Author:
Louise Ward
Date Of Creation:
10 February 2021
Update Date:
28 June 2024
Content
Escherichia coli or E. coli are a group of bacteria that normally live in the intestinal tract of humans and animals without causing any problems. In fact, gut bacteria are an important factor in human health. However, certain types of E. coli bacteria can cause illness and lead to stomach pain and bloody diarrhea. The E. coli bacteria that cause illness can be transmitted through contaminated water or food or through poor personal hygiene. E. coli infection can have symptoms like many other diseases.On the other hand, it is important to correctly identify the cause of the symptom, as some E. coli infections (especially the O157: H7 strain) can be fatal if symptoms or complications are left untreated. treatment.
Steps
Part 1 of 2: Recognize the most common symptoms
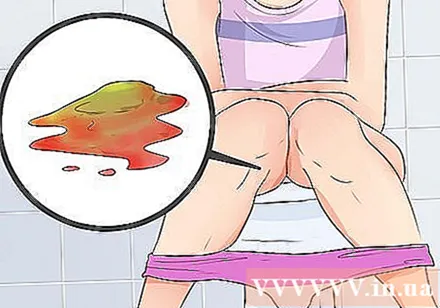
Symptoms of bloody diarrhea. Most E. coli bacteria are completely harmless and others cause short-term mild diarrhea. However, some more potent strains of the disease, such as E. coli O157: H7, can cause severe stomach pain and bloody diarrhea. The most pathogenic strain of E. coli, including O157: H7, produces a powerful toxin that damages the stomach lining, leading to the appearance of bright red blood in the stool during diarrhea. This toxin is called Shiga and the bacteria that produce it are called Shiga toxin-producing E. coli or STEC. Another strain of STEC that is quite popular in European countries is strain 0104: H4.- Bleeding diarrhea caused by E. coli O157: H7 infection usually begins 3-4 days after exposure or may appear within 24 hours or after a week.
- Diagnosing a serious E. coli infection is quite simple, including sending a stool sample to a lab for testing and culture. The therapist will look for signs of the toxin and strain STEC.
- Unlike other pathogenic bacteria, the STEC strain can cause serious infections even if you swallow only a relatively small amount.

Stomach symptoms. You will experience abdominal pain caused by the Shiga toxin, which will eventually erode and cause ulcers of the colon lining. The pain is often severe contractions associated with a burning sensation. The discomfort can cause the sick person to bend over and be unable to get out of the house or even move around the house. However, unlike other common causes of abdominal pain, STEC infections do not cause severe bloating or gas.- Sudden onset of cramps and abdominal pain usually appear 24 hours after bleeding diarrhea.
- E. coli infections can occur at any age, most commonly in children, the elderly, and people with poor immune systems.
- In the US, there are about 265,000 STEC infections each year, of which infections caused by the O157: H7 strain account for about 36%.

Note that some bacterial infections can cause vomiting. In addition to abdominal cramps and bloody diarrhea, people infected with E. coli may experience nausea and vomiting. Although the cause is unknown, Shiga toxin is not a direct cause of nausea and vomiting but is caused by intense pain caused by bacteria invading deep into the intestinal mucosa. Pain stimulates the production of the hormone adrenaline and other hormones, leading to nausea and vomiting. Therefore, you should stay hydrated when fighting E. coli infections, and avoid fatty, fatty foods that cause nausea.- Other symptoms of E. coli infection include low-grade fever (less than 38 degrees C) and fatigue.
- The most common route of E. coli infection is through contaminated foods such as contaminated ground beef, unpasteurized milk, and unwashed vegetables.
Be aware of serious kidney complications. Unlike other pathogenic E. coli strains on the intestinal membrane, the STEC strain will invade. After proliferating rapidly, they will adhere to the intestinal mucosa and invade the mucosa, thereby facilitating the absorption of toxins through the intestinal wall. In the circulatory system, the Shiga toxin attaches to the white blood cells and is delivered to the kidneys, causing acute inflammation and organ failure (known as hemolytic uremic syndrome or HUS). Common symptoms of HUS syndrome include bloody urination, decreased urination, pale skin, unexplained bruising, confusion and discomfort, and swelling all over the body. People with HUS syndrome need to be hospitalized until the kidneys recover.
- Most people with HUS recover, but there are a few cases of permanent kidney damage or death from the disease.
