Author:
Charles Brown
Date Of Creation:
2 February 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- To step
- Method 1 of 6: Calculate the volume of a cube
- Method 2 of 6: Calculate the volume of a bar.
- Method 3 of 6: Calculate the volume of a cylinder
- Method 4 of 6: Calculate the volume of a regular pyramid
- Method 5 of 6: Calculate the volume of a cone
- Method 6 of 6: Calculate the volume of a sphere
The volume of a figure is the three-dimensional space that the figure occupies. You can think of volume as the amount of water (or air, sand, etc.) that would fit into the mold if it were completely full. Common units of measure of volume are cubic centimeters and cubic meters. This article will teach you how to calculate the volume of six different three-dimensional shapes commonly encountered on math tests, including the cube, sphere, and cone. You will see that there are many similarities that make it easy to remember. Watch if you can find those matches!
To step
Method 1 of 6: Calculate the volume of a cube
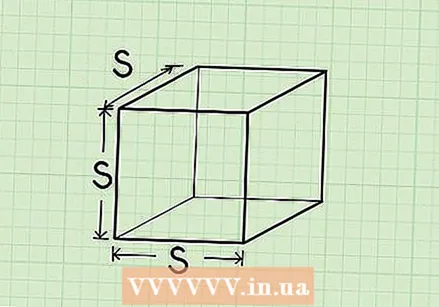 Recognize a cube. A cube is a three-dimensional shape with six identical square faces. In other words, it's a box with equal sides all over.
Recognize a cube. A cube is a three-dimensional shape with six identical square faces. In other words, it's a box with equal sides all over. - A die is a good example of a cube you may have at home. Children's sugar cubes or blocks are also often cubes.
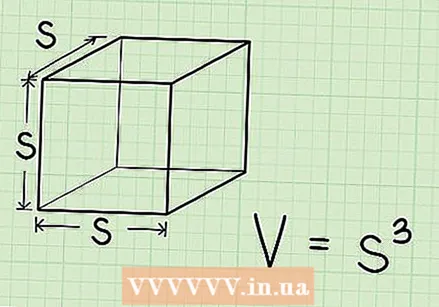 Learn the formula to calculate the volume of the cube. Since all side lengths of the cube are the same, the formula for calculating the cube's volume is very easy. The place where two sides meet is called the rib. We shorten the volume to "V". We call the ribs, or the length of the side, "s" here. The formula then becomes V = s³
Learn the formula to calculate the volume of the cube. Since all side lengths of the cube are the same, the formula for calculating the cube's volume is very easy. The place where two sides meet is called the rib. We shorten the volume to "V". We call the ribs, or the length of the side, "s" here. The formula then becomes V = s³ - To find s³, multiply s three times by itself: s³ = s x s x s
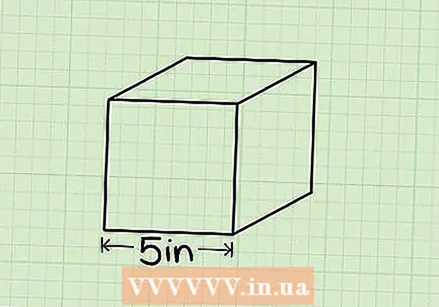 Find the length of one side of the cube. Depending on the assignment, this information may already be there, but you may also need to measure it yourself with a ruler. Remember, because it's a cube, all side lengths should be equal, so it doesn't matter which one you measure.
Find the length of one side of the cube. Depending on the assignment, this information may already be there, but you may also need to measure it yourself with a ruler. Remember, because it's a cube, all side lengths should be equal, so it doesn't matter which one you measure. - If you are not 100% sure that your shape is a cube, measure all sides to see if they are the same. If they are not, you will need to use the method below to calculate the volume of a beam. Note: In the example images the measurements are given in inches (in), however we use centimeters (cm).
