Author:
Joan Hall
Date Of Creation:
2 July 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Part 1 of 3: Growing Basil from Seeds
- Part 2 of 3: Taking care of your basil
- Part 3 of 3: Collecting Basil Leaves
- Tips
- What do you need
Basil is a popular aromatic herb that is widely used in cooking. There are over 100 varieties of basil with slightly different flavors, from sweet Italian to Thai spicy basil. Most species grow well in outdoor gardens, and with a little tweak, you can grow basil indoors without much hassle. As long as you provide the basil with enough sunlight and water, it will grow well just about anywhere.
Steps
Part 1 of 3: Growing Basil from Seeds
 1 Purchase basil seeds from a safe place. Visit your gardening store or plant nursery and select the seed variety that suits you, or order them online. Often bags of more than a hundred seeds are sold at a very low price.
1 Purchase basil seeds from a safe place. Visit your gardening store or plant nursery and select the seed variety that suits you, or order them online. Often bags of more than a hundred seeds are sold at a very low price. - If you are ordering seeds online, visit several sites and select the best seeds.
 2 Use coarse, well-drained soil for planting seeds. Basil requires a nutrient-rich soil that allows water to pass through to grow properly. This soil can be purchased at a garden supply store or ordered online.
2 Use coarse, well-drained soil for planting seeds. Basil requires a nutrient-rich soil that allows water to pass through to grow properly. This soil can be purchased at a garden supply store or ordered online.  3 Fill the pot with soil about ¾. You can use a clay, plastic, stone, or concrete pot with sufficient drainage. Spray the soil lightly with water from a spray bottle before pouring it into the pot to keep it dry, otherwise it will then expand when watering and fill the entire pot.
3 Fill the pot with soil about ¾. You can use a clay, plastic, stone, or concrete pot with sufficient drainage. Spray the soil lightly with water from a spray bottle before pouring it into the pot to keep it dry, otherwise it will then expand when watering and fill the entire pot. - Regardless of the material of the pot, there should be drainage holes in the bottom of the pot. This is necessary for the normal drainage of excess water and plant health. Remember to place the pot on a pallet so that the water from the drainage holes does not flood everything around.
- Many people use clay pots or plastic seedling trays.
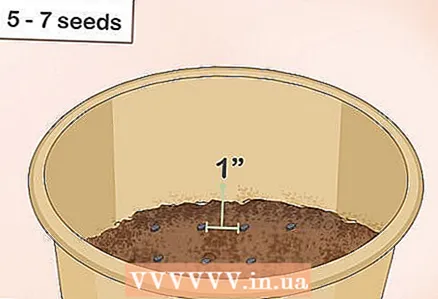 4 Scatter seeds over the soil. If you are using a small seedling tray, plant three seeds in each cell. If you have a larger pot, place 5-7 seeds on the ground at about the same distance from each other.
4 Scatter seeds over the soil. If you are using a small seedling tray, plant three seeds in each cell. If you have a larger pot, place 5-7 seeds on the ground at about the same distance from each other. - More than one seed should be planted in each cell in case some of them do not sprout.
- Place the seeds 2–3 centimeters apart.
- There is no need to press the seeds into the soil.
 5 Sprinkle the seeds lightly with dry soil. Do not add a lot of soil - a layer about five millimeters thick will be enough to cover the seeds. This layer of soil will protect the seeds and at the same time will not interfere with their growth.
5 Sprinkle the seeds lightly with dry soil. Do not add a lot of soil - a layer about five millimeters thick will be enough to cover the seeds. This layer of soil will protect the seeds and at the same time will not interfere with their growth. - Do not compact the soil after pouring it into the pot.
 6 Pour the soil with a spray bottle. Lightly spray the soil (especially the added top coat) with water from a spray bottle. If you do not have such a bottle, wet your hands under the tap or in a cup of water and sprinkle it on the ground.
6 Pour the soil with a spray bottle. Lightly spray the soil (especially the added top coat) with water from a spray bottle. If you do not have such a bottle, wet your hands under the tap or in a cup of water and sprinkle it on the ground. - Place the pot or tray on a drip tray to collect any water that runs out.
