Author:
Sara Rhodes
Date Of Creation:
14 February 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 4: Treating the bite site
- Method 2 of 4: How to Treat a Tick Bite
- Method 3 of 4: How to prevent insect bites
- Method 4 of 4: Knowing What to Do
- Tips
Bites of all insects (mosquitoes, midges, horseflies, fleas, ticks, bedbugs) are unpleasant. Although the bite itself may be very small, the itching and swelling from the bite can cause significant discomfort. There are many ways to combat these bite effects, with or without medication. Treatment will relieve pain and speed up healing.
Steps
Method 1 of 4: Treating the bite site
 1 Clean the bite site. Before starting treatment, you need to process the bite site. Wash the wound with warm soapy water. If there is swelling at the site of the bite, apply a cold compress or ice pack to the bite. The cold will temporarily relieve pain, swelling and itching.
1 Clean the bite site. Before starting treatment, you need to process the bite site. Wash the wound with warm soapy water. If there is swelling at the site of the bite, apply a cold compress or ice pack to the bite. The cold will temporarily relieve pain, swelling and itching. - Keep the compress for no more than 10 minutes at a time. After ten minutes, sit for another 10 minutes without a compress. Repeat for an hour.
 2 Do not scratch the bite site. Most likely, the bite site will itch and you will try to scratch it, but you should not do this. Try to endure this feeling. If you scratch the bite site, you can infect the wound.
2 Do not scratch the bite site. Most likely, the bite site will itch and you will try to scratch it, but you should not do this. Try to endure this feeling. If you scratch the bite site, you can infect the wound.  3 Apply an anti-itch cream or lotion to the bite. If the bite continues to itch, apply Calamine Lotion, a topical antihistamine, or corticosteroid cream to the wound. All of these products are available over the counter at the pharmacy. If you are not sure which remedy is right for you, talk to your pharmacist.
3 Apply an anti-itch cream or lotion to the bite. If the bite continues to itch, apply Calamine Lotion, a topical antihistamine, or corticosteroid cream to the wound. All of these products are available over the counter at the pharmacy. If you are not sure which remedy is right for you, talk to your pharmacist. 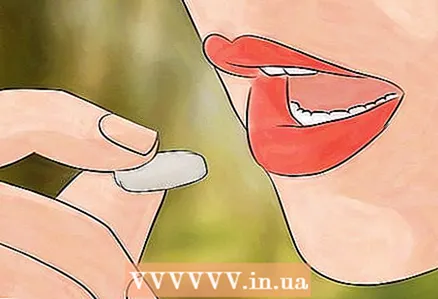 4 Take your medications. You can take paracetamol (Efferalgan), ibuprofen (Nurofen), antihistamines (Claritin) to relieve pain and itching.
4 Take your medications. You can take paracetamol (Efferalgan), ibuprofen (Nurofen), antihistamines (Claritin) to relieve pain and itching. - If you are already taking an allergy medication, you may not be able to combine it with other antihistamines. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you can increase your dosage or combine the drug with another.
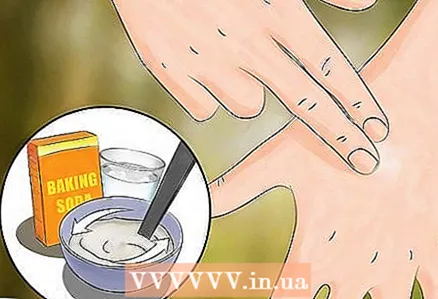 5 Make a baking soda paste. Mix a little water and baking soda to make a paste. Apply the paste to the bite site. This will temporarily relieve the itching. Wash off the paste after 15-20 minutes.
5 Make a baking soda paste. Mix a little water and baking soda to make a paste. Apply the paste to the bite site. This will temporarily relieve the itching. Wash off the paste after 15-20 minutes. - It is best to make a paste with three parts baking soda and one part water.