 Put the length of the side in the formula V = s³ and calculate it. For example, if you measured that the side length of your cube is 5 cm, you write the formula as follows: V = (5) ³. 5 x 5 x 5 = 125 cm³, so that is the volume of your cube!
Put the length of the side in the formula V = s³ and calculate it. For example, if you measured that the side length of your cube is 5 cm, you write the formula as follows: V = (5) ³. 5 x 5 x 5 = 125 cm³, so that is the volume of your cube!  Make sure to write your answer in cubic centimeters. In the example above, the cube was measured in centimeters, so the answer must be given in cubic centimeters. If the length of the side of the cube had been 3 meters, the volume would have been V = (3 m) ³ = 27 m³.
Make sure to write your answer in cubic centimeters. In the example above, the cube was measured in centimeters, so the answer must be given in cubic centimeters. If the length of the side of the cube had been 3 meters, the volume would have been V = (3 m) ³ = 27 m³.
Method 2 of 6: Calculate the volume of a bar.
 Recognize a bar. A bar is a figure consisting of six rectangular faces. So it is actually a three-dimensional rectangle, a kind of box.
Recognize a bar. A bar is a figure consisting of six rectangular faces. So it is actually a three-dimensional rectangle, a kind of box. - Basically a cube is just a special beam, where all sides are equal.
 Learn the formula to calculate the volume of a bar. The formula for the volume of a beam is V = length (l) x width (w) x height (h), or V = l x w x h. Note: In the pictures for these examples, "w" stands for width.
Learn the formula to calculate the volume of a bar. The formula for the volume of a beam is V = length (l) x width (w) x height (h), or V = l x w x h. Note: In the pictures for these examples, "w" stands for width. Find the length of the bar. The length is the longest side of the beam that is parallel to the ground or surface on which it rests. The length may already be indicated on the picture, or you may need to measure it with a ruler.
Find the length of the bar. The length is the longest side of the beam that is parallel to the ground or surface on which it rests. The length may already be indicated on the picture, or you may need to measure it with a ruler. - Example: The length of this beam is 4 cm, so l = 4 cm.
- Don't worry too much about which side is the length, etc. As long as you measure three different sides, the outcome will be the same.
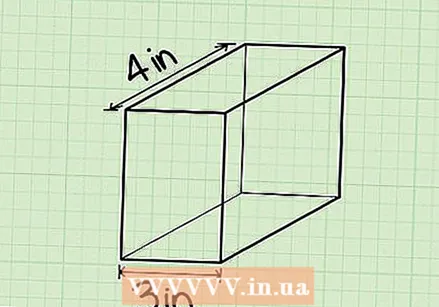 Find the width of the beam. You can find the width of the beam by measuring the short side that is parallel to the ground or the surface on which it rests. Again, first check if it is already indicated on the picture, and measure it otherwise with your ruler.
Find the width of the beam. You can find the width of the beam by measuring the short side that is parallel to the ground or the surface on which it rests. Again, first check if it is already indicated on the picture, and measure it otherwise with your ruler. - Example: The width of this beam is 3 cm, so b = 3 cm.
- If you're measuring the bar with a ruler or tape measure, don't forget to write everything down in the same unit of measure.
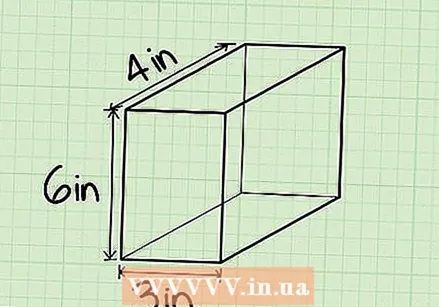 Find the height of the beam. Height is the distance from the ground or surface that the beam rests on to the top of the beam. See if it is already indicated in the picture and measure it otherwise with your ruler or tape measure.
