Author:
Lewis Jackson
Date Of Creation:
6 May 2021
Update Date:
25 June 2024

Content
Accounting, meticulous recording of financial transactions, is an extremely important process that is essential to the success of every small and large business. While large firms typically have a large-scale accounting department with many employees (as well as using the services of independent auditing firms), smaller firms may have only one accountant. In a one-member company, the business owner may have to take care of the accounting on his own without using any other employees. Whether you want to manage your own finances or are interested in applying for an accounting position in another business, learning the basics of accounting is also a useful first step for you.
Steps
Part 1 of 4: Reinforcing accounting skills
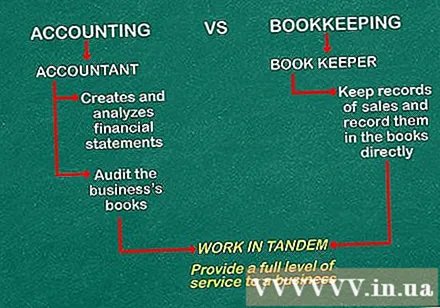
Understand the difference between bookkeeping and accounting. Bookkeeping and accounting are two terms that are often used interchangeably. However, there is a certain difference in skills and responsibility between them.Bookkeepers usually record sales transactions and record them directly in financial books. Their daily work ensures that all revenues and expenditures of the business are recognized. As for accountants, they create and analyze financial statements and also audit the books of the business to ensure the accuracy and validity of reports.- Bookkeepers and accountants can work together, providing the highest level of service for the business.
- In many cases, the difference between the two titles is formalized from a degree, certificate or industry organization.
Get used to create a spreadsheet. Microsoft Excel or other spreadsheet programs are invaluable to accountants: they help you keep track of data graphically and perform calculations to create financial spreadsheets. Even with the basics of your knowledge, you can still improve and learn intermediate and advanced skills for creating spreadsheets, charts and graphs.
Reading accounting books. You can visit your local library to find books about accounting or buy books from your favorite bookstore. Look for accounting brochures written by authors with industry experience, such as well-researched informational books.- Introduction to Accounting by Pru Marriott, JR Edwards, and Howard J Mellett are widely used syllabus and are considered excellent introductory books for accounting in particular and all disciplines in general.
- College Accounting: A Career Approach by Cathy J. Scott is a college curriculum widely used for accounting and financial management courses. You can also choose to buy Quickbooks Accounting software CD-ROM with CD-ROM: it can be an invaluable asset to enthusiastic accountants.
- Financial Statements: A Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding and Creating Financial Reports by Thomas R. Ittelson is the best-selling financial reporting brochure and it could be the perfect start to your entry into accounting.
Take an accounting course. You can find accounting courses at your local community college or take free online accounting courses. Try sites like Coursera or any other online education forum and find free courses taught by elite experts in the accounting field. advertisement
Part 2 of 4: Practicing basic accounting profession
Understand what double entry is. The accountant makes two or more entries for each transaction recorded by the enterprise. It can be understood that it is an increase in one or more accounts and a corresponding decrease in one or more other accounts. For example, when a business receives payment for a previously bear sale, the cash account increases and the accounts receivable (money from customers, who bought but not paid for it, owed the business. ) will decrease. The value increase and decrease in these accounts are the same (and equal to the value of the order).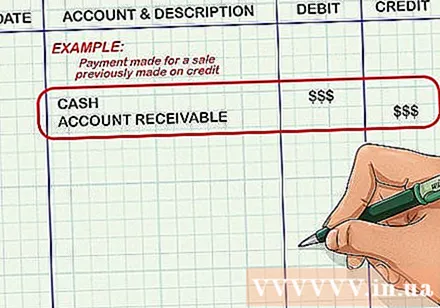
Debit and yes. Dual book entry is done through debit and credit. Debit and can show an increase or decrease in certain accounts when a transaction is made. When you remember the two points below, you will notice that the credit and debit are related: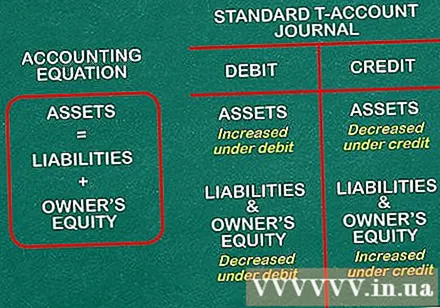
- Debit is the entry recorded on the left side of the T-account and there is an entry recorded on the right side. Here, we are talking about the standard T-account log used to record fluctuations on either side of the vertical part of the "T".
