Author:
Louise Ward
Date Of Creation:
4 February 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
As a sacred symbol for Buddhists and Hindus, the lotus is also the national flower of India. This resilient aquatic plant is native to South Asia and Australia, but it can grow in almost any temperate climate if the conditions are right. You can plant lotus seeds or bulbs. Lotus plants grown from seeds usually do not bloom during the first year.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Growing lotus from seeds
Shave the seeds with a nail file. Use a metal nail file to scrape off the hard shell of the seed to reveal the cream-colored core in the middle. Try not to file the offense on the core, otherwise the seeds will not sprout. File the seed coat so that the water can contact the inner core.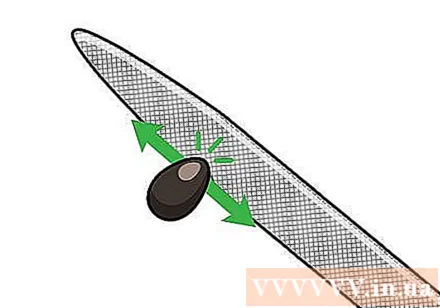
- If you don't have a metal nail file available, you can use a sharp knife, you can even rub the lotus seed pods onto the concrete surface, just be careful not to shave off too much of the seed.
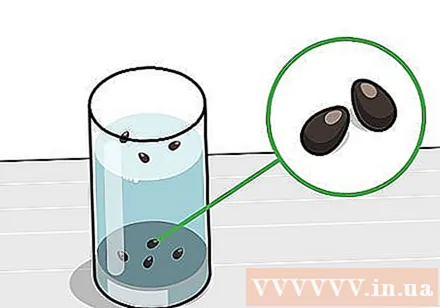
Soak the seeds in warm water. Soak the lotus seeds in a glass or clear container so you can see the seeds begin to sprout. Use chlorinated water and have a temperature of about 24-27 degrees Celsius.- After being soaked for a day, the lotus seeds will sink to the bottom and expand to almost double the original size. The seeds floating in water are almost impossible to germinate. Remove these seeds to prevent them from clouding the water.
- Change the water daily, even after the seeds have started to sprout. Be careful when removing the seedlings to change the water - they are very fragile.
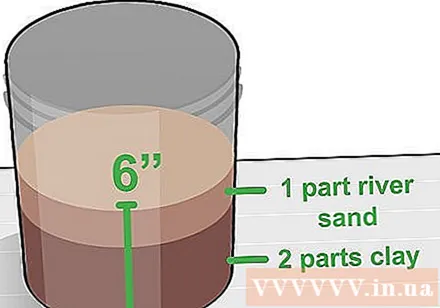
Fill pots with 10-20 liters of soil. This pot size is enough for the lotus seedlings to have room for growth. The black plastic bucket is capable of retaining heat for the seedlings better.- Ideal lotus soil type consists of 2 parts clay and 1 part river sand. If you use a potting mix of soil, the soil will float up when you put the pot in the water.
- Remember that the potted plant should be one that has no drainage holes. Lotus plants can track drainage holes, go outward, and do not grow well.
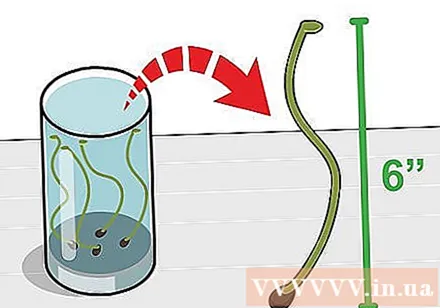
Remove the seedlings from the water once they are about 15 cm long. Lotus seeds will begin to sprout 4 or 5 days after soaking. However, the plant may die if you re-pot it too soon.- When soaking for longer than necessary, the seedlings will begin to grow leaves. You should still be able to plant this now - just be careful not to get the leaves on the ground.
Press the sprouted lotus seeds into the soil, about 10 cm apart. There is no need to completely bury the lotus seeds in the ground; Simply place the seeds on the ground, then sprinkle a thin layer of soil on top to keep the seeds. Lotus seeds will take root.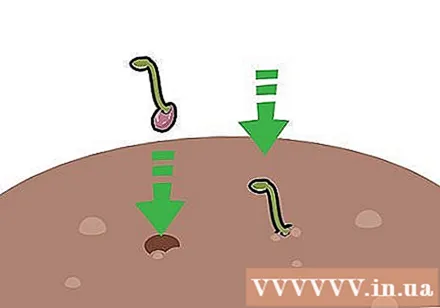
- You can use a little clay to wrap them under each lotus seed to keep the seeds sink by weight. When the lotus is placed in a pond, the un-held lotus seeds can leave the soil and float to the surface of the water.