- You can cover the pot or tray with plastic wrap to trap moisture.
 7 Place the pot in a well-lit indoor area. Basil requires a lot of sunlight and needs to be in the sun for at least six hours a day to grow properly. It is best to place the basil pot by a warm, sunlit window.
7 Place the pot in a well-lit indoor area. Basil requires a lot of sunlight and needs to be in the sun for at least six hours a day to grow properly. It is best to place the basil pot by a warm, sunlit window. - Be careful if you plan to place the pot directly on the windowsill. Basil can overheat or freeze more quickly near a window pane than elsewhere.
- If you live in the Northern Hemisphere, it is best to place the basil by the southern window. If your home does not have an area with at least six hours of sunshine a day, consider using an additional light source.
 8 After 5-10 days, watch how the seeds germinate. The exact germination time of seeds depends on the amount of sunlight, soil temperature and humidity. Be patient and keep the soil moist and warm.
8 After 5-10 days, watch how the seeds germinate. The exact germination time of seeds depends on the amount of sunlight, soil temperature and humidity. Be patient and keep the soil moist and warm.
Part 2 of 3: Taking care of your basil
 1 Water the basil twice a week to keep it hydrated. When doing this, pour water onto the soil at the base of the stem, not the leaves or stem. In this case, the roots will absorb moisture normally, and you will not get the leaves wet.
1 Water the basil twice a week to keep it hydrated. When doing this, pour water onto the soil at the base of the stem, not the leaves or stem. In this case, the roots will absorb moisture normally, and you will not get the leaves wet. - To check the moisture content of the soil, immerse your finger in it about 2–3 centimeters. If the soil is dry even at this depth, lightly water the plant.
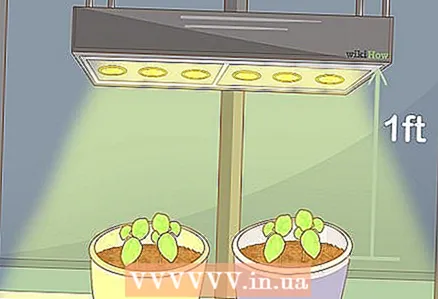 2 Use an artificial light source if necessary. If you are unable to provide enough sunlight for the basil, use fluorescent plant lamps or special high intensity lamps. If the basil does not receive natural sunlight, it should be illuminated with lamps for 10-12 hours a day.
2 Use an artificial light source if necessary. If you are unable to provide enough sunlight for the basil, use fluorescent plant lamps or special high intensity lamps. If the basil does not receive natural sunlight, it should be illuminated with lamps for 10-12 hours a day. - Place standard fluorescent lights about five centimeters away, and more powerful or compact fluorescent lights about 30 centimeters from the tops of the plants.
- High intensity lamps should be placed 60-120 centimeters above the plants.
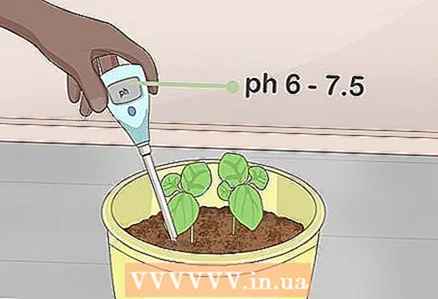 3 Check the soil pH level once a month. A suitable pH is usually 6.0-7.5. If necessary, keep it within this interval with fertilizers, which can be purchased at a garden supply store or ordered online. Just add organic fertilizer to the soil and check the pH level with test strips.
3 Check the soil pH level once a month. A suitable pH is usually 6.0-7.5. If necessary, keep it within this interval with fertilizers, which can be purchased at a garden supply store or ordered online. Just add organic fertilizer to the soil and check the pH level with test strips. - Since basil is used primarily for culinary purposes, many inorganic fertilizers can pose a potential hazard.
