Author:
Christy White
Date Of Creation:
3 May 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- To step
- Part 1 of 3: Using compressed air
- Part 2 of 3: Cleaning stains on the printed circuit board
- Part 3 of 3: Removing bad rust
If the speed at which your computer processes data is much slower than normal, chances are there is dirt or rust on the circuit board and you need to clean it. Depending on the severity of the problem, there are a few different treatments for it. Dust and dirt can usually be treated with compressed air, while dirt deposits or rust can be cleaned separately. However, severe rust should be treated with baking soda.
To step
Part 1 of 3: Using compressed air
 Turn off your computer. Turn off your computer and disconnect all cables. Injecting compressed air into your computer while it is still running can potentially damage the components and cause your own electrocution.
Turn off your computer. Turn off your computer and disconnect all cables. Injecting compressed air into your computer while it is still running can potentially damage the components and cause your own electrocution. - You can shut down your computer by clicking on the main menu, selecting "Shut Down" and confirming your selection in the pop-up window that appears.
 Inject the compressed air into the central processing unit (CPU) in short bursts of air. Insert the compressed air canister nozzle into the exhaust ports of the fan, which are usually located at the top of the back of the console. Make sure to keep the can upright as you spray, and spray in short, steamy thrusts.
Inject the compressed air into the central processing unit (CPU) in short bursts of air. Insert the compressed air canister nozzle into the exhaust ports of the fan, which are usually located at the top of the back of the console. Make sure to keep the can upright as you spray, and spray in short, steamy thrusts. - If you turn the can upside down or spray for too long, the air will cool and the parts of your computer can freeze.
 Use a screwdriver to open the CPU. Use a screwdriver to remove the screws on the back of the CPU that secure the side panel to the device. Then gently slide the side panel back and away from the unit. You can now get to the circuit board.
Use a screwdriver to open the CPU. Use a screwdriver to remove the screws on the back of the CPU that secure the side panel to the device. Then gently slide the side panel back and away from the unit. You can now get to the circuit board. - You will likely need a Phillips screwdriver, but you may need a flat screwdriver or a hex screwdriver instead.
 Spray compressed air on the PCB. The circuit board is most likely green with squiggly silver lines on it. Spray compressed air on the plate in short bursts, keeping the can upright and the nozzle a few inches away from the circuit board. This also gives you the opportunity to search for dirt and rust that may need more extensive cleaning.
Spray compressed air on the PCB. The circuit board is most likely green with squiggly silver lines on it. Spray compressed air on the plate in short bursts, keeping the can upright and the nozzle a few inches away from the circuit board. This also gives you the opportunity to search for dirt and rust that may need more extensive cleaning. - A particularly large amount of dirt and rust, or an accumulation of it near a heat generator or on the circuit paths, must be removed.
Part 2 of 3: Cleaning stains on the printed circuit board
 Dampen a cotton swab with isopropyl alcohol. You must use isopropyl alcohol that contains at least 90% to 100% alcohol. Pour a little alcohol into a small bowl and dip the cotton swab in it. Then squeeze out the excess moisture so that the cotton swab is only slightly damp.
Dampen a cotton swab with isopropyl alcohol. You must use isopropyl alcohol that contains at least 90% to 100% alcohol. Pour a little alcohol into a small bowl and dip the cotton swab in it. Then squeeze out the excess moisture so that the cotton swab is only slightly damp. - The cotton swab should not drip or leave puddles on the circuit board. Excess moisture on the circuit paths can cause damage.
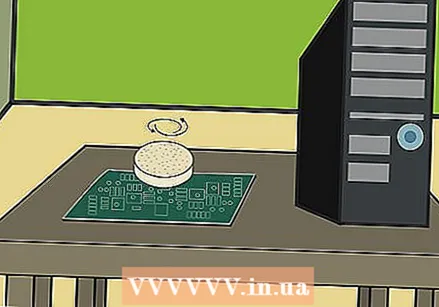 Run the cotton swab over the dirt to loosen it. Look for deposits near heat generators and on top of circuit paths. Lightly run the cotton swab over any dirt deposits you find until it comes off.
Run the cotton swab over the dirt to loosen it. Look for deposits near heat generators and on top of circuit paths. Lightly run the cotton swab over any dirt deposits you find until it comes off. - Work with patience rather than force. If you've been working on the dirt for a while and can't get it off, stop applying pressure. You should now just switch to using baking soda.
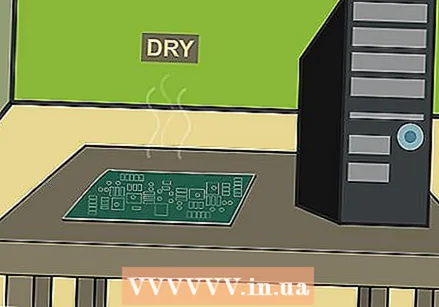 Let the alcohol dry. Wait for the alcohol to dry. This will take no more than an hour, usually much less. In the meantime, you can continue to brush on particularly tricky dirt areas to try to get them off.