Place the pot in the pond. Lotus is an aquatic plant, so the water layer above the ground should be at least 5-10 cm deep. If you plant tall lotus seeds, the water level can be as deep as 45 cm. Mini lotus varieties need a water level of 5-30 cm deep.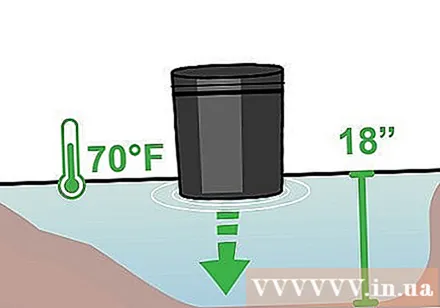
- The minimum temperature of lotus water should be 21 degrees Celsius. In regions with relatively cold climates, shallower water levels can make plants warmer.
- Lotus seeds grown from seeds rarely bloom during the first year. You should limit fertilization for the first year and wait for the plant to adapt to the environment.
Method 2 of 3: Growing lotus from tubers
Buy lotus root from early spring. You can buy lotus bulbs at a nursery or garden center or online. Because of transport is difficult, usually lotus bulbs are not available after being interrupted in late spring. However, you can still buy locally grown lotus bulbs.
- For rarer hybrids, you may need to purchase them online. If there is an active aquarium group nearby, ask them to recommend. Some aquarium associations also sell plants.
Drop lotus root in a bowl of water that is 21-31 degrees Celsius. Gently drop the lotus root on the water. Place the bowl of water on a window sill that is warm and sunny, but not in direct sunlight.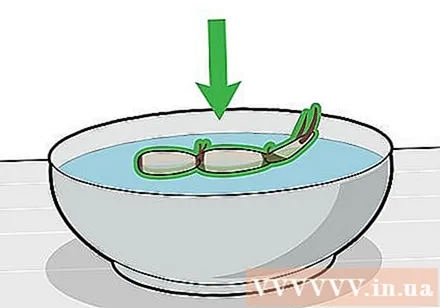
- If you are going to move the lotus plant into the lake, use the water in the tank to soak it (if the water is warm enough). Change water every 3 to 7 days or change when the water is cloudy.
Choose a round pot 90 -120 cm in diameter. If grown freely, the lotus will occupy the entire planting area. The potted plant will restrain the lotus plant from occupying the entire lake.
- The deep pot will prevent the lotus plant from reaching out and spreading throughout the lake. The round pot will keep the plant from getting stuck in the corner, which can stunt or kill the plant.
Pour soil tightly into the pot. The soil suitable for growing lotus is a mixture of 60% clay and 40% river sand. Fill the pot with soil about 7.5 to 10 cm from the top of the pot.
- You can also use rehabilitated soil with a layer of loose sand about 5-7.5 cm thick above the soil surface. Be sure to leave enough distance from the ground to the top of the pot.
Press the lotus root into the topsoil. Gently press the lotus root against the sand layer, then carefully put the stone on top so that the lotus root does not float to the surface of the water before taking the roots.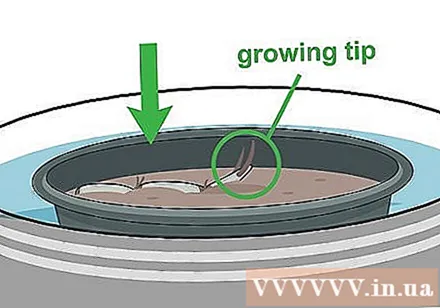
- Don't bury the lotus root in the ground - it will rot. Remember to just gently press the lotus root against the ground.
Place the pot in the pond, about 15-30 cm below the water surface. Choose a sunny place, avoid running water and have enough space for the plant to grow. Once the lotus has settled, you can place it in the selected place.
- When placed in the lake, the lotus root will attach itself by reaching to the ground and growing roots.
Method 3 of 3: Caring for the lotus plant
Maintain a minimum water temperature of 21 degrees Celsius. The lotus plant will begin to grow strongly when the water surface reaches this temperature. Sen can only grow when grown in warm water, preferably the temperature in the air reaches 21 degrees Celsius.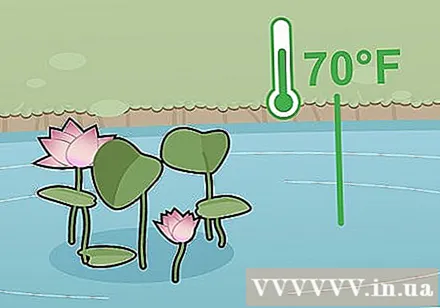
- The lotus plant will begin to bloom after a few days in water above 21 degrees Celsius and bloom after 3-4 weeks when the water temperature reaches above 27 degrees Celsius.
- Check the water temperature every two days. If you live in a colder climate, you may need to use a pool heater to maintain the correct temperature.
