Content
Yeast infections mainly appear on the skin, mouth or vaginal area, caused by many types of bacteria of the genus Candida spp, including more than 20 strains that can affect people. The most common cause of this disease is fungus Candida albicans overgrowth.Yeast infections are very uncomfortable for the sick person, so start treatment as soon as you notice symptoms. This type of infection is very common in the United States and there is no age group with a predominant number of cases. The frequency of disease development has not been thoroughly studied, but it is estimated that there are 50,000 - 100,000 cases per year in the United States. If you think you have a yeast infection, there are steps you can take to prevent it from developing.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Fight a more advanced yeast infection

Eat raw yeast yogurt. This type of yogurt contains beneficial bacteria that can prevent yeast from growing. Women often use yogurt with lactobacillus acidophilus by eating or applying it directly to the vagina to prevent a yeast infection from developing. Lactobacillus acidophilus are beneficial bacteria that fight off the bacteria that cause yeast infections. You can buy this yogurt at most supermarkets. Be sure to check the label to make sure the lactobacillus acidophilus bacteria are still alive.- Many studies show that yogurt is effective in reducing symptoms in some women, but other studies have shown that yogurt doesn't work for anyone.

Bathe twice daily. While bathing twice a day can ruin your daily routine, it is still important to keep your body as clean as possible to fight infections. You should not use soap or shower gel made from chemicals, they will kill off the beneficial bacteria needed to fight infection, while not significantly reducing infection.- Women with vaginal yeast should take a bath instead of a shower. Taking a bath helps to clear the yeast from the vaginal area.
- Do not take a bath in water that is too hot as the yeast can multiply.
Use a clean towel. After bathing or swimming, you must dry your body completely to remove any residual moisture, as yeast thrives in warm and humid places. If you are using towels that have been used before, then it is more likely that the towels have yeast because they will grow well on the moisture left by the last bath. Instead, wash the towels after each use.
Wear loose-fitting clothing. When you have a yeast infection on your skin or vagina, wear loose clothing to allow your skin to breathe. This is especially important if you have vaginal yeast. Wear cotton underwear and avoid silk or nylon underwear as the air cannot pass through the two fabrics.
- Avoid activities that generate a lot of heat, sweat and increase humidity in the fungal area to prevent yeast growth.
Avoid certain skin products. When you have a yeast infection, avoid using any product that worsens the infection. In particular, avoid soaps that kill beneficial bacteria, as well as feminine hygiene powders and sprays. You also shouldn't use certain types of body oils, as they moisturize the skin, causing the skin to retain heat and moisture.
- People often want to use sprays or powders to eliminate the side effects of a yeast infection, but they actually make your skin more irritated.
Method 2 of 3: Treat a yeast infection with medication
Use a topical medication. There are several medications that can fight yeast infections on the skin. For skin infections, doctors usually prescribe antifungal creams to be applied directly to the infected skin, which usually cure the disease within a few weeks. The two most common antifungal creams for yeast on the skin are miconazole and oxiconazole. They come with general instructions for use, but you must follow your doctor's instructions.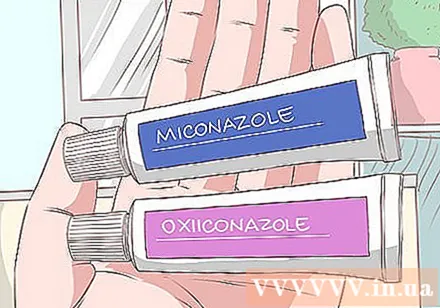
- Before using the cream, you must clean the infected area and then dry it completely, making sure your skin is dry. Apply the cream exactly as recommended by your doctor or the manufacturer. Let the cream soak into your skin before dressing or doing anything that could cause the newly applied skin to rub against other objects.
Treat vaginal yeasts. To treat vaginal yeast, you can either use an over-the-counter medication or ask your doctor to prescribe it. For occasional fungal infections with mild to moderate symptoms, you should use an over-the-counter medication in the form of a cream, pill, or pill inserted directly into the vagina.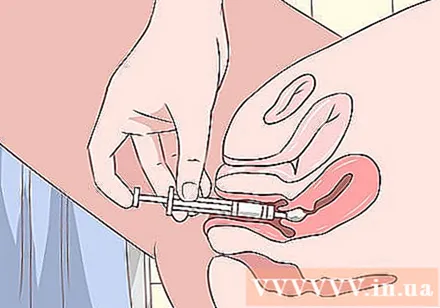
- Common yeast treatment creams are miconazole (Monistat) and terconazole (Terazol). They are produced as a daily vaginal suppository or cream before bedtime, for the duration of use indicated in the instructions. The duration of the drug usually lasts 1-7 days.
- You can also take antifungals like clotrimazole (Myecelex) and fluconazole (Diflucan).
- Clotrimazole is also produced in the form of 100mg tablet inserted vaginally every day before bedtime, duration of treatment from 6-7 days, 200mg tablet used every night for 3 days or 500mg tablet for 1 day.