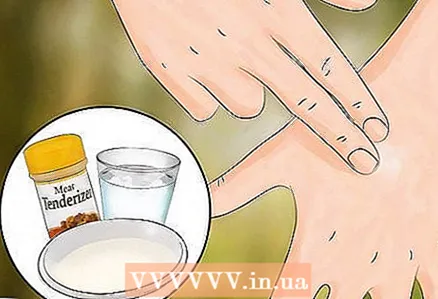 6 Try using a powder to soften the meat. Yes, meat powder! Mix the unspiced meat tenderizer powder with water to form a paste. Apply the paste to the bite to relieve itching. Wash off the paste after 15-20 minutes.
6 Try using a powder to soften the meat. Yes, meat powder! Mix the unspiced meat tenderizer powder with water to form a paste. Apply the paste to the bite to relieve itching. Wash off the paste after 15-20 minutes. 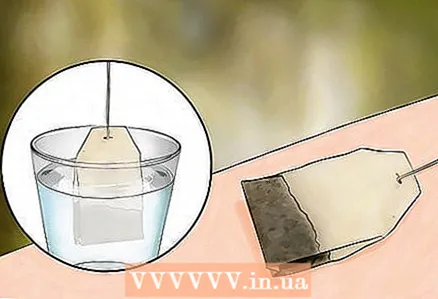 7 Try applying a wet tea bag to the bite. Brew a bag in warm water, hold it in water and attach it to the bite site. If you want to use the tea bag you have brewed for drinking, chill the tea bag first. Leave it on the skin for 15-20 minutes.
7 Try applying a wet tea bag to the bite. Brew a bag in warm water, hold it in water and attach it to the bite site. If you want to use the tea bag you have brewed for drinking, chill the tea bag first. Leave it on the skin for 15-20 minutes.  8 Chop up some fruits and vegetables. Certain fruits and vegetables contain enzymes that can reduce swelling and itchiness. Try the following foods:
8 Chop up some fruits and vegetables. Certain fruits and vegetables contain enzymes that can reduce swelling and itchiness. Try the following foods: - papaya - attach a piece for an hour;
- onion - rub the onion over the bite;
- garlic - crush the head of garlic and apply to the bite.
 9 Treat the bite with apple cider vinegar. Immediately after the bite (if possible), dip the bite in vinegar and hold for a few minutes. If the bite still itches, soak a cotton ball with vinegar, apply to the bite, and secure with tape.
9 Treat the bite with apple cider vinegar. Immediately after the bite (if possible), dip the bite in vinegar and hold for a few minutes. If the bite still itches, soak a cotton ball with vinegar, apply to the bite, and secure with tape.  10 Crush an acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) tablet. Crush the tablet in a spoon or mortar. Add a little water to make a gruel, and apply the gruel to the skin. You can leave the gruel on the skin (as is the case with Kalamin) and rinse off the next time you shower or bathe.
10 Crush an acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) tablet. Crush the tablet in a spoon or mortar. Add a little water to make a gruel, and apply the gruel to the skin. You can leave the gruel on the skin (as is the case with Kalamin) and rinse off the next time you shower or bathe.  11 Apply some tea tree oil to the bite. Apply a drop of tea tree oil to the bite every day. This will not relieve the itching, but it may reduce or relieve swelling.
11 Apply some tea tree oil to the bite. Apply a drop of tea tree oil to the bite every day. This will not relieve the itching, but it may reduce or relieve swelling. - Instead of tea tree oil, use 1-2 drops of lavender or peppermint oil. This will help fight the itching.
 12 Seek help from a homeopath. There are homeopathic remedies that deal effectively with stings. However, the type and dosage are selected individually. Contact a homeopath and ask for a prescription that is right for you.
12 Seek help from a homeopath. There are homeopathic remedies that deal effectively with stings. However, the type and dosage are selected individually. Contact a homeopath and ask for a prescription that is right for you.
