Author:
Tamara Smith
Date Of Creation:
25 January 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- To step
- Method 1 of 4: The area of a regular hexagon with a given side
- Method 2 of 4: The area of a regular hexagon with a known apothem
- Method 3 of 4: Calculate the area of an irregular hexagon with given vertices
- Method 4 of 4: Other Methods for Calculating the Area of a Hexagon
A hexagon or hexagon is a polygon with six sides and corners. A regular hexagon has six equal sides and angles and is made up of six equilateral triangles. There are a number of ways to calculate the area of an irregular or regular hexagon. If you want to know how, follow these steps.
To step
Method 1 of 4: The area of a regular hexagon with a given side
 Write down the formula for calculating the area of a hexagon if you know the length of one side. Because a regular hexagon consists of six equilateral triangles, the formula for finding the area of a hexagon is derived from the formula for calculating the area of an equilateral triangle. The formula for this is: Area = (3√3 s) / 2 where "s" is the length of one side of the regular hexagon.
Write down the formula for calculating the area of a hexagon if you know the length of one side. Because a regular hexagon consists of six equilateral triangles, the formula for finding the area of a hexagon is derived from the formula for calculating the area of an equilateral triangle. The formula for this is: Area = (3√3 s) / 2 where "s" is the length of one side of the regular hexagon. 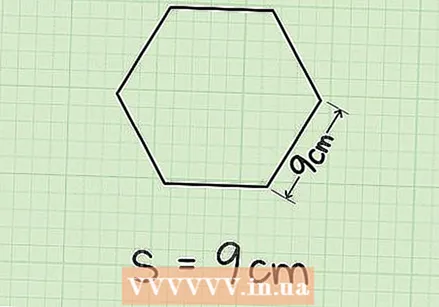 Determine the length of the side. If you already know the length, write it down. In this case, the length of one side is 9 cm. If you don't know the length but you know how long the circumference is, or you know the apothem (the length of the line from the center of the hexagon that is perpendicular to one side), you can still get the length of the side of calculate a hexagon. You can read how to do that here:
Determine the length of the side. If you already know the length, write it down. In this case, the length of one side is 9 cm. If you don't know the length but you know how long the circumference is, or you know the apothem (the length of the line from the center of the hexagon that is perpendicular to one side), you can still get the length of the side of calculate a hexagon. You can read how to do that here: - If you know the circumference, divide it by 6 to get the length of one side. For example: the length of the circumference is 54 cm; divide this by 6 and you get 9 cm for the length of the side.
- If you only know the apothem, you can find the length of a side by entering the value of the apothem in the formula a = x√3 and multiplying the answer by 2. This is true because the apothem is the side of a 30-60-90 triangle. For example, if the apothem is 10√3, then x equals 10 and the length of one side is 10 x 2 = 20.
- If you know the circumference, divide it by 6 to get the length of one side. For example: the length of the circumference is 54 cm; divide this by 6 and you get 9 cm for the length of the side.
 Enter the length of the side in the formula. Since you know that the length of one side of the triangle is 9, you can just enter it in the original formula. It looks like this: Area = (3√3 x 9) / 2
Enter the length of the side in the formula. Since you know that the length of one side of the triangle is 9, you can just enter it in the original formula. It looks like this: Area = (3√3 x 9) / 2  Simplify your answer. Find the value of the equation and write down your answer. Remember, since you are calculating the area, the answer must be in square meters. You can read how to do this here
Simplify your answer. Find the value of the equation and write down your answer. Remember, since you are calculating the area, the answer must be in square meters. You can read how to do this here - (3√3 x 9) / 2 =
- (3√3 x 81) / 2 =
- (243√3)/2 =
- 420.8/2 =
- 210.4 cm
Method 2 of 4: The area of a regular hexagon with a known apothem
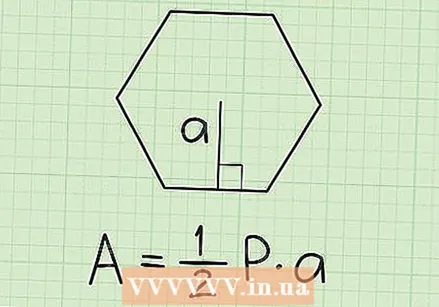 Write down the formula for calculating the area of a hexagon with a given apothem. The formula is simple: Area = 1/2 * circumference * apothem.
Write down the formula for calculating the area of a hexagon with a given apothem. The formula is simple: Area = 1/2 * circumference * apothem.  Write down the apothem. Suppose the apothem is 5√3 cm.
Write down the apothem. Suppose the apothem is 5√3 cm. 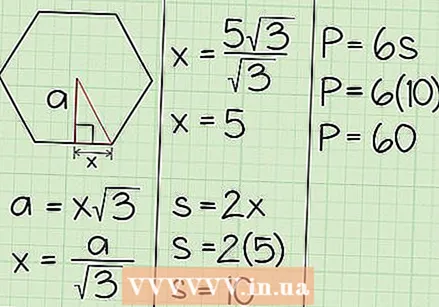 Use the apothem to find the outline. Since the apothem is perpendicular to the side of the hexagon, it forms one side of a 30-60-90 triangle. The sides of a 30-60-90 triangle have the ratio: xx√3-2x, where x is the length of the shortest side (opposite the 30 degree angle), x√3 is the length of the long side (opposite the angle of 60 degrees), and 2x the hypotenuse.