Find the height of the beam. Height is the distance from the ground or surface that the beam rests on to the top of the beam. See if it is already indicated in the picture and measure it otherwise with your ruler or tape measure. - Example: The height of this beam is 6 cm, so h = 6 cm.
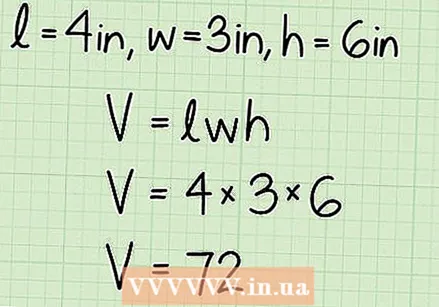 Enter the dimensions in the formula and calculate it. Remember that V = l x w x h.
Enter the dimensions in the formula and calculate it. Remember that V = l x w x h. - In this example, l = 4, b = 3, and h = 6. Therefore, the result is V = 4 x 3 x 6 = 72.
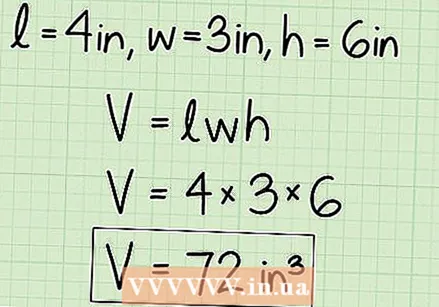 Make sure to write your answer in cubic centimeters. The result is therefore 72 cubic centimeters, or 72 cm³.
Make sure to write your answer in cubic centimeters. The result is therefore 72 cubic centimeters, or 72 cm³. - If the dimensions of the beam had been in meters, you would have, for example, l = 2 m, w = 4 m and h = 8 m. The volume would then be 2 m x 4 m x 8 m = 64 m³.
Method 3 of 6: Calculate the volume of a cylinder
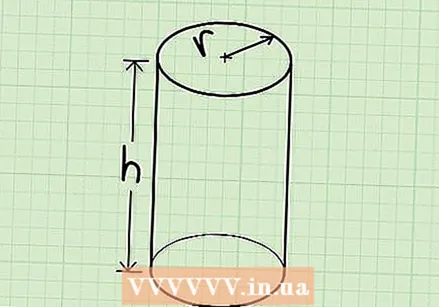 Learn how to identify a cylinder. A cylinder is a three-dimensional shape with two identical round ends connected by a single curved side. It is actually a straight round rod.
Learn how to identify a cylinder. A cylinder is a three-dimensional shape with two identical round ends connected by a single curved side. It is actually a straight round rod. - A can is a good example of a cylinder, or AA battery.
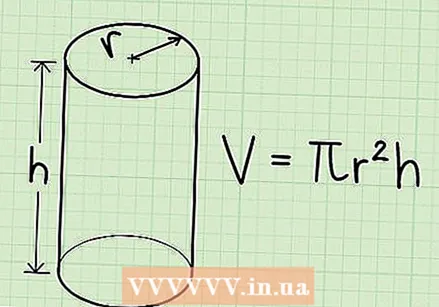 Memorize the formula for the volume of a cylinder. To calculate the volume of a cylinder, you need to know its height and the radius of the circular base. The radius is the distance from the center of the circle to the edge. The formula is V = π x r² x h, where V is the volume, r the radius, h the height, and π the constant pi.
Memorize the formula for the volume of a cylinder. To calculate the volume of a cylinder, you need to know its height and the radius of the circular base. The radius is the distance from the center of the circle to the edge. The formula is V = π x r² x h, where V is the volume, r the radius, h the height, and π the constant pi. - In most cases it is sufficient to round pi to 3.14. Ask your teacher what he / she wants.
- The formula for finding the volume of a cylinder is actually pretty much the same as that of the volume of a beam: you multiply the height of the shape by the area of the base. With a beam the area of the base is l x b, with a cylinder it is π x r², the area of a circle with radius r.