Method 2 of 4: How to Treat a Tick Bite
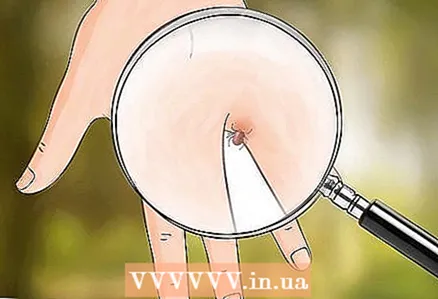 1 Look for ticks. The mites are very small and live outdoors. Unlike other insects, they don't just bite - they stick to the skin and continue to feed on human or animal blood. They like small areas of skin covered with hair: on the head, behind the ear, in the armpit, in the groin, between the fingers and toes. If you need to examine a person, start with these areas, but check the entire body just in case.
1 Look for ticks. The mites are very small and live outdoors. Unlike other insects, they don't just bite - they stick to the skin and continue to feed on human or animal blood. They like small areas of skin covered with hair: on the head, behind the ear, in the armpit, in the groin, between the fingers and toes. If you need to examine a person, start with these areas, but check the entire body just in case. 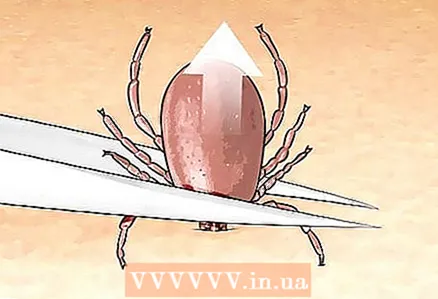 2 Remove the tick. The tick must be removed. A person who has been bitten by a tick will need the help of another person, especially if the tick is in a hard-to-reach place. Do not touch the tick with your bare hands.
2 Remove the tick. The tick must be removed. A person who has been bitten by a tick will need the help of another person, especially if the tick is in a hard-to-reach place. Do not touch the tick with your bare hands. - If you are alone, nervous, do not know what to do, or do not have the necessary tools, go to the clinic. If you do not have a severe allergic reaction to the bite, you do not need to call an ambulance.
- Use the forceps to grasp the head or mouth of the tick with the forceps.
- Keep the tick as close to the skin as possible.
- Do not press too hard with the forceps.
- Pull the tick up slowly and carefully. Don't turn your hand to the side.
- Do not use petroleum jelly, thinner, knife, or matches.
- If part of the tick remains in the wound, remove all residues.
- Do not discard the tick, even if a piece comes off.
 3 Save the tick. You will need to save the tick as it will need to be taken to a laboratory for analysis. Since ticks are carriers of borreliosis and can cause encephalitis, you should check the tick even if you have no symptoms. If the test is positive, you will need additional treatment.
3 Save the tick. You will need to save the tick as it will need to be taken to a laboratory for analysis. Since ticks are carriers of borreliosis and can cause encephalitis, you should check the tick even if you have no symptoms. If the test is positive, you will need additional treatment. - Place the tick in a zippered plastic bag or small container (such as a pill bottle).
- If the tick is still alive, store it in the refrigerator for up to 10 days.
- If the tick is dead, keep it in the freezer for up to 10 days.
- If it is not possible to donate a tick for analysis within 10 days, discard it. Even if you keep the tick in the refrigerator or freezer, after 10 days it will not be suitable for analysis.
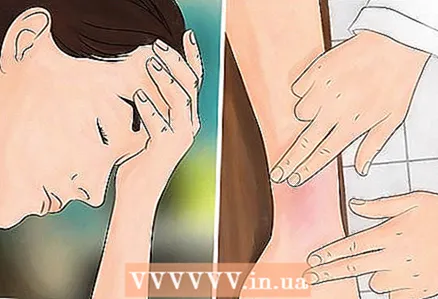 4 See a doctor. If the tick sits deep, or you were able to remove only part of the tick, you will need to see your doctor so that the tick can be removed. You will also need to see your doctor if you develop symptoms of borreliosis or encephalitis.
4 See a doctor. If the tick sits deep, or you were able to remove only part of the tick, you will need to see your doctor so that the tick can be removed. You will also need to see your doctor if you develop symptoms of borreliosis or encephalitis. - The most common symptom of borreliosis is a circular rash around the bite site.