- Assets = Liabilities + Equity. This is the accounting equation, the most important equation of all. Recite this equation by heart. It will serve as a guide for debit and credit entries. On the left side of "=", liabilities increase the value of the account and credits decrease it. On the right side, debits decrease the value of the account and credits increase its value.
- Think that when debiting an asset account, such as a cash account, that account increases. However, when debiting with debit accounts, such as payables, those accounts decrease.
- Practice recognizing common transactions, such as payments for electricity bills or receiving cash payments from customers.
Create and maintain an accounting ledger. The ledger is the place to record double entry entries. Each entry (consisting of multiple debit balances and in the same transaction) is carried out in the appropriate account in the ledger. With cash bill payments, for example, one credit is made to the cash account and another independent is applied to the accrual expenses account. Although everything will become extremely simple with accounting software, the manual recognition is not too complicated.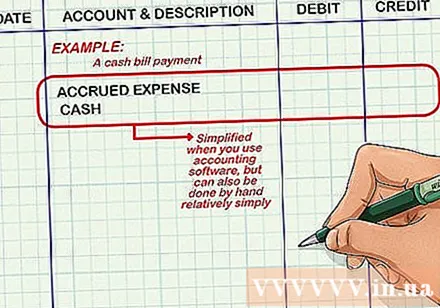
Distinguish between immediate and accrual payments. Instant trading is the type of transaction that occurs when a customer buys a box of candy from the store, you receive payment on the spot and deliver the candy to them at that moment. Accruals take into account factors such as buying debt, invoicing and invoicing instead of paying directly at the time of transaction. At the same time, they also take into account intangible assets like reputation. advertisement
Part 3 of 4: Learn about financial statements
Understand how to prepare financial statements. Financial statements reflect the current financial health of the business and its financial performance for the most recent accounting period. Financial statements are made from information contained in an accounting ledger. At the end of the accounting period, each account will be added up, forming a trial balance sheet. Total debt and equity of all accounts must be equal. If this is not the case, the accountant is required to check the balance sheets of each account and correct or correct errors as necessary.
- Once the accounts are adjusted and correct, the accountant can enter a summary of the information contained in those accounts into the financial statements.
Learn how to prepare financial statements. Business results reporting is the most basic component of accounting. It records the company's profit margin over a specified period of time, from a week to a year. Reporting business results is determined by two factors: revenue and cost of the business.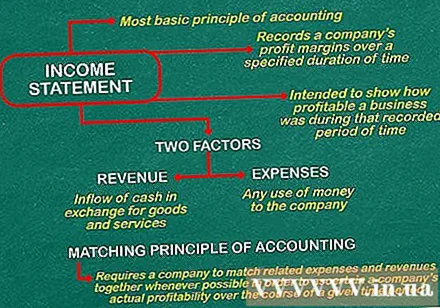
- Revenue is the cash inflow over time that a business derives from the provision of goods and services. Here, however, the money doesn't necessarily have to be paid off in that accounting period. Revenue can include spot transactions and accruals. When accruals are included in the income statement, sales for that week or month will recognize invoices sent out during that period, even if the funds have not been collected until the next reporting period. . Therefore, the purpose of the business results report is to show how profitable a business is during the period of recording, not quite the amount it earned during that period.
- Cost is the total amount of money the company spends, whether it is material costs or labor costs. As with revenue, expenses are reported for the period in which they arise, not necessarily at the time the company actually pays them.
- Appropriateness principles of accounting require enterprises to recognize revenues and costs as appropriate when possible in order to determine its true profitability over a given period of time. When the business is profitable, it is likely that we will get a cause-and-effect relationship where an increase in sales increases the revenue as well as the corresponding operating cost: the need to purchase for The store and sales commissions, if any, will both increase.
Make a balance sheet. While the business results report shows the business performance of the business over a period of time, the balance sheet is like a picture of the whole business at a particular point in time. can. A balance sheet has three important components: assets, liabilities of the business and equity at a given time. You can think of it as an equilibrium equation with one side being the company's assets, the other being debt and equity.In other words, what you have is always comprised of what is in your possession and what is currently in your place.