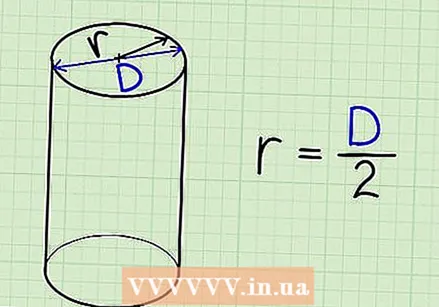 Find the radius of the base. If it is already indicated on the picture, just fill it in. If you got the diameter instead of the radius, just divide it by 2 to find the radius (d = 2 x r).
Find the radius of the base. If it is already indicated on the picture, just fill it in. If you got the diameter instead of the radius, just divide it by 2 to find the radius (d = 2 x r). 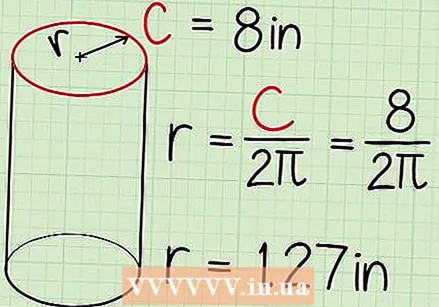 Measure the shape if the radius is not given. Note that it can be difficult to measure the exact radius of a circle. One option is to measure the circle at the widest point with your ruler from top to bottom, and divide that by two.
Measure the shape if the radius is not given. Note that it can be difficult to measure the exact radius of a circle. One option is to measure the circle at the widest point with your ruler from top to bottom, and divide that by two. - Another option is to measure the circumference of the circle (the distance around it) with a piece of string or a tape measure. Put the result in this formula: C (circumference) is 2 x π x r. Divide the circumference by 2 x π (6.28) and you have the radius.
- For example, if the circumference you measured is 8 cm, the radius is 1.27 cm.
- If you really need an exact measurement, you can use either method to see if the results are the same. If not, check it again. The outline method usually gives a more accurate result.
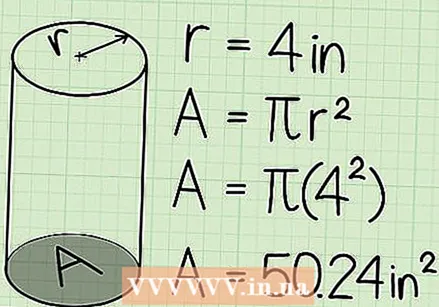 Calculate the area of the circle at the base. Put the radius in the formula π x r². Multiply the radius by itself and multiply that result by π. For instance:
Calculate the area of the circle at the base. Put the radius in the formula π x r². Multiply the radius by itself and multiply that result by π. For instance: - If the radius is 4 cm, then the area of the circle is A = π x 4².
- 4² = 4 x 4, or 16. 16 x π = 16 x 3.14 = 50.24 cm².
- If the diameter of the base is known, instead of the radius, remember that d = 2 x r. Then you have to divide the diameter by two to find the radius.
 Find the height of the cylinder. This is simply the distance between the two circular bases, or the distance from the surface on which the cylinder rests to the top of the cylinder. See if the length is already indicated in the picture, or measure it otherwise with your ruler or tape measure.
Find the height of the cylinder. This is simply the distance between the two circular bases, or the distance from the surface on which the cylinder rests to the top of the cylinder. See if the length is already indicated in the picture, or measure it otherwise with your ruler or tape measure.  Multiply the area of the base by the height of the cylinder to find the volume. Put the values in the formula V = π x r² x h. In our example with a radius of 4 cm and a height of 10 cm:
Multiply the area of the base by the height of the cylinder to find the volume. Put the values in the formula V = π x r² x h. In our example with a radius of 4 cm and a height of 10 cm: - V = π x 4² x 10
- π x 4² = 50.24
- 50.24 x 10 = 502.4
- V = 502.4
 Remember to write your answer in cubic centimeters. In this example, the cylinder was measured in centimeters, so the answer should be written in cubic centimeters: V = 502.4cm³. If the cylinder was measured in meters, the volume should be written in square meters (m³).