 4 Turn on the fan to simulate natural conditions. Direct an electric fan at the plants and blow on the leaves for at least two hours a day. Thus, you imitate a fresh breeze, and air will not stagnate around the plants.
4 Turn on the fan to simulate natural conditions. Direct an electric fan at the plants and blow on the leaves for at least two hours a day. Thus, you imitate a fresh breeze, and air will not stagnate around the plants. - Set the fan to the slowest setting.
 5 Thin the plants after two pairs of leaves appear on the seedlings. So that the basil is not crowded, the distance between individual plants should be 15-30 centimeters. To thin out the basil, pluck out excess plants at soil level or pull them out with the root.
5 Thin the plants after two pairs of leaves appear on the seedlings. So that the basil is not crowded, the distance between individual plants should be 15-30 centimeters. To thin out the basil, pluck out excess plants at soil level or pull them out with the root. - Gently break the soil around the base of the shoot with your fingers, an ice cream stick or tongue spatula.
- Insert a stick under the developing roots or gently "loosen" the shoot and pull it out of the ground along with the exposed roots.
- The shoot taken out of the ground can be transplanted into another or the same pot at a distance of 15-30 centimeters from other plants.
 6 Remove the tops after the shoots are 15 centimeters tall. When the plant has three groups of leaves, it can be pruned. Take sharp scissors and cut the stem just above the top leaves.
6 Remove the tops after the shoots are 15 centimeters tall. When the plant has three groups of leaves, it can be pruned. Take sharp scissors and cut the stem just above the top leaves. - Removing the top will stimulate the growth of the leaves, as a result, the basil will not grow with long and thin stems.
- Prune basil once every two weeks. In doing so, remove weak, stunted and damaged leaves. The cut leaves can be eaten.
 7 Water the plant if it starts to wilt. Withering is usually a sign that the basil is running out of water. In this case, water the soil and wait until the water is completely absorbed before adding it. It is also advisable to move the plant away from sunlight for several hours so that it moves away.
7 Water the plant if it starts to wilt. Withering is usually a sign that the basil is running out of water. In this case, water the soil and wait until the water is completely absorbed before adding it. It is also advisable to move the plant away from sunlight for several hours so that it moves away. - After you water the plant and remove it from sunlight, it should look healthier in about 4 hours.
- If you find dead leaves, cut them off with clean garden shears.
Part 3 of 3: Collecting Basil Leaves
 1 Harvest before flowering. At this time, the leaves are the freshest and largest. If the basil has bloomed, remove the flowers to re-channel all the energy into the growth of the leaves.
1 Harvest before flowering. At this time, the leaves are the freshest and largest. If the basil has bloomed, remove the flowers to re-channel all the energy into the growth of the leaves. - Basil flowers are clearly visible and you can easily find that the plants have bloomed.
 2 Tear off individual leaves if you need some basil. You can pinch off the leaves with your fingers or cut them off with sharp scissors. If you pick only a few leaves, you will not harm the plant in any way.
2 Tear off individual leaves if you need some basil. You can pinch off the leaves with your fingers or cut them off with sharp scissors. If you pick only a few leaves, you will not harm the plant in any way. - Try not to pick off more than a third of the leaves, unless you harvest all of them. This will help the basil store energy for further growth.
 3 To keep the plants thicker, cut the stems just above where the two large leaves emerge. In this case, more leaves will grow on the basil. Trim the stems above the leaves to stimulate further growth and the plants will live longer.
3 To keep the plants thicker, cut the stems just above where the two large leaves emerge. In this case, more leaves will grow on the basil. Trim the stems above the leaves to stimulate further growth and the plants will live longer. - If you cut the stem under a pair of leaves, it may stop growing further.
Tips
- Rotate the basil pot or tray as it grows so the plants don't tilt in one direction.
- If you covered the pot with plastic wrap after planting the seeds, remove it after the sprouts emerge from the soil.
What do you need
- Basil seeds
- Fertile soil
- Pot or Tray
- Spray bottle
- Scissors
- Artificial lighting (if necessary)
- Electric fan
- PH test strips