Author:
Carl Weaver
Date Of Creation:
21 February 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Part 1 of 4: Preparing for Breeding Regular Guinea Pigs
- Part 2 of 4: Breeding a Selected Pair
- Part 3 of 4: Confirming Pregnancy and Assisting Childbirth
- Part 4 of 4: Handling Guinea Pigs Postpartum
- Tips
- Warnings
- What do you need
- Additional articles
If you are the owner of regular guinea pigs, you may wish to breed them for yourself or sell them to other guinea pig lovers. Breeding guinea pigs should not be taken lightly, as this activity can be risky and will require a lot of care and serious responsibility on your part. It is critical for successful breeding of guinea pigs to carefully select the correct female and male, and to provide them and their offspring with proper care.
Steps
Part 1 of 4: Preparing for Breeding Regular Guinea Pigs
 1 Be aware of the risks involved in breeding guinea pigs. Breeding guinea pigs carries significant risks, including the high mortality rate of pregnant females. Learn about the risks of breeding guinea pigs and consider whether you are making the right decision for yourself and your animals.
1 Be aware of the risks involved in breeding guinea pigs. Breeding guinea pigs carries significant risks, including the high mortality rate of pregnant females. Learn about the risks of breeding guinea pigs and consider whether you are making the right decision for yourself and your animals. - Never breed guinea pigs for fun. This activity is risky and can injure or even kill your beloved pet.
- The high mortality rate of pregnant female guinea pigs is associated with pregnancy ketosis, which is a metabolic problem when the female gradually becomes poisoned and subsequently dies of blood poisoning. Cubs of guinea pigs are also quite large, therefore, guinea pigs may experience complications during childbirth (however, more often they die precisely from blood poisoning).
- If you are considering using your female guinea pig for breeding, adhere to the recommended age limits for animals in this matter to minimize the risk of possible complications.
- If a female needs a caesarean section due to a complication of labor, then be aware that the survival rate in this case is very low.
- Do not breed guinea pigs until you have picked up future cubs or those animals that you do not want to keep, potential new owners. Be aware that many people who confidently declare that they will take pets disappear without a trace after their birth.
 2 Make sure you have all the supplies you need to breed and care for your guinea pigs. If you plan on breeding guinea pigs, the number in your home is likely to increase. Make sure you have sufficient supplies to care for the breeding pair and their cubs.
2 Make sure you have all the supplies you need to breed and care for your guinea pigs. If you plan on breeding guinea pigs, the number in your home is likely to increase. Make sure you have sufficient supplies to care for the breeding pair and their cubs. - You will need enough space in the cages to accommodate all the animals. Remember that you will need to separate males and females to prevent them from breeding.
- Cages should have suitable bedding and hay, so consider purchasing these materials for future use so you always have a supply in case you need to clean your guinea pig cage. Also consider purchasing additional accessories in the form of toys and shelters to keep your guinea pigs from getting bored.
- Make sure you have enough pellets and drinkers to keep your guinea pigs healthy.
- Allow sufficient time for proper daily, weekly and monthly cage cleaning to keep the animals healthy.
 3 Find breeding guinea pigs. You need to select the best quality guinea pig breeding pair. The correct choice of animals can ensure the production of quality, healthy and viable offspring.
3 Find breeding guinea pigs. You need to select the best quality guinea pig breeding pair. The correct choice of animals can ensure the production of quality, healthy and viable offspring. - Professionals usually adhere to the “best with the best” breeding rule when choosing a pair for breeding. This means that exceptionally the best female guinea pigs mate exclusively with the best males.
- Where possible, the pedigree history of both guinea pigs should be checked. There are some hereditary diseases that can affect guinea pigs and their offspring, or lead to their death or the birth of seriously abnormal pups.
- Make sure the male and female are at the right age for breeding.
- If you are unsure about the sex of your guinea pigs, you can check by looking at the upside-down guinea pig just above the anus. The male will show a groove or pronounced testicles. The female will have a Y-shaped skin fold above the anus.
