Content
Normally, the liver is responsible for producing bile, a fluid used in the small intestine to digest fatty foods and absorb important vitamins. The gallbladder is a place to store bile. However, sometimes the cholesterol in the bile increases excessively, and cholesterol stones will form in the bile. Women are more susceptible to gallstones than men because estrogen increases the cholesterol level in the bile. Obesity is another risk factor for gallstones. 20% of gallstones are pigmented stones composed of calcium salts and bilirubin, a product of the breakdown of red blood cells. This form of gallstones is often caused by liver disease, anemia, or infection of the bile duct. The most common treatment for gallstones is laparoscopic surgery to remove the gallbladder, but there are a number of other treatment options that do not require surgery.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Use non-surgical treatments

Consider oral stone dissolution therapy. Your doctor may prescribe ursodiol to dissolve gallstones without surgery. This drug is basically bile acid in pill form. In particular, ursodiol is a popular drug, as it is one of the safest drugs on the market.- Oral stone dissolution therapy is most successful when treating small stones (less than 1.5 cm in diameter) with high cholesterol. About 30% of people with gallstones can use this method.
- If you have a pigment stone, you are more likely to need other treatments.
- This method is often less successful in obese patients.
Use shock wave therapy. This therapy is often used in conjunction with oral stone dissolution therapy, although it is currently rarely performed because laparoscopic surgery is so common. Shock wave therapy, also known as lithotripsy, uses sound waves to break gallstones into more soluble pieces.- This method is most effective when treating gallstones less than 2 cm in diameter.
- This treatment is quite rare because it is only done in a few places.

Understand that gallstones often reappear after treatment with non-surgical methods. Gallstones recur in the majority of patients using the lithotripsy method, so these methods are no longer common. Usually, this method applies to patients who are not fit for surgery. advertisement
Method 2 of 3: Try alternative therapies
Treatment of gallstones with phytochemicals. Scientific experiments on a formula exclusively blended with plant compounds called Rowachol have shown encouraging results. A 6-month course of treatment completely or partially dissolved gallstones in 29% of a study of 27 patients.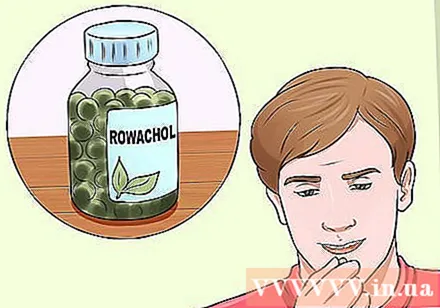
- These phytochemicals appear to stimulate liver bile production and inhibit the formation of cholesterol stones.
- Rowachol also increases the efficacy of other solvents.
Consider a method of detoxification of the gallbladder. Opinions differ on the effectiveness of liver and gallbladder detoxification. There is no scientific evidence to prove that this method is effective, but word of mouth has been reported about its success. Note that most of the "evidence" in feces after detox is not actually gallstones but a byproduct of the detoxification process. However, you can try the following options:
- Fasting for 12 hours. Starting at 7pm, drink 4 tablespoons of olive oil, followed by 1 tablespoon of lemon juice. Repeat every 15 minutes for an 8 hour session.
- Another way is to eat just one apple and a vegetable juice for the whole day. At around 5 or 6pm, drink 18 ml of olive oil, followed by 9 ml of fresh lemon juice. Repeat every 15 minutes until all 240 ml of olive oil is gone.
- The process of detoxification often causes pain and diarrhea.
- The next morning, you will usually have a green or brown soft round seeds. Again, these are not gallstones but a byproduct of detox therapy.
Try acupuncture. This method may not completely remove existing gallstones, but can help reduce spasm, enhance bile flow, and restore function of the liver and gallbladder.
Treat the symptoms of gallbladder disease with herbs or homeopathic remedies. Keep in mind that these therapies will not remove gallstones, but will only ease the symptoms so you can tolerate gallstones already in your body.
- Green tea, milk thistle, artichoke, and turmeric can all help with liver and gallbladder function. Consult a healthcare professional before using an herbal regimen. If used incorrectly, these herbs can trigger gallbladder pain or cause unwanted side effects.
- Homeopathic therapies for gallstones include colocynthis (bitter melon), chelidonium, and lycopodium, which are formulated in certain concentrations. Note that there is no evidence to support the effectiveness of homeopathic therapy.
Method 3 of 3: Prevent gallstones from forming
Adherence to a diet has been shown to help prevent gallstones. Some of the ways of eating have been linked to a low incidence of gallbladder disease include:
- Use polyunsaturated fats and monounsaturated fats.
- Eat plenty of fiber.
- Consume caffeine as part of your daily diet.
- Eat a vegetarian diet.
- Avoid excessive intake of refined sugars such as sucrose and fructose.
- Some indirect evidence suggests that eating a lot of beans can increase the risk of gallbladder disease.
- Limit alcohol intake to the lowest.
- Consider eating 30 grams of peanuts or other nuts several times a week. This has been shown to be effective in a number of studies, especially in female subjects.
- Eat in moderation; avoid skipping meals.
Use nutritious foods that have a preventive effect. Nutritional foods containing vitamin C, soy lecithin and iron, have been shown to effectively prevent the development of gallstones.
Lose weight slowly and maintain a healthy weight. Rapid weight loss can increase your risk of developing gallstones. Although obesity is a risk factor for gallbladder disease, it is important to eliminate this risk gradually with careful weight loss. Losing weight slowly and evenly 0.5 kg - 1 kg per week is best.
Get tested for allergies and eliminate allergenic foods from your diet. Identifying and avoiding allergenic foods can reduce the risk of gallstones. advertisement
Advice
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the standard treatment for symptomatic gallstones. For patients with asymptomatic gallstones, very few doctors provide treatment.
- Non-surgical methods of treating symptomatic gallstones are usually for patients who refuse surgery or are unable to do it.