one charge is enough for six months. Lithium-ion batteries
Charge to 30-50% of maximum capacity as soon as the battery voltage drops below 2.5 volts. Do not recharge the battery if the voltage drops to 1.5 volts.
Typically, a single charge lasts several months.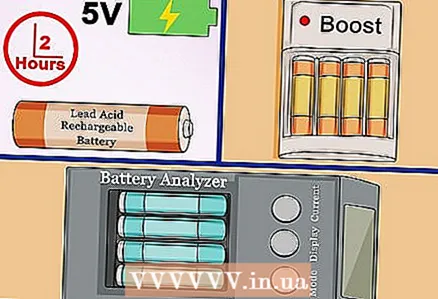 2 Recover dead batteries. If after some time (more than a few days) the charge of the rechargeable batteries has dropped to a low level, they will most likely have to undergo special treatment before further use:
2 Recover dead batteries. If after some time (more than a few days) the charge of the rechargeable batteries has dropped to a low level, they will most likely have to undergo special treatment before further use:
Lead acid batteries
Batteries are usually recharged, but their capacity is reduced. If the small lead-acid battery does not recharge, run a very low current at a high (~ 5V) voltage through it for 2 hours.
It is not recommended to use desulfation devices without proper experience. Lithium-ion batteries
The battery may not recharge due to falling into "sleep mode". Use a charger with fast charging function and make sure the polarity of the connected contacts is correct.
Never use the quick-charge function on a battery that has not exceeded 1.5V for a week or longer - it is dangerous because it is damaged. Nickel based (Ni-MH, NiZn, NiCd)
There are no hard and fast rules. Sometimes a battery needs several charge and full discharge cycles to restore full capacity.
If you frequently use batteries, consider purchasing a battery analyzer to help you recover them.
Tips
- Remove batteries from rarely used electronic devices. If batteries are stored separately, they will discharge much more slowly than in electronic devices.
Warnings
- Lead acid batteries are not recommended to be stored in high humidity. These batteries must be stored in a dry place to prevent corrosion.
What do you need
- Batteries
- Plastic bag (optional)
- Battery storage box (optional)
Additional articles
 How to recharge batteries How to get light from batteries
How to recharge batteries How to get light from batteries  How to make a galvanic cell with your own hands
How to make a galvanic cell with your own hands  How to clean a leaking battery
How to clean a leaking battery  How to charge an external battery
How to charge an external battery  How to kill a fly quickly
How to kill a fly quickly  How to use fans to cool your home How to open a lock How to open a lock with a hairpin or hairpin
How to use fans to cool your home How to open a lock How to open a lock with a hairpin or hairpin  How to calculate the power consumption of an electrical appliance
How to calculate the power consumption of an electrical appliance  How to kill flying ants
How to kill flying ants  How to break through a toilet without a plunger
How to break through a toilet without a plunger  How to burn incense sticks
How to burn incense sticks  How to cool off in hot weather
How to cool off in hot weather