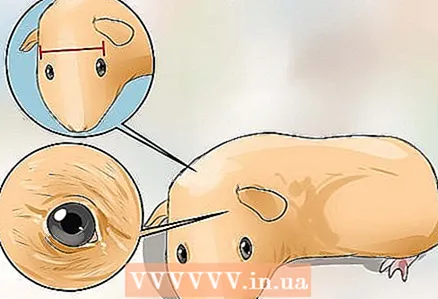 4 Select a breeding male to mate with the female. Part of the selection of a suitable pair for breeding is the selection of a breeding male. A quality breeding male can ensure that the female produces healthy, good quality pups.
4 Select a breeding male to mate with the female. Part of the selection of a suitable pair for breeding is the selection of a breeding male. A quality breeding male can ensure that the female produces healthy, good quality pups. - A good breeding male guinea pig will have a broad head and lively look.
- On average, males at the age of five months are suitable for the first mating. However, most guinea pigs reach sexual maturity by 10 weeks.
 5 Choose a breeding female to mate with the male. Choosing a good quality breeding female is just as important as choosing a breeding male. A well-chosen female can ensure a high-quality, healthy offspring.
5 Choose a breeding female to mate with the male. Choosing a good quality breeding female is just as important as choosing a breeding male. A well-chosen female can ensure a high-quality, healthy offspring. - The female's head should have the correct shape, lively eyes and a good muzzle.
- Most guinea pigs reach sexual maturity by 10 weeks of age. However, it is possible to mate a female for the first time only at the age of 4-7 months.
- It is very important that for the first pregnancy the female is not older than 7 months in order to avoid symphysis and pathological childbirth.
- When re-breeding, choose a female that has had the opportunity to rest after the previous birth to ensure good quality of the subsequent litter.
Part 2 of 4: Breeding a Selected Pair
 1 Check the health status of each guinea pig. You cannot mate a male and a female until you are sure that both animals are healthy. Show them to your veterinarian to minimize your risks in case one of the animals becomes sick.
1 Check the health status of each guinea pig. You cannot mate a male and a female until you are sure that both animals are healthy. Show them to your veterinarian to minimize your risks in case one of the animals becomes sick. - If you regularly treat guinea pigs for fleas, then the last procedure should be carried out no later than two weeks before mating to prevent possible effects of ivermectin on the offspring.
 2 Quarantine the new guinea pigs for two weeks. If you decide to mate your guinea pig with someone else's guinea pig, quarantine the other guinea pig for two weeks. This will make sure that the animal is not sick or infected with parasites.
2 Quarantine the new guinea pigs for two weeks. If you decide to mate your guinea pig with someone else's guinea pig, quarantine the other guinea pig for two weeks. This will make sure that the animal is not sick or infected with parasites. - You can keep your guinea pigs in quarantine by simply placing their cages in separate rooms. Also remember to wash your hands after handling animals and touching food and bedding.
- Keep guinea pigs out of contact during the quarantine period.
- If you are going to mate your own animals, then there is no need to quarantine them.
 3 Introduce the breeding pair. After you make sure that both animals are healthy, you can introduce the breeding pair. It may take a few days for guinea pigs to get used to each other.
3 Introduce the breeding pair. After you make sure that both animals are healthy, you can introduce the breeding pair. It may take a few days for guinea pigs to get used to each other. - Keep the mate in her usual cage to reduce her stress and increase the chances of a successful pregnancy. If the female is not ready to mate, she can reject the male by spitting on him or showing her teeth.
- Never admit more than one male to a female, as serious conflicts can arise between males.
- If you keep several females in the same cage, remove the remaining females from the breeding female, which you are not going to mate, to save them from unnecessary stress. Maintain the friendship between the females by allowing them to socialize on walks outside the cage, and keep the breeding pair together the rest of the time.
 4 Do not disturb the breeding pair during the duration of the female's sexual cycle. The sexual cycle of a female guinea pig is about 15-17 days. The breeding couple should be kept together during this period to increase the chances of pregnancy.