Remember to write your answer in cubic centimeters. In this example, the cylinder was measured in centimeters, so the answer should be written in cubic centimeters: V = 502.4cm³. If the cylinder was measured in meters, the volume should be written in square meters (m³).
Method 4 of 6: Calculate the volume of a regular pyramid
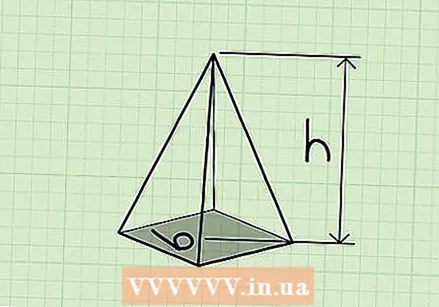 Know what a regular pyramid is. A pyramid is a three-dimensional shape with a polygon as a base and side faces that taper to the top (the tip of the pyramid). A regular pyramid is a pyramid whose base is a regular polygon, which means that all sides and angles of it are polygon are equal.
Know what a regular pyramid is. A pyramid is a three-dimensional shape with a polygon as a base and side faces that taper to the top (the tip of the pyramid). A regular pyramid is a pyramid whose base is a regular polygon, which means that all sides and angles of it are polygon are equal. - Typically, a pyramid is depicted with a square base and sides tapering to a point, but the base of a pyramid can actually have 5, 6 or 100 sides!
- A pyramid based on a circle is called a cone, which we will discuss in the next method.
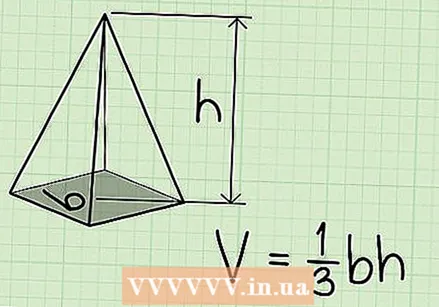 Learn the formula for calculating the volume of the regular pyramid. The formula for the volume of a regular pyramid is V = 1/3 x w x h, where b is the area of the base, and h is the height of the pyramid, or the vertical distance from the base to the top.
Learn the formula for calculating the volume of the regular pyramid. The formula for the volume of a regular pyramid is V = 1/3 x w x h, where b is the area of the base, and h is the height of the pyramid, or the vertical distance from the base to the top. - The formula for straight pyramids, where the top is directly above the center of the base, is the same as that for oblique pyramids, where the top is off-center.
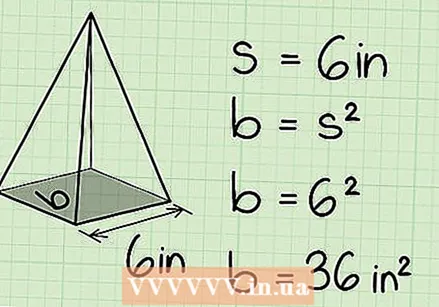 Calculate the area of the base. The formula for this depends on the number of sides of the base. In our example, the base is a square with sides of 6 cm. Remember that the formula for calculating the area of a square is A = s². So with our pyramid that is 6 x 6 = 36 cm².
Calculate the area of the base. The formula for this depends on the number of sides of the base. In our example, the base is a square with sides of 6 cm. Remember that the formula for calculating the area of a square is A = s². So with our pyramid that is 6 x 6 = 36 cm². - The formula for the area of a triangle is A = 1/2 x w x h, where b is the base and h is the height.
- It is possible to calculate the area of any regular polygon with the formula A = 1/2 xpxa, where A is the area, p is the perimeter and a is the apothem, which is the distance from the center of the shape to the center of one of the sides. You can also make it easy on yourself and use an online regular polygon calculator.