- More complex fungal infections require 7-14 days of treatment instead of 1-7 days.
Ask your doctor about boric acid. Boric acid is sold as a vaginal suppository and is a prescription medicine. This medication can cure frequent fungal infections if conventional medications don't work as expected. In addition, boric acid became more resistant to strains of candida that have become resistant to certain antibiotics over time.
- Boric acid is toxic, especially when absorbed into the body, and can cause skin irritation.
- Avoid oral sex while using boric acid so your partner doesn't swallow this toxin.
Cure a fungal infection of the mouth with a medical mouthwash. Medical mouthwash can cure a fungal infection of the mouth thanks to its anti-fungal properties. To use, you rinse the solution in your mouth for a short time before swallowing. It will aid the inner surface of the mouth as well as support from inside the body after you swallow. Ask your doctor about oral supplements to treat oral yeast, which are available in oral tablets and lozenges.
- If you have a very weak immune system and are fighting diseases such as cancer or HIV, your doctor often prescribes Amphotericin B, which treats oral yeast infections that have become resistant to antifungal drugs.
Method 3 of 3: Find out a yeast infection
Recognize the signs. If you want to prevent a yeast infection from developing you must be aware of its signs. There are three types of yeast infections that affect the skin, mouth, and vagina.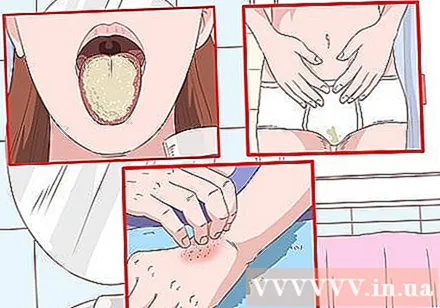
- A symptom of a fungal infection of the mouth, also known as thrush, is a formation of fine white patches in the throat or in the area of the mouth, or a crack in the corner of the mouth.
- Fungal infections of the skin cause blisters, red patches or rashes, mainly between the toes and fingers, under the breasts and around the groin area. Infection on the skin can also affect the penis. The symptoms are similar, but patches of white or damp skin will appear on the penis, with white matter accumulating in the skin folds.
- Vaginal yeast infections are fairly common and cause increased vaginal mucus, which is thick, curd-like white, mild to moderate itch, skin irritation in the vagina, and redness.
Consider general risk factors. There are many risk factors that contribute to a yeast infection. If you have a disease that weakens your immune system, such as HIV, then your chance of getting infected is higher because the immune system cannot protect the body against an outside source. If you are taking antibiotics, you are also at higher risk for a yeast infection. Antimicrobial therapies like taking antibiotics to treat infections, but at the same time antibiotics also reduce the amount of bacteria living in the body and play a role in protecting you from other infections like yeast infections. In this case a fungal infection can occur if there is a surface conducive to yeast to multiply, such as the skin, penis or vagina.
- People who are overweight are also at a higher risk of yeast infections, as they have too many skin folds that allow bacteria and yeast to grow.
- Babies are also susceptible to yeast infections, which manifest as a rash in a diaper or in the mouth.
Risk factors related to gender. Women whose hormone levels fluctuate because of menopause, oral contraceptives, pregnancy or premenstrual syndrome are at a higher risk of yeast infections, because hormonal changes cause a lot of stress. physically. Women are also susceptible to vaginal yeast infections if they use a chemical douche with irritants. Although for the purpose of hygiene, it is douching that changes the natural pH balance in the vagina, which is the environment that helps the vagina fight the effects of external bacteria.
- Men are more likely to get a yeast infection if they are not circumcised, as the yeast bacteria can thrive underneath the foreskin.
Reduce your chances of getting a yeast infection. There are many ways you can prevent this disease, such as using antibiotics only when absolutely necessary because your body needs to retain beneficial natural bacteria in order to fight yeast bacteria from growing. Since steroids cause immune system problems, you need to minimize or minimize the use of inhaled steroids and other forms. Try to stay away from environment and damp clothing. If your clothes get wet, change them as soon as possible.
- Yeast can grow in the mouth, especially in diabetics and those wearing dentures. To prevent problems caused by dentures you must keep them clean and use dentures that fit properly. There are cases when the yeasts are inactive until a stimulating factor develops, such as when using antibiotics.
- Women should avoid douching if possible.
- For diabetics, always try to control the disease and keep skin healthy.
Warning
- If your yeast infection recurs frequently, it's a good idea to see your doctor instead of continuing to take an over-the-counter medicine, as it may not be a yeast but another strain that is less common. You will also need to be tested for other medical conditions (like diabetes).
- Some self-medicating treatments can fight symptoms and even contribute to the cure of a yeast infection, but it's better to combine these with prescription medications. Always consult your doctor to understand the risks and benefits of using an alternative therapy. Some studies show positive results, but more studies are needed before solid recommendations can be made.