Author:
Ellen Moore
Date Of Creation:
14 January 2021
Update Date:
27 June 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 4: Calculate Frequency from Wavelength and Velocity
- Method 2 of 4: Frequency of Electromagnetic Waves in a Vacuum
- Method 3 of 4: Calculate Frequency over Time
- Method 4 of 4: Calculate Frequency from Angular Frequency
- What do you need
Frequency (or frequency of a wave) is the number of complete oscillations or cycles of a wave performed per unit of time. There are several different ways to calculate the frequency, depending on the information given to you.
Steps
Method 1 of 4: Calculate Frequency from Wavelength and Velocity
 1 Formula:f = V / λ
1 Formula:f = V / λ- where f is the frequency, V is the wave speed, λ is the wavelength.
- Example: Calculate the frequency of a sound wave if the wavelength is 322 nm and the speed of sound is 320 m / s.
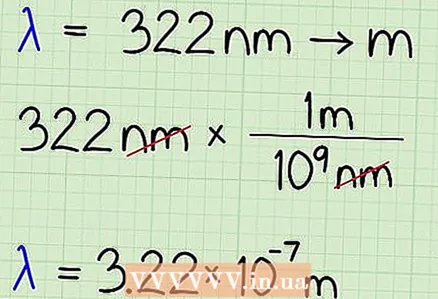 2 Convert wavelength units to meters (if necessary). If the wavelength is given in nanometers, you need to convert that value to meters by dividing by the number of nanometers in one meter.
2 Convert wavelength units to meters (if necessary). If the wavelength is given in nanometers, you need to convert that value to meters by dividing by the number of nanometers in one meter. - Note that when working with very small or very large numbers, it is best to write them in exponential format. In this article, numbers will be given in both regular and exponential formats.
- Example: λ = 322 nm
- 322 nm x (1 m / 10 ^ 9 nm) = 3.22 x 10 ^ -7 m = 0.000000322 m
 3 Divide the speed of the wave by its length. To calculate the frequency (f), divide the speed of the wave (V) by its length (λ), expressed in meters.
3 Divide the speed of the wave by its length. To calculate the frequency (f), divide the speed of the wave (V) by its length (λ), expressed in meters. - Example: f = V / λ = 320 / 0.000000322 = 993788819.88 = 9.94 x 10 ^ 8
 4 Write down your answer. Next, put the unit of frequency measurement - Hertz (Hz).
4 Write down your answer. Next, put the unit of frequency measurement - Hertz (Hz). - Example: The frequency of this wave is 9.94 x 10 ^ 8 Hz.
Method 2 of 4: Frequency of Electromagnetic Waves in a Vacuum
 1 Formula:f = C / λ... The formula for calculating the frequency of a wave in a vacuum is almost identical to the formula for calculating the frequency of a wave in media. In a vacuum, there are no factors affecting the speed of a wave, therefore, the formula uses a constant value of the speed of light, with which electromagnetic waves propagate in a vacuum.
1 Formula:f = C / λ... The formula for calculating the frequency of a wave in a vacuum is almost identical to the formula for calculating the frequency of a wave in media. In a vacuum, there are no factors affecting the speed of a wave, therefore, the formula uses a constant value of the speed of light, with which electromagnetic waves propagate in a vacuum. - In the formula, f is the frequency, C is the speed of light, λ is the wavelength.
- Example: Calculate the frequency of an electromagnetic wave if its length is 573 nm.
 2 Convert wavelength units to meters (if necessary). If the wavelength is given in nanometers, you need to convert that value to meters by dividing by the number of nanometers in one meter.
2 Convert wavelength units to meters (if necessary). If the wavelength is given in nanometers, you need to convert that value to meters by dividing by the number of nanometers in one meter. - Note that when working with very small or very large numbers, it is best to write them in exponential format. In this article, numbers will be given in both regular and exponential formats.
- Example: λ = 573 nm
- 573 nm x (1 m / 10 ^ 9 nm) = 5.73 x 10 ^ -7 m = 0.000000573
 3 Divide the speed of light by the wavelength. The speed of light is constant, which is 3.00 x 10 ^ 8 m / s. Divide this value by the wavelength (in meters).
3 Divide the speed of light by the wavelength. The speed of light is constant, which is 3.00 x 10 ^ 8 m / s. Divide this value by the wavelength (in meters). - Example: f = C / λ = 3.00 x 10 ^ 8 / 5.73 x 10 ^ -7 = 5.24 x 10 ^ 14
 4 Write down your answer. Next, put the unit of measurement for frequency - Hertz (Hz).
4 Write down your answer. Next, put the unit of measurement for frequency - Hertz (Hz). - Example: The frequency of this wave is 5.24 x 10 ^ 14 Hz.
Method 3 of 4: Calculate Frequency over Time
 1 Formula:f = 1 / T... Frequency is inversely proportional to the time it takes to complete one waveform.
1 Formula:f = 1 / T... Frequency is inversely proportional to the time it takes to complete one waveform. - In the formula, f is the frequency, T is the time it takes to complete one wave oscillation.
- Example A: Calculate the frequency of a wave if it needs 0.32 s to make one swing.
- Example B: In 0.57 seconds, the wave makes 15 oscillations. Calculate the frequency of this wave.
 2 Divide the number of hesitations by the time. If the problem gives the time spent on 1 oscillation, then in this case, simply divide 1 by the time (T). If the problem gives the time spent on several oscillations, then in this case divide the given number of oscillations (n) by the time (T).
2 Divide the number of hesitations by the time. If the problem gives the time spent on 1 oscillation, then in this case, simply divide 1 by the time (T). If the problem gives the time spent on several oscillations, then in this case divide the given number of oscillations (n) by the time (T). - Example A: f = 1 / T = 1 / 0.32 = 3.125
- Example B: f = n / T = 15 / 0.57 = 26.316
 3 Write down your answer. Next, put the unit of frequency measurement - Hertz (Hz).
3 Write down your answer. Next, put the unit of frequency measurement - Hertz (Hz). - Example A: The wave frequency is 3.125 Hz.
- Example B: The wave frequency is 26.316 Hz.
Method 4 of 4: Calculate Frequency from Angular Frequency
 1 Formula:f = ω / (2π)
1 Formula:f = ω / (2π)- where f is the frequency, ω is the angular frequency, π is the pi number (mathematical constant).
- Example: A wave rotates at an angular frequency of 7.17 radians per second. Calculate the frequency of this wave.
 2 Multiply Pi by two.
2 Multiply Pi by two.- Example: 2 * π = 2 * 3.14 = 6.28
 3 Divide the angular frequency (in radians per second) by twice pi (6.28).
3 Divide the angular frequency (in radians per second) by twice pi (6.28).- Example: f = ω / (2π) = 7.17 / (2 * 3.14) = 7.17 / 6.28 = 1.14
 4 Write down your answer. Next, put the unit of measurement for frequency - Hertz (Hz).
4 Write down your answer. Next, put the unit of measurement for frequency - Hertz (Hz). - Example: The wave frequency is 1.14 Hz.
What do you need
- Calculator
- Pencil
- Paper