Let the alcohol dry. Wait for the alcohol to dry. This will take no more than an hour, usually much less. In the meantime, you can continue to brush on particularly tricky dirt areas to try to get them off. - Alcohol dries up much faster than water.
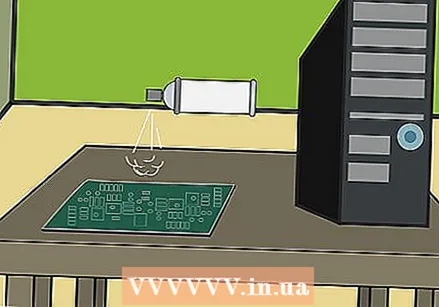 Use compressed air to blow out the loosened dirt. Hold the can upright and the mouthpiece a few inches from the circuit board. Spray in short bursts on and around the areas you just cleaned.
Use compressed air to blow out the loosened dirt. Hold the can upright and the mouthpiece a few inches from the circuit board. Spray in short bursts on and around the areas you just cleaned. - If you see rust from batteries or stubborn dirt that won't come off, you probably need to use baking soda to remove it.
Part 3 of 3: Removing bad rust
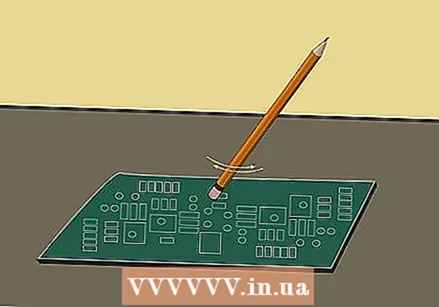 Try to rub away the rust lightly with a pencil eraser. If your circuit board has bad rust that you didn't get clean, you can try rubbing it off lightly with a pencil eraser.
Try to rub away the rust lightly with a pencil eraser. If your circuit board has bad rust that you didn't get clean, you can try rubbing it off lightly with a pencil eraser. - This is a good temporary solution so you don't have to use baking soda as it can cause damage to the circuit board if not used carefully.
- The eraser method is also very useful for cleaning printed circuit boards with copper components.
 Mix baking soda and water together and apply to rusty areas. Mix baking soda and a little bit of water in a small bowl until you have a liquid paste. Then dip a cotton swab in the mixture and gently apply it to the rusty parts of the circuit board, until they are completely covered.
Mix baking soda and water together and apply to rusty areas. Mix baking soda and a little bit of water in a small bowl until you have a liquid paste. Then dip a cotton swab in the mixture and gently apply it to the rusty parts of the circuit board, until they are completely covered. - The cotton swab should be nearly dripping so that as much of the mixture as possible soaks into the rusty areas.
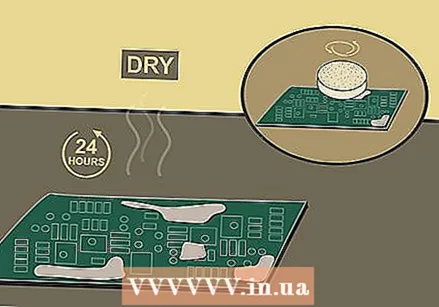 Let the paste dry for a day and then remove the rust. Wait for the paste to dry completely on the PCB, which usually takes about 24 hours. Then moisten a cotton swab with isopropyl alcohol (90% - 100% alcohol) and squeeze out the excess moisture. Use the damp cotton swab to lightly remove the dried paste and rust. Be patient and don't use too much force.
Let the paste dry for a day and then remove the rust. Wait for the paste to dry completely on the PCB, which usually takes about 24 hours. Then moisten a cotton swab with isopropyl alcohol (90% - 100% alcohol) and squeeze out the excess moisture. Use the damp cotton swab to lightly remove the dried paste and rust. Be patient and don't use too much force. 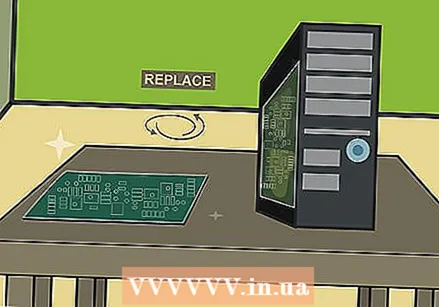 Replace the battery that caused the rust. Rust is usually caused by acid leaking from a battery located near the circuit board. You should be able to find the leaking battery quite easily as it will also be full of rust. Remove the battery with rubber gloves, remove any rust left by the battery in the battery well and insert the replacement battery.
Replace the battery that caused the rust. Rust is usually caused by acid leaking from a battery located near the circuit board. You should be able to find the leaking battery quite easily as it will also be full of rust. Remove the battery with rubber gloves, remove any rust left by the battery in the battery well and insert the replacement battery. - You can recycle your old battery by taking it to an electronics store or recycling center, or by sending it to a specialized recycling service.
- The information you need to find a replacement battery can usually be found in your computer's documentation and on the battery itself.
- If you can't find the information you need to replace the battery, you can put the battery in a bag and take it to an electronics store for identification.