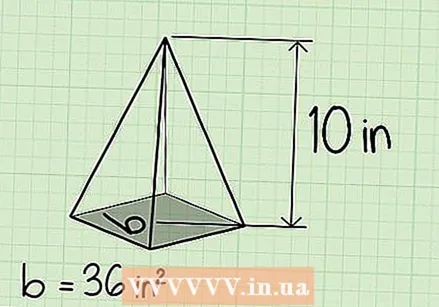 Find the height of the pyramid. In most cases it will be indicated on the picture. In our example, the height of the pyramid is 10 cm.
Find the height of the pyramid. In most cases it will be indicated on the picture. In our example, the height of the pyramid is 10 cm.  Multiply the area of the pyramid's base by the height and divide by 3 to find the volume. Remember that the formula is V = 1/3 x w x h. In our example, the pyramid has a base with an area of 36 and a height of 10, so the volume is then 36 x 10 x 1/3 = 120.
Multiply the area of the pyramid's base by the height and divide by 3 to find the volume. Remember that the formula is V = 1/3 x w x h. In our example, the pyramid has a base with an area of 36 and a height of 10, so the volume is then 36 x 10 x 1/3 = 120. - If we had another pyramid with a base with an area of 26 and a height of 8, the result would have been 1/3 x 26 x 8 = 69.33.
 Remember to write the result in cubic units. The dimensions of the pyramid in the example were given in centimeters, so the result should be written in cubic centimeters, 120 cm³. If the dimensions were given in meters, you write the answer in cubic meters (m³).
Remember to write the result in cubic units. The dimensions of the pyramid in the example were given in centimeters, so the result should be written in cubic centimeters, 120 cm³. If the dimensions were given in meters, you write the answer in cubic meters (m³).
Method 5 of 6: Calculate the volume of a cone
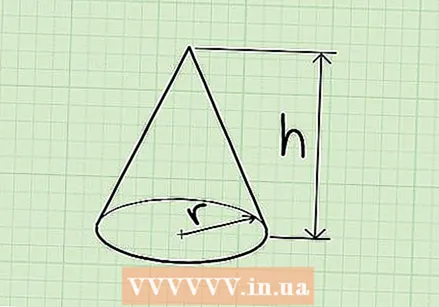 Learn what the properties of a cone are. A cone is a three-dimensional shape with a circular base and a single point on the opposite face. Another way to see a cone is that it is a special kind of pyramid with a circular base.
Learn what the properties of a cone are. A cone is a three-dimensional shape with a circular base and a single point on the opposite face. Another way to see a cone is that it is a special kind of pyramid with a circular base. - If the tip of the cone is directly above the center of the base, you call it a straight cone. If it is not directly above the center, you call it an oblique cone. Fortunately, the formula to calculate volume is the same for both types of cones.
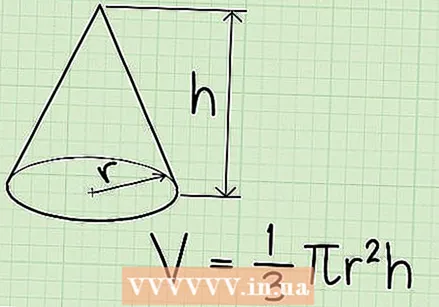 Know the formula for calculating the volume of the cone. This formula is V = 1/3 x π x r² x h, where r is the radius of the circle at the base, h the height of the cone and π the constant pi, which can be rounded to 3.14.
Know the formula for calculating the volume of the cone. This formula is V = 1/3 x π x r² x h, where r is the radius of the circle at the base, h the height of the cone and π the constant pi, which can be rounded to 3.14. - The portion π x r² refers to the area of the circle that is the base of the cone. So the formula for the volume of the cone is 1/3 x w x h, just like the formula for the pyramid in the method above!
