Author:
John Stephens
Date Of Creation:
28 January 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
You probably also know to wear sunscreen when going to the beach. But you know, dermatologists also recommend that people wear sunscreen whenever they're outside for longer than 20 minutes, even in winter. You should apply sunscreen even on shady or overcast days. The sun's UV (ultraviolet) rays can start to damage the skin in as little as 15 minutes! Lesions on the skin can even lead to cancer. Prevention is always better than cure, and the best way to prevent sunburn is to wear sunscreen every time you are outdoors during the day.
Steps
Part 1 of 3: Choosing a sunscreen type
See SPF number. "SPF" is an acronym for "sun protective factor", which means the ability to block UVB rays. The SPF number indicates how long it took to start sunburn when sunscreen was applied compared to when it was not.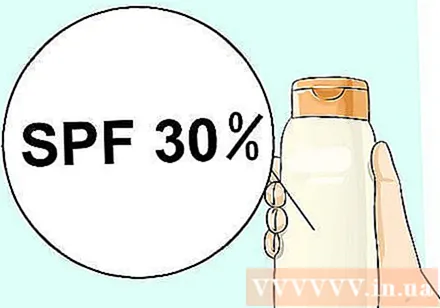
- For example, SPF 30 means you can stay out in the sun 30 times longer without sunburn than without wearing any sunscreen. Thus, if normally you will be sunburned after 5 minutes, then in theory, a product with SPF 30 allows you to stay out in the sun for up to 150 minutes (30 x 5) without getting sunburned. However, factors such as skin condition, activity level, and sun intensity all affect the effectiveness of a sunscreen, so you may need to use more than others.
- The significance of the SPF number is troublesome, since the level of protection does not increase proportionally with the number. Thus, SPF 60 is not twice as effective as SPF 30. SPF 15 blocks 94% of UVB rays, SPF 30 blocks about 97%, and SPF 45 blocks about 98%. No sunscreen blocks 100% of UVB rays.
- The American Academy of Dermatology recommends a product with SPF 30 or higher. The effectiveness of products with an extremely high SPF number does not differ significantly and is not worth the difference.

Choose a sunscreen that says "broad spectrum". SPF indicates only the ability to block UVB rays from causing sunburn. However, the sun also emits UVA rays, which are the culprits of skin damage, such as signs of age, wrinkles and dark or pale spots. Both UVA and UVB rays increase the risk of skin cancer. A broad spectrum sunscreen is resistant to both UVA and UVB rays.- Some sunscreens may not show “broad spectrum” on the package, but if the product is effective against UVB rays and also UVA will always be specified.
- Most broad spectrum sunscreens contain "inorganic" ingredients like titanium dioxide or zinc oxide, and "organic" ingredients like avobenzone, cinoxate, oxybenzone, or octyl methoxycinnamate.

Look for water-resistant sunscreen. Your body gets rid of water through sweat, so look for products that are water resistant. This is especially important if you are going to be physically active, such as running or hiking, or doing water activities.- There are no sunscreens that are "waterproof" or "sweat proof". In the US, sunscreen products are not allowed to be advertised as "waterproof".
- Even if you use water-resistant sunscreen, you must reapply after 40-80 minutes as directed on the package.