4 Do not disturb the breeding pair during the duration of the female's sexual cycle. The sexual cycle of a female guinea pig is about 15-17 days. The breeding couple should be kept together during this period to increase the chances of pregnancy. - A couple can mate several times during this period, but pregnancy can occur only in a short window of a cycle lasting 24-48 hours.
- Check the breeding couple regularly to keep track of their health and well-being, and to reassure them that you are looking after them.
Part 3 of 4: Confirming Pregnancy and Assisting Childbirth
 1 Check if the female is pregnant. After at least 18 days, you should check the female's pregnancy. You can do it yourself (for this read the article “How to determine the pregnancy of your guinea pig”), but only a veterinarian can give you the exact answer to this question.
1 Check if the female is pregnant. After at least 18 days, you should check the female's pregnancy. You can do it yourself (for this read the article “How to determine the pregnancy of your guinea pig”), but only a veterinarian can give you the exact answer to this question. - A pregnant female may experience several pregnancy symptoms, including an enlarged belly and an increase in the amount of food and water consumed. During pregnancy, the female can eat 2-3 times more than usual.
- Your veterinarian will also be able to provide you with an estimated due date.
- For a female to become pregnant, you may need to wait several of her sexual cycles. Be patient and don't stress your guinea pigs.
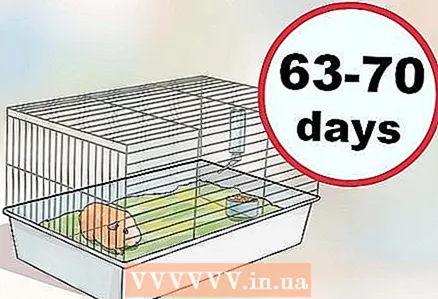 2 Take care of the female during pregnancy. If your female has a pregnancy, know that this period lasts 63-70 days. At this time, it is important to protect the female from stress as much as possible.
2 Take care of the female during pregnancy. If your female has a pregnancy, know that this period lasts 63-70 days. At this time, it is important to protect the female from stress as much as possible. - Do not make sudden changes to the female's cage and shield her from any factors that can cause stress, such as loud noise.
- Handle the female as little as possible during pregnancy and do not touch her at all in the last two weeks of pregnancy. For childbirth, you can persuade the female to sit on a towel or in a box.
- For the female's peace of mind, you can leave the male in the cage with her before giving birth.
- It is recommended that the remaining guinea pigs be removed from the giving birth female to allow her to give birth alone.
 3 Increase the amount of food for the female. During pregnancy the amount of food and water consumed by the female will increase. Give her an increased amount of food to ensure she is getting all the nutrients she needs for the development of her pups.
3 Increase the amount of food for the female. During pregnancy the amount of food and water consumed by the female will increase. Give her an increased amount of food to ensure she is getting all the nutrients she needs for the development of her pups. - Increase the amount of fresh vegetables to 1.5-2 cups (240 ml each) per day.
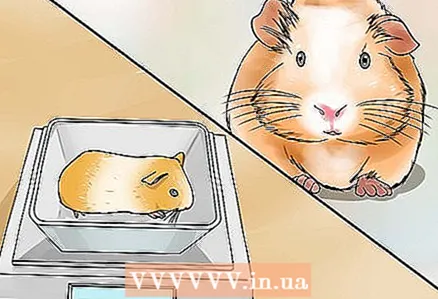 4 Check the female's health during pregnancy. Pregnancy carries a serious risk for the female, as the cubs develop very large. Examine the female carefully daily for signs of ailment and weigh her.
4 Check the female's health during pregnancy. Pregnancy carries a serious risk for the female, as the cubs develop very large. Examine the female carefully daily for signs of ailment and weigh her. - Signs of illness include discharge from the eyes, nose, or ears, and loss of fur.
- The female should gradually gain weight, but the exact parameters of weight gain depend on the individual characteristics and the size of the litter.
- Make sure the female is eating well. The first sign of developing blood poisoning is loss of appetite. Any pregnant female who has not eaten for more than 12 hours should be seen by a veterinarian.
- If you notice any problems with your guinea pig, including insufficient fetal movement in the abdomen, see your veterinarian.