- See your doctor if you experience any of the following: fatigue, chills or fever, headaches, cramps, weakness, numbness or tingling, swollen lymph nodes, rash.
- In more serious cases, cognitive impairment, disorders of the nervous system, arthritis, and changes in the heartbeat are possible.
 5 Rinse the bite site. Wash the bite with warm water and soap. Apply some antiseptic to the wound. You can use rubbing alcohol, hand sanitizer. Then wash your hands.
5 Rinse the bite site. Wash the bite with warm water and soap. Apply some antiseptic to the wound. You can use rubbing alcohol, hand sanitizer. Then wash your hands. 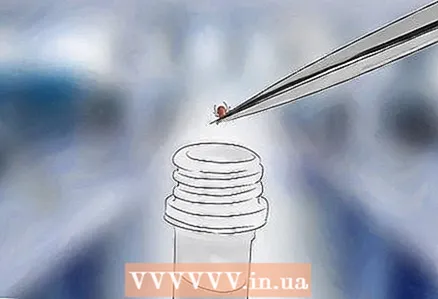 6 Take the tick for analysis. Usually analyzes are carried out in a special laboratory. Find out if there is such a laboratory in your city. The laboratory will check if the tick is infected. If the tick appears dangerous or suspicious, additional testing may be required.
6 Take the tick for analysis. Usually analyzes are carried out in a special laboratory. Find out if there is such a laboratory in your city. The laboratory will check if the tick is infected. If the tick appears dangerous or suspicious, additional testing may be required. - Perhaps in your city, this research is carried out by a center for hygiene and epidemiology.
- If your city does not have a laboratory where you can do the analysis, contact your local laboratory.
- If you develop symptoms and still have no test results, do not delay treatment. Remember that the test result can be false positive. Perhaps you were bitten by another tick and you didn't notice.
Method 3 of 4: How to prevent insect bites
 1 Do not use perfumed products. Some insects are attracted to certain smells or even the fact that they smell an unfamiliar smell. Do not use perfumes or scented skin lotions outside.
1 Do not use perfumed products. Some insects are attracted to certain smells or even the fact that they smell an unfamiliar smell. Do not use perfumes or scented skin lotions outside.  2 Use a repellent. Insect repellents come in spray and lotion form. Apply the insect repellent to your skin and clothing before going outside to prevent insects from settling on you. The spray is easier to cover all skin and clothing. The lotion is applied to the skin and is suitable for treating open areas.
2 Use a repellent. Insect repellents come in spray and lotion form. Apply the insect repellent to your skin and clothing before going outside to prevent insects from settling on you. The spray is easier to cover all skin and clothing. The lotion is applied to the skin and is suitable for treating open areas. - Read the instructions for use - it is possible that you cannot apply the product on the skin of the face. Do not apply repellent to the eye area.
- The most effective remedies are diethyltoluamide.
- If you've just applied sunscreen, wait at least 30 minutes.
 3 Wear protective clothing. You can wear not only long-sleeved clothes and pants, but also special items with protection against insects. There are special hats with a mesh that covers the face, neck and shoulders. If you know that there will be a lot of insects somewhere, this is the best option.
3 Wear protective clothing. You can wear not only long-sleeved clothes and pants, but also special items with protection against insects. There are special hats with a mesh that covers the face, neck and shoulders. If you know that there will be a lot of insects somewhere, this is the best option. - Try tucking your pants into your socks to prevent insects from biting your ankles.
 4 Get rid of standing water. Mosquitoes can grow in puddles, ditches, and any standing water. If there is standing water near your home, drain the area to keep mosquitoes out. If you are out in the countryside, avoid places with stagnant water.
4 Get rid of standing water. Mosquitoes can grow in puddles, ditches, and any standing water. If there is standing water near your home, drain the area to keep mosquitoes out. If you are out in the countryside, avoid places with stagnant water.  5 Use citronella candles. Candles with citronella, linalool and geraniol can repel insects, especially mosquitoes.Scientists have found that citronella can reduce the number of female mosquitoes in a certain area by 35%, linalool by 65%, and geraniol by 82%!