Use the apothem to find the outline. Since the apothem is perpendicular to the side of the hexagon, it forms one side of a 30-60-90 triangle. The sides of a 30-60-90 triangle have the ratio: xx√3-2x, where x is the length of the shortest side (opposite the 30 degree angle), x√3 is the length of the long side (opposite the angle of 60 degrees), and 2x the hypotenuse. - The apothem is the side x√3. That is why you can enter this value in the formula a = x√3. For example, if the length of the apothem is 5√3, then the formula holds: 5√3 cm = x√3, or x = 5 cm.
- By solving x you found the length of the short side of the triangle, x = 5. Since that is half the length of one side of the hexagon, you can multiply this by 2 to get the full length of the side to get. 5 cm x 2 = 10 cm.
- Now that you know that the full length of one side equals 10, all you have to do is multiply it by 6 to get the hexagon's perimeter. 10 cm x 6 = 60 cm
 Enter all known values in the formula. Calculating the circumference was the hardest part. Now all you have to do is solve for the apothem and the perimeter using the formula:
Enter all known values in the formula. Calculating the circumference was the hardest part. Now all you have to do is solve for the apothem and the perimeter using the formula: - Area = 1/2 x circumference x apothem
- Area = 1/2 x 60 cm x 5√3 cm
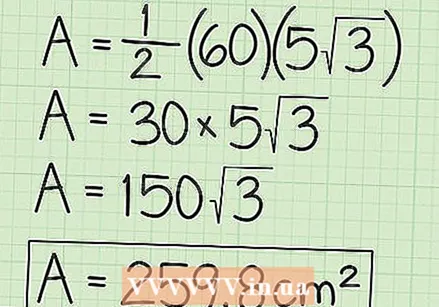 Simplify your answer. Simplify the expression until you have removed all roots from the equation. Make sure your final answer is in square meters.
Simplify your answer. Simplify the expression until you have removed all roots from the equation. Make sure your final answer is in square meters. - 1/2 x 60 cm x 5√3 cm =
- 30 x 5√3 cm =
- 150√3 cm =
- 259.8 cm
Method 3 of 4: Calculate the area of an irregular hexagon with given vertices
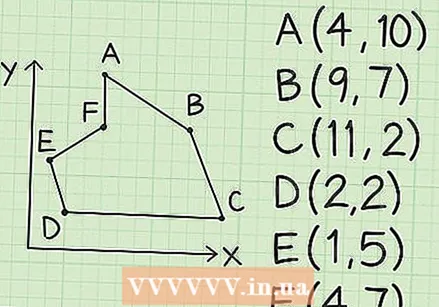 List the x and y coordinates of all vertices. If you know the vertices of the hexagon, the first thing to do is create a table with two columns and seven rows. Each row is named after the six points (Point A, Point B, Point C, etc) and each column is named after the x or y coordinates of those points. List the x and y coordinates from Point A to Point F. Repeat the coordinates from Point A at the end of the list. Let's take the following example, in the format Name: (x, y):
List the x and y coordinates of all vertices. If you know the vertices of the hexagon, the first thing to do is create a table with two columns and seven rows. Each row is named after the six points (Point A, Point B, Point C, etc) and each column is named after the x or y coordinates of those points. List the x and y coordinates from Point A to Point F. Repeat the coordinates from Point A at the end of the list. Let's take the following example, in the format Name: (x, y): - A: (4, 10)
- B: (9, 7)
- C: (11, 2)
- D: (2, 2)
- E: (1,5)
- F: (4, 7)
- A (again): (4, 10)
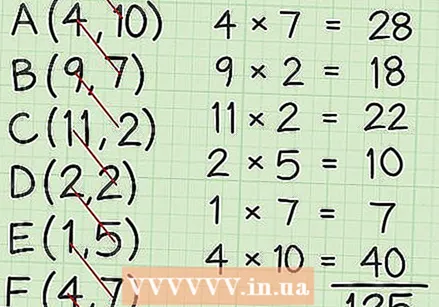 Multiply the x coordinate of each point by the y coordinate of the next point. Place the results to the right of the table. Then add up the results.
Multiply the x coordinate of each point by the y coordinate of the next point. Place the results to the right of the table. Then add up the results. - 4 x 7 = 28
- 9 x 2 = 18
- 11 x 2 = 22
- 2 x 5 = 10
- 1 x 7 = 7
- 4 x 10 = 40
- 28 + 18 + 22 + 10 + 7 + 40 = 125
 Multiply the y coordinate of each point by the x coordinate of the next point. Add up the results.