Plant lotus plants in direct sunlight. Lotus species grow well in full sun 5-6 hours per day. If the lake is partially obscured, you should prune or remove the sun-blocking foliage around the lake.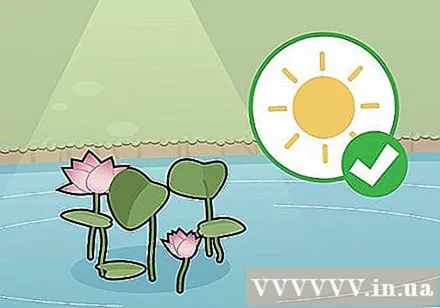
- In North America, the lotus season is from mid-July to early August. The flowers bloom early in the morning and begin to close in mid-afternoon. The lotus is stable for 3-5 days before falling. This cycle repeats throughout the rest of the plant's growth months.
Cut away dying lotus flowers and yellow or damaged leaves. If the lotus plant begins to take over the pond, you can remove the new shoots, but remember that they will grow again until you repot the lotus in another pot when spring comes.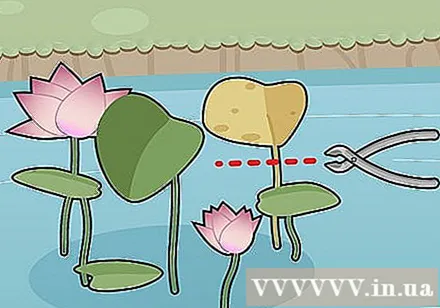
- Never cut flowers or stalks below the water's surface. Lotus roots and tubers get oxygen through the leaf stalks.
Use pelleted fertilizers for the aquarium to supplement nutrition for the lotus. This fertilizer is specially formulated for aquatic plants. You should wait for the lotus root to grow 6 leaves and then fertilize, and remember not to put the fertilizer tablet directly on the lotus root.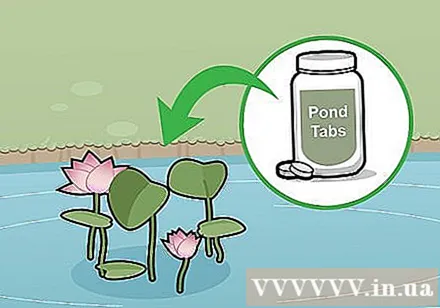
- Small varieties of lotus only need 2 tablets, while larger varieties need 4 capsules. Every 3-4 weeks, you should fertilize the plant once and stop in mid-July. If you continue to fertilize after this point has passed, the lotus will not be able to prepare for hibernation.
- With a lotus grown from seeds, you should not fertilize the first year.
Beware of pests. Although the pests vary by geographic region, lotus leaves often attract aphids and caterpillars. A little powdered pesticide sprinkled directly on the leaves will protect the lotus from pests.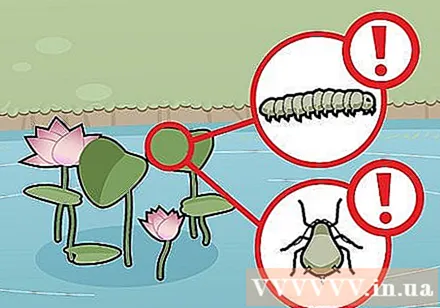
- Liquid pesticides, including organic ones, contain oils and detergents that can damage lotus plants.
Move the lotus plant to deeper water in autumn. The lotus plant can survive winters in lakes in remote northern regions like Michigan or Minnesota if the water in the lake is deep enough that the tubers won't freeze. The lotus root should be located below the depth of freezing; This depth will vary by region.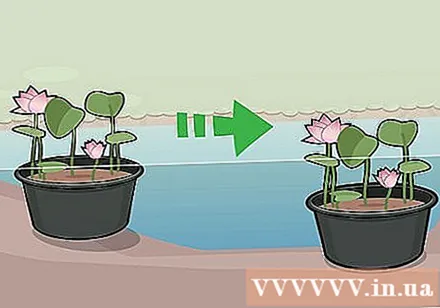
- If your lotus pond is relatively shallow, you can move the pot into the garage or basement until spring. Place mulch around the above ground lotus pots to keep the tubers warm.
Re-plant the lotus root every year. In early spring, when you notice the first signs of a tree coming, replace the root with new soil and put it back in the old pot (unless the pot is damaged). Return the lotus pot to the lake at the same depth as before.
- If the lotus plant occupied the entire lake in the previous year, check to see if the pot is cracked. You may need to repot a larger one if the plant is growing out of the top of the pot.
Advice
- Try organic kelp or fishmeal organic fertilizers if you want to avoid chemical fertilizers.
- Lotus root is very fragile. Be gentle when handling and do not break the tip (the "eye"). The lotus will not sprout if the root eye is damaged.
- Lotus flowers, lotus seeds, young lotus leaves and lotus stalks are all edible, although they can cause mild intoxication.
- Lotus seeds can survive for hundreds - even thousands of years.