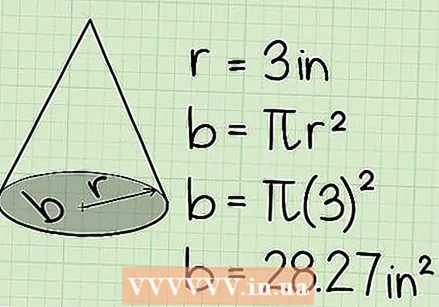 Calculate the area of the circular base of the cone. To do this you need to know the radius of the base, which should be indicated on your picture. If you got the diameter instead of the radius, just divide that number by 2, because the diameter is 2 times the radius (d = 2 x r). Then put the radius in the formula A = π x r² to calculate the area.
Calculate the area of the circular base of the cone. To do this you need to know the radius of the base, which should be indicated on your picture. If you got the diameter instead of the radius, just divide that number by 2, because the diameter is 2 times the radius (d = 2 x r). Then put the radius in the formula A = π x r² to calculate the area. - In this example the radius is 3 cm. If we put it in the formula, we get: A = π x 3².
- 3² = 3 x 3, or 9, so A = π x 9.
- A = 28.27cm².
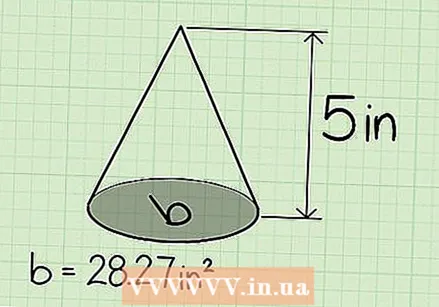 Find the height of the cone. This is the vertical distance from the base of the cone to the top. In our example, the height of the cone is 5 cm.
Find the height of the cone. This is the vertical distance from the base of the cone to the top. In our example, the height of the cone is 5 cm.  Multiply the height of the cone by the area of the base. In our example, the area of the base is 28.27cm² and the height is 5 cm, so w x h = 28.27 x 5 = 141.35.
Multiply the height of the cone by the area of the base. In our example, the area of the base is 28.27cm² and the height is 5 cm, so w x h = 28.27 x 5 = 141.35.  Now multiply this result by 1/3 (or divide by 3) to get the volume of the cone. In the step above we actually calculated the volume of a cylinder, which is a cone where the walls would be upright and end up in a different circle. Dividing it by 3 gives you the volume of the cone.
Now multiply this result by 1/3 (or divide by 3) to get the volume of the cone. In the step above we actually calculated the volume of a cylinder, which is a cone where the walls would be upright and end up in a different circle. Dividing it by 3 gives you the volume of the cone. - In our example, that's 141.35 x 1/3 = 47.12, the volume of the cone.
- Again: 1/3 x π x 3² x 5 = 47.12.
 Remember to write the result in cubic units. Our cone was measured in centimeters, so the volume should be expressed in cubic centimeters: 47.12 cm³.
Remember to write the result in cubic units. Our cone was measured in centimeters, so the volume should be expressed in cubic centimeters: 47.12 cm³.
Method 6 of 6: Calculate the volume of a sphere
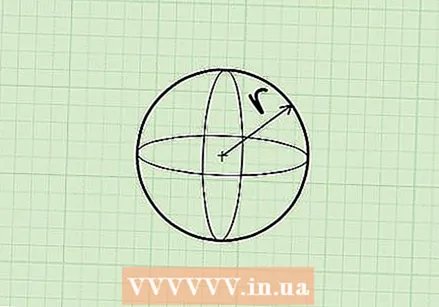 Recognize a sphere. A sphere is a perfectly round three-dimensional shape, where every point on the surface is equidistant from the center. In other words, it's a ball.