Choose the type of sun protection product you like. Some people like spray bottles, others like thick creams or gels. Whatever you choose, you must apply a thick, even layer of cream. How to apply the cream is just as important as the SPF: if you don't use it correctly, the sunscreen won't work.- Spray products are best when applied to hairy areas, and creams are usually best for dry skin. Alcohol or gel products are good for oily skin.
- You can also buy a wax-stick sunscreen that's great for applying to the skin near your eyes. Wax form is also a good choice for children, as you can avoid getting it in your child's eyes. In addition, they also have the benefit of not spilling (when stored in a bag) and can be applied to the skin without having to spill on your hands.
- “Sports-type” water-resistant sunscreens are usually very sticky and are not suitable for applying under makeup.
- If you have acne-prone skin, you should be careful when choosing a sunscreen. Look for products that are specifically designed for the face and that do not clog pores. These products generally have a high SPF (15 or higher) and are less likely to clog pores or break out pimples.
- Many people with acne prone skin find zinc dioxide-based sunscreens the best fit.
- Look for products that say "non-comedogenic" (non-comedogenic), "will not clog pores", "for sensitive skin" (for sensitive skin), or "for acne-prone skin. "(for acne prone skin).
Try a small amount of sunscreen on your wrist. If you see any signs of side effects or any other problem, you must purchase another. Repeat this procedure until you find a suitable product, or ask your doctor to recommend labels for sensitive or allergic skin if necessary.
- Itching, redness, burning, or blistering are all signs of an allergic reaction. Titanium dioxide and zinc oxide generally cause less skin allergies.
Part 2 of 3: Apply sunscreen
Check expiration date. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) requires sunscreens to maintain a sun protection effect for a minimum of 3 years from the date of manufacture. However, you should still pay attention to the product's expiration date. If the expiration date has passed, you must dispose of and buy a new product.
- If the product does not show the expiration date when first purchased, you should write down the date of purchase with a marker on the package. This way, you will know when you bought this product.
- Visible changes such as discoloration, water separations or a change in texture are indications that a product has expired.
Apply sunscreen before going out in the sun. The chemicals in sunscreen take time to penetrate the skin and take effect. You need to apply cream before outdoors.
- You should apply sunscreen to your skin at least 30 minutes before going out in the sun. Sunscreen lipstick should be applied 45-60 minutes before.
- Sunscreen takes time to "absorb" on the skin to maximize its effect. This is especially true when you are using a water-resistant cream. If you've been jumping into the pool five minutes after you've applied the cream, the cream is largely lost.
- This is also very important when you are looking after children. Children are inherently active and impatient, but when they are eager before their outdoor adventure, it is even more difficult not to move; After all, who can stay still while the turn is in right in front of you right? Instead, apply cream to your child before leaving home, while waiting for the bus, or when in the car park.
Use enough cream. One of the biggest mistakes when using sunscreen is not applying enough. Adults usually need 30 ml of sunscreen (about a handful of palm-filled hand or a glass of brandy) to cover exposed skin.
- To apply sunscreen cream or gel, squeeze the cream onto your palm and spread it over sun-exposed skin. Rub the sunscreen on your skin until the white cream streaks are no longer visible.
- To use the spray, hold the bottle upright and move it across the skin surface. Comfortable spray into an even layer on skin. Make sure the sunscreen is not blown away by the wind before it touches your skin. Avoid inhaling the cream when spraying. Be careful when applying sunscreen around your face, especially when children are around.
Apply sunscreen all over. Don't forget skin areas like ears, neck, on the instep and hands, and even the parting line in the hair. Any area of skin that will be exposed to the sun must be applied with cream.
- It is difficult to apply the cream evenly on difficult to reach areas such as the back. Ask someone to help you apply cream.
- Thin clothing is not usually sufficient to protect the skin from the sun. For example, a white T-shirt has only an SPF of 7. Wear clothing designed to block UV rays, or apply sunscreen underneath your clothes.
Don't forget to apply the cream to your face. Facial skin even needs sunscreen more than the rest of the body, as many cases of skin cancer occur on the face, especially on the nose and around the nose. Some cosmetics or lotions also contain sunscreen. However, if you plan to be outside for more than 20 minutes (total time, not once), you should also apply sunscreen on your face.
- Many face sunscreens come in creams or lotions. If you are using a spray product, spray on your palms first, then apply to your face. It is best to avoid spraying on the face if possible.
- The Anti-Skin Cancer Association has a list of recommended facial sunscreen products.
- Use lip balm or sunscreen with a minimum SPF 15.
- If you are bald or with thinning hair, be sure to put sunscreen on your head. You can also wear a hat to protect your skin from the sun.
Reapply sunscreen after 15-30 minutes. Research has shown that reapplying creams 15-30 minutes after going out in the sun is more effective than after 2 hours.
- After applying sunscreen for the first time, you should reapply every 2 hours or as directed on the product label.
Part 3 of 3: Stay safe in the sun
Stay in the shade. Even if you apply sunscreen, you are still exposed to strong rays from the sun. You should stay in the shade or cover an umbrella to avoid the harmful effects of sunlight.
- Avoid "rush hour." The sun is at its highest between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m. If possible, stay out of the sun during this time. Look for shade if you are outdoors during peak hours.
Wear sunscreen clothing. Clothing comes in many varieties, but long sleeves and pants can help protect your skin from sun damage. Wear a hat to shade and protect the scalp.
- Choose clothes with a tight, dark textile, as they work best. Outdoor activists can buy specially designed sun-protective clothing, often sold in specialized stores or online.
- Remember to wear sunglasses! UV rays from the sun can cause cataracts, so buy sunglasses that block UVB and UVA rays.
Do not expose children to the sun. Sunlight, especially during peak hours from 10am to 2pm, is especially harmful to young children. Look for sunscreens formulated for babies and babies. Consult with your pediatrician about which types are safe for children.
- Infants under 6 months of age should not wear sunscreen or stay in the sun. Newborn skin is not yet mature, so it can absorb more of the chemicals in sunscreen. Protect your baby from the sun if you have to take him outdoors.
- If your baby is over 6 months old, you can apply sunscreen to your baby with a minimum SPF 30. Be careful when applying near eyes.
- Dress young children in sun-protective clothing, such as hats, long-sleeved shirts, and gentle pants.
- Wear UV-resistant sunglasses.
Advice
- Even with sunscreen on, you should still not expose yourself to too much sun.
- Buy a sunscreen specifically intended for facial skin. If you have oily skin or are prone to clogging your pores, look for “oil-free” (oil-free) or “noncomedogenic” (non-clogged) sunscreen. Products specially formulated for sensitive skin are also available.
- Reapply after skin gets wet, every 2 hours, or as directed on the label. Sunscreen is not a "apply once is done" product.
Warning
- There is no such thing as a "safe" tan. The UV light of the bed browns the skin and natural sunlight can both cause skin cancer. Copper brown skin looks great, but it's not worth your life. Consider using other methods, such as a tanning spray.