- Assets are all of the things that a company owns. It can be seen as all the resources that the company has discretion to, such as the vehicles, cash, supplies and equipment owned by the company at a given time. Assets can be tangible (such as factories, equipment) or intangible (patents, trademarks, reputation).
- Debt is any debt the business still owes at the time of its balance sheet. Liabilities can include liabilities, merchandise purchases or unpaid employee salaries.
- Capital is the difference between assets and liabilities. Equity is sometimes seen as the "book value" of a company or business. If it is a large corporation, the capital may belong to the shareholders. When the company belongs to an individual, we have equity.
Create a cash flow report. Basically, cash flow statements show how money is created and used by businesses as well as their investments and finances over a given period. Cash flow statements are almost drawn from the balance sheet and report on production and business activities for the same period. advertisement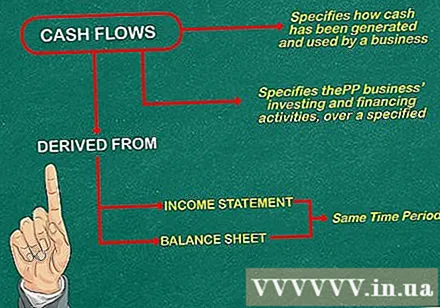
Part 4 of 4: Learn accounting principles
Adhere to generally recognized accounting principles (GAAP). These fundamentals guide accounting practices based on a set of principles and assumptions designed to ensure transparency and integrity of all transactions.
- Economic entity assumption: an accountant working for a private company (company owned by an individual) must have a separate ledger for business transactions and is not included in the costs or expenses. owner's personal transactions.
- The assumption of a currency is the agreement under which economic activity, at least in the United States, will be measured in US Dollars and, therefore, only activity convertible to US Dollars will be recognized.
- The time period assumption is the agreement under which all economic transactions are performed over certain time periods and these times will be accurately recorded. They are usually relatively short: At least the company should have an annual report. However, in many companies, reports are usually made weekly. The report should also state the start and end of the period for which it records. In other words, just mentioning the date of the report is not enough: the accountant must clarify that the report is made for a week, a month, a quarter or an economic year.
- The cost principle refers to the amount of money spent at the time of a transaction, not taking into account inflation.
- The full information principle requires the accountant to disclose relevant financial information to all interested parties, especially investors and creditors. This information must be disclosed in the body or disclosures at the end of the financial statements.
- The Continuity Principle assumes that the company will continue to operate for the foreseeable future enough and requires the accountant to disclose any information relating to a negative future or unavoidable public failure. ty. In other words, if you believe that the company will go bankrupt in the near future enough, the accountant is obligated to disclose that information to the investor and any other interested parties.
- The proportionality principle requires that the cost be consistent with the revenue in every financial report.
- The revenue recognition principle is the agreement whereby revenue will be recognized at the time the transaction is completed, not when the money is actually being paid to the business.
- A material principle is an indication under which, based on professional judgment, the accountant can judge whether a certain amount is significant to report. However, this principle does not mean that accountants can make false statements. Instead, it refers to an accountant's decision, such as rounding off numbers, in financial transactions.
- The principle of caution states that an accountant can report potential losses of a business (in fact, reporting them is the accountant's obligation) but cannot report potential revenues. like the actual collection. Since then, investors should not have an inaccurate view of the company's financial situation.
Comply with the Accounting and Financial Standards Board (FASB) principles and standards. The FASB has put in place extensive principles and standards to ensure that interested parties have accurate, reliable information, have an ethical professional accountant, and produce honest reports. You can refer to the detailed layout of FASB conceptual framework at their website.
Adhere to widely accepted industry practices. That is the expectation between accounting and accounting, contributing to the direction of the industry. These include:
- The principle of authentication, verifiable and objective requires that the reported parameters of this accountant be approved by other accountants. It is not only about the professional dignity of the accountant, but also to ensure that all future transactions will be fair and honest.
- Consistency requires the accountant to be consistent in applying financial reporting practices and procedures. For example, when there is a change in the firm's cost-flow assumptions, the firm's accountant is obligated to report the change.
- Comparability requires accountants to adhere to certain standards, such as GAAP, in order to easily compare financial statements between companies.
Advice
- To become a licensed practicing accountant (CPA), you need a bachelor's degree in accounting and economics related disciplines and pass the CPA and the Ethics test.