Multiply the y coordinate of each point by the x coordinate of the next point. Add up the results. - 10 x 9 = 90
- 7 x 11 = 77
- 2 x 2 = 4
- 2 x 1 = 2
- 5 x 4 = 20
- 7 x 4 = 28
- 90 + 77 + 4 + 2 + 20 + 28 = 221
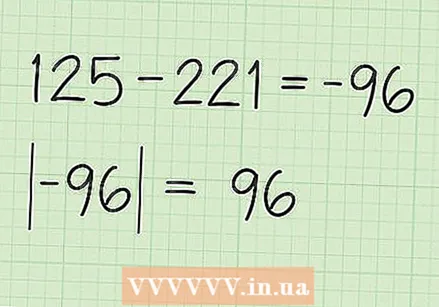 Subtract the second sum from the first sum. Subtract 221 from 125.125-221 = -96. Now take the absolute value of this answer: 96. Area can only be positive.
Subtract the second sum from the first sum. Subtract 221 from 125.125-221 = -96. Now take the absolute value of this answer: 96. Area can only be positive. 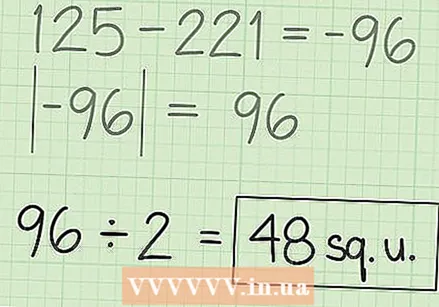 Divide the calculated difference by two. Dividing 96 by 2 gives you the area of the irregular hexagon. 96/2 = 48. Remember that the unit of your answer is the square meter. So the answer to the question is 48 m.
Divide the calculated difference by two. Dividing 96 by 2 gives you the area of the irregular hexagon. 96/2 = 48. Remember that the unit of your answer is the square meter. So the answer to the question is 48 m.
Method 4 of 4: Other Methods for Calculating the Area of a Hexagon
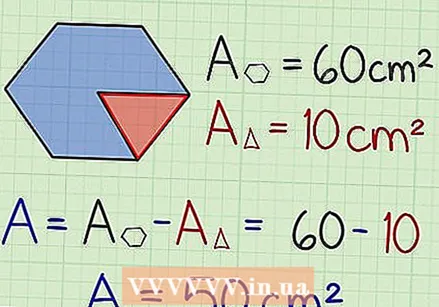 Finding the area of a hexagon where a vertex is unknown. If you know that you are dealing with a regular hexagon with missing triangles, the first thing to do is calculate the area, as if the hexagon is complete. Then simply calculate the area of the triangles formed by the vertices and subtract it from the total area. This returns the area of the irregular hexagon.
Finding the area of a hexagon where a vertex is unknown. If you know that you are dealing with a regular hexagon with missing triangles, the first thing to do is calculate the area, as if the hexagon is complete. Then simply calculate the area of the triangles formed by the vertices and subtract it from the total area. This returns the area of the irregular hexagon. - An example: If you calculated that the area of the regular hexagon is 60 cm and you know that the area of the missing triangles is 10 cm, then the area of the irregular hexagon is: 60 cm - 10 cm = 50 cm.
- If you know that the hexagon is missing exactly one triangle, it is also possible to find the area of the irregular hexagon by multiplying the area of the regular hexagon or the total area by 5/6, because the irregular hexagon occupies an area that exists. out of 5 of the 6 triangles of the regular hexagon. If two are missing, multiply by 4/6, and so on.
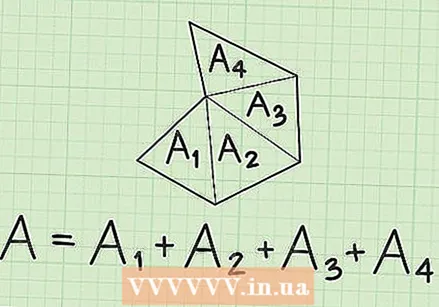 Break an irregular hexagon into other triangles. The irregular hexagon may be made up of four triangles of unequal shape. To find the whole area of this hexagon you have to find the area of each individual triangle and then add them together. There are several ways to find the area of a triangle, depending on what you know.
Break an irregular hexagon into other triangles. The irregular hexagon may be made up of four triangles of unequal shape. To find the whole area of this hexagon you have to find the area of each individual triangle and then add them together. There are several ways to find the area of a triangle, depending on what you know. 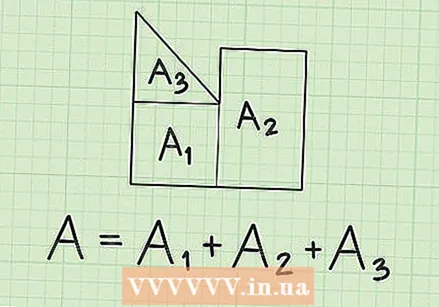 Look for other shapes in the irregular hexagon. If you can't find triangles, see if you can find other shapes - maybe a square or a rectangle. When you have discovered the other shapes, add the areas together to find the whole hexagon.
Look for other shapes in the irregular hexagon. If you can't find triangles, see if you can find other shapes - maybe a square or a rectangle. When you have discovered the other shapes, add the areas together to find the whole hexagon. - One type of irregular hexagon consists of two parallelograms. To calculate their areas, multiply the base times the height, just like a rectangle, and then add their areas.