Recognize a sphere. A sphere is a perfectly round three-dimensional shape, where every point on the surface is equidistant from the center. In other words, it's a ball. 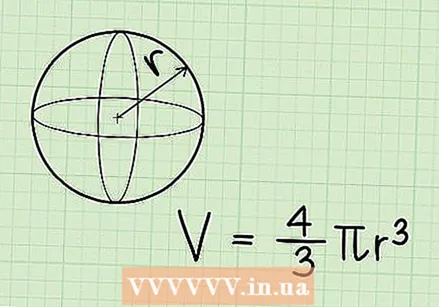 Learn the formula for calculating the volume of a sphere. The formula is V = 4/3 x π x r³ (ie, "four thirds times pi times cubic r"), where r is the radius of the sphere, and π is the constant pi (3.14).
Learn the formula for calculating the volume of a sphere. The formula is V = 4/3 x π x r³ (ie, "four thirds times pi times cubic r"), where r is the radius of the sphere, and π is the constant pi (3.14).  Find the radius of the sphere. If the radius is already given in the picture, it is easy. If the diameter is given, you have to divide this number by 2 to get the radius. The radius of the sphere in this example is 3 centimeters.
Find the radius of the sphere. If the radius is already given in the picture, it is easy. If the diameter is given, you have to divide this number by 2 to get the radius. The radius of the sphere in this example is 3 centimeters.  Measure the sphere if the radius is not given. If you need to measure a sphere (like a tennis ball, for example) to find the radius, find a piece of string long enough to wrap all the way around it. Then wrap it around the object at its widest point and mark the point where the string meets again. Then measure this portion of the string with a ruler to know the circumference of the sphere. Divide that by 2 x π, or 6.28, to get the radius.
Measure the sphere if the radius is not given. If you need to measure a sphere (like a tennis ball, for example) to find the radius, find a piece of string long enough to wrap all the way around it. Then wrap it around the object at its widest point and mark the point where the string meets again. Then measure this portion of the string with a ruler to know the circumference of the sphere. Divide that by 2 x π, or 6.28, to get the radius. - For example, if you measure the ball and see that its circumference is 6 inches, divide that by 6 inches, and you know the radius is 2 inches.
- It can be tricky to measure a sphere, so it's best to measure it three times, then take the average (add the three measurements together and divide by three) to make the measurement as accurate as possible.
- For example, if you measured three times and the results were 18 cm, 17.75 cm, and 18.2 cm, add that together (18 + 17.5 + 18.2 = 53.95) and divide it by 3 (53.95 / 3 = 17.98). You use this average in your calculation of the volume.
 Raise the radius to the cube to find r³. Raising to the cube simply means multiplying the number three times by itself, so r³ = r x r x r. In our example r = 3 that becomes 3 x 3 x 3 = 27.
Raise the radius to the cube to find r³. Raising to the cube simply means multiplying the number three times by itself, so r³ = r x r x r. In our example r = 3 that becomes 3 x 3 x 3 = 27.  Multiply your answer by 4/3. You can do it with a calculator, or just do it yourself and simplify the fraction. In our example, it is 27 x 4/3 = 180/3, or 36.
Multiply your answer by 4/3. You can do it with a calculator, or just do it yourself and simplify the fraction. In our example, it is 27 x 4/3 = 180/3, or 36.  Multiply the result by π to find the volume of the sphere. The last step in calculating the volume is to multiply the result so far by π. Round π to two decimal places, which is sufficient for most math problems (unless your teacher wants it otherwise), so multiply it by 3.14 and you have your answer.
Multiply the result by π to find the volume of the sphere. The last step in calculating the volume is to multiply the result so far by π. Round π to two decimal places, which is sufficient for most math problems (unless your teacher wants it otherwise), so multiply it by 3.14 and you have your answer. - So in our example it becomes 36 x 3.14 = 113.09.
 Write your answer in cubic units. In our example, we measured in centimeters, so the answer is V = 113.09 cm³.
Write your answer in cubic units. In our example, we measured in centimeters, so the answer is V = 113.09 cm³.