- STEC infection is identified as the most common cause of kidney failure in infants and young children.
- In addition, your doctor may order a complete blood test (CBC) and kidney test if you have signs of HUS syndrome.
Part 2 of 2: Identify health problems that can cause similar symptoms
Find out about other causes of bloody diarrhea. There are many other causes of bloody diarrhea, and unlike serious STEC infections, most of these are less life-threatening. There are many types of bacteria that can cause bloody diarrhea, including Salmonella and Shigella. Other diseases that can cause bloody stools include: anal fissures, hemorrhoids, blood vessels ruptured from excessive wiping, diverticulitis, ulcerative colitis, stomach ulcers, parasitic infections, colorectal cancer, take blood thinners like warfarin and chronic alcoholism. On the other hand, an E. coli infection usually starts suddenly, and bloody diarrhea usually occurs 24 hours after a severe abdominal contraction.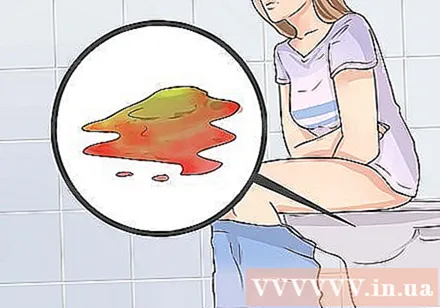
- Bright red blood in the stool is a sign of a problem with the lower digestive tract (like the large intestine). In contrast, the blood from your stomach or small intestine often makes your stools black or tarry.
- The health problem that has the most similar symptoms to an STEC infection is ulcerative colitis (an inflammatory bowel disease), but it can be diagnosed by looking at the bowel through a small bronchoscope.
Find out other causes of severe spasms. Most causes of cramping and / or abdominal pain are benign and not worrying, but only discomfort. For example, less serious causes include indigestion, constipation, lactose intolerance, food allergies, irritable bowel syndrome, gastroenteritis, kidney stones, and menstruation. More serious causes of constriction and / or bloating include: appendicitis, abdominal aneurysm, intestinal obstruction, stomach or colon cancer, cholecystitis, diverticulitis, Crohn's disease , ulcerative colitis, pancreatitis and stomach (stomach) ulcer. Of the above diseases, only colon cancer, diverticulitis and ulcerative colitis have diarrhea that is most similar to STEC, but E. coli infection occurs suddenly and without warning symptoms. .
- Foods with a high risk of E. coli poisoning include raw burgers, soft cheese made from unpasteurized milk, unpasteurized milk, unpasteurized apple juice and vinegar.
- Although the cause is unknown, it has been found that in the US, the majority of E. coli infections occur between June and September, the time of summer.
Be cautious with medications that increase the risk of E infection. coli. Although the medicine does not cause E. coli infections, some medications can create certain conditions that make it harder for your body to fight off the pathogenic bacteria (the bacteria you come into contact with more than you think). For example, people undergoing chemotherapy or taking the organ transplant rejection vaccine or taking long-term antivirals (to prevent AIDS or liver failure due to hepatitis) are at high risk for E. coli infection and many Other infections caused by weakened immune systems. In addition, people taking stomach acid-lowering drugs are also at a higher risk of E. coli infection due to hydrochloric acid that helps protect the stomach from bacteria.
- Avoid taking diarrhea medicine during E. coli infection because it will slow digestion and prevent the body from eliminating toxins.
- Avoid taking Salicylate medications such as aspirin and ibuprofen because it can increase your risk of bleeding bowel.
Advice
- See your doctor if you have diarrhea for more than 3 days, high fever, severe stomach pain or cramps, blood in your stool, frequent vomiting, or less urinating than usual.
- To reduce the risk of poisoning caused by E. coli, you should handle and cook meat thoroughly, wash vegetables and fruits and avoid drinking unpasteurized milk and juices.
- Always wash your hands after using the toilet, changing diapers and before eating or preparing food.
- Avoid swallowing water in pools, rivers, lakes and streams.
- If an E. coli infection is warned, you should follow your healthcare professional's instructions on what foods / drinks should be avoided to protect yourself and your family from infection.
Warning
- See your doctor right away if you suddenly experience bleeding diarrhea and abdominal pain.
- Do not take antibiotics to treat E. coli infections as there is no evidence that antibiotics are helpful and taking antibiotics can increase the risk of kidney failure.