5 Use citronella candles. Candles with citronella, linalool and geraniol can repel insects, especially mosquitoes.Scientists have found that citronella can reduce the number of female mosquitoes in a certain area by 35%, linalool by 65%, and geraniol by 82%! - You can buy special citronella sachets that can be attached to clothing.
 6 Make an essential oil repellent. Certain essential oils repel insects. If you dilute the oil in water and apply it to your skin, insects will not land on you. Instead of a candle lamp, you can use a special diffuser.
6 Make an essential oil repellent. Certain essential oils repel insects. If you dilute the oil in water and apply it to your skin, insects will not land on you. Instead of a candle lamp, you can use a special diffuser. - The following oils are suitable: eucalyptus, cloves, citronella. You can use neem oil or cream, as well as camphor and menthol gels.
- If you choose to apply the mixture directly to your skin, be careful not to get the mixture in your eyes.
Method 4 of 4: Knowing What to Do
 1 Know the symptoms of an insect bite. In order to choose a treatment method, it is important to make sure that you are having an insect bite and not a reaction to some kind of toxic plant. Some symptoms are similar to those of other diseases, especially if you are allergic to a specific insect bite.
1 Know the symptoms of an insect bite. In order to choose a treatment method, it is important to make sure that you are having an insect bite and not a reaction to some kind of toxic plant. Some symptoms are similar to those of other diseases, especially if you are allergic to a specific insect bite. - The following symptoms are usually observed at or near the site of the bite: pain, swelling, redness, itching, warmth, rash, slight bleeding. You may have one, several, or even all of the symptoms. The reaction to insect bites is individual and depends on the insect.
- The following symptoms are more serious and may indicate a life-threatening allergic reaction: cough, sore throat, tightness in the throat or chest, trouble breathing, wheezing, nausea or vomiting, dizziness or loss of consciousness, sweating , anxiety, itching and rashes on other parts of the body.
 2 Know when to call an ambulance. If the person is bitten inside the mouth, nose, or throat, or if the person has a severe allergic reaction, call an ambulance at 103 (mobile) or 03 (landline), or take the person to the hospital as soon as possible. People with allergies may need the help of a doctor to breathe and medications to relieve symptoms (such as adrenaline, corticosteroids, etc.).
2 Know when to call an ambulance. If the person is bitten inside the mouth, nose, or throat, or if the person has a severe allergic reaction, call an ambulance at 103 (mobile) or 03 (landline), or take the person to the hospital as soon as possible. People with allergies may need the help of a doctor to breathe and medications to relieve symptoms (such as adrenaline, corticosteroids, etc.). - If a person who has been bitten by an insect knows that they are allergic to insect bites, they may have an epinephrine autoinjector with them. In this case, read the instructions and inject as soon as possible. Instructions can also be found on the EpiPen website.
- The person will still need to be taken to the doctor.
 3 Know when to see a doctor. If a person does not have a severe allergic reaction (or is bitten outside the respiratory tract), they may be fine for a while. If after a while the symptoms described below develop, he should see a doctor and start treatment.
3 Know when to see a doctor. If a person does not have a severe allergic reaction (or is bitten outside the respiratory tract), they may be fine for a while. If after a while the symptoms described below develop, he should see a doctor and start treatment. - If you scratch the bite and damage your skin, you can get an infection. The skin is the first barrier to bacteria.
- Signs of infection include persistent pain or itching and high fever.
- If an infection develops, the person will most likely need antibiotics.
Tips
- If you have been bitten by a flying insect (wasp or bee), you must first remove the sting from the wound. This can be done with forceps if your fingers are not working.
- If you can't swallow an allergy pill that will relieve the bite reaction, try crushing it and stirring it in a liquid. The liquid may taste strange, but you will be able to swallow the medicine.