 5 Prepare for the cubs. You should be ready to give birth to a female around the ninth week of pregnancy. By carefully preparing the medical supplies you may need during childbirth, you can better cope with possible complications.
5 Prepare for the cubs. You should be ready to give birth to a female around the ninth week of pregnancy. By carefully preparing the medical supplies you may need during childbirth, you can better cope with possible complications. - Guinea pigs do not show clear signs of approaching labor and do not begin to make any special preparations for them, so it is difficult to determine exactly when your female might start labor.
- Just before giving birth, you may notice a slight expansion of the pelvic bones in the female.
- Stock up on a syringe that you may need to cleanse newborn babies.
- It is a good idea to alert the veterinarian when the female is nine weeks old, so that he is prepared for the fact that his help may be required if the female has complications during labor.
 6 If there are no complications, labor should be quick. An uncomplicated delivery usually takes 10-30 minutes. If they drag on and last more than an hour, call your veterinarian or take the female to him for help.
6 If there are no complications, labor should be quick. An uncomplicated delivery usually takes 10-30 minutes. If they drag on and last more than an hour, call your veterinarian or take the female to him for help. - Don't crowd around a giving birth guinea pig. Only one person should observe the course of labor, while he should not touch the female.
- Between births of cubs should pass 5-10 minutes. Usually, the female gives birth to one to five cubs.
- The female will give birth while sitting, bending over or dropping to the ground.
- If there are complications during labor, take your guinea pig to your veterinarian. For example, if childbirth lasts longer than an hour, if there is more than 15 minutes between births of pups, if there is a lot of bleeding, if the guinea pig cries very much.
Part 4 of 4: Handling Guinea Pigs Postpartum
 1 Let the guinea pig clean its cubs. As soon as the female gives birth, let her scrub her cubs herself. This will reduce the risk of your babies contaminating the babies with your help, or the likelihood of the mother abandoning the babies.
1 Let the guinea pig clean its cubs. As soon as the female gives birth, let her scrub her cubs herself. This will reduce the risk of your babies contaminating the babies with your help, or the likelihood of the mother abandoning the babies. - The mother who has given birth or her cage neighbors will eat the placenta and membranes.
 2 Expect live and full-fledged cubs. Cubs of guinea pigs are born outwardly similar to a fully "functional" copy of adult animals. If the cub does not look normal, consult your veterinarian about it.
2 Expect live and full-fledged cubs. Cubs of guinea pigs are born outwardly similar to a fully "functional" copy of adult animals. If the cub does not look normal, consult your veterinarian about it. - Newborn cubs of guinea pigs have fur, wide-open eyes, a full set of teeth, and they themselves are able to run like the rest of the guinea pigs.
- Babies do not need an incandescent lamp or heating pad for heating if the room is warm. They must be kept at the same temperature that is comfortable for the parents.
- The mother may abandon one of the cubs, usually the smallest of the offspring. However, he may be fine on his own, so continue hand-feeding him and bringing him back to his mother. Try leaving him alone for a while with his mother.
 3 Wait 24 hours before picking up mother and cubs. Guinea pigs are not very protective and protective of their young, however, you must give the mother a full 24 hours after giving birth before touching them. After that, you can pick them up as much as you like.
3 Wait 24 hours before picking up mother and cubs. Guinea pigs are not very protective and protective of their young, however, you must give the mother a full 24 hours after giving birth before touching them. After that, you can pick them up as much as you like. - It is recommended that you handle the cubs to better socialize them.
 4 Continue to provide the mother with a nutrient-dense diet. Give her alfalfa hay and extra pellets while she nurses her cubs. This will allow her to stay healthy throughout the nursing period and minimize the risk of deteriorating milk quality.
4 Continue to provide the mother with a nutrient-dense diet. Give her alfalfa hay and extra pellets while she nurses her cubs. This will allow her to stay healthy throughout the nursing period and minimize the risk of deteriorating milk quality. - The female may stop feeding the cubs at about 14 to 21 days of age. However, babies can already start eating solid food from 5 days of age (since they are born well developed), so if the mother abandons one of the cubs, ensure that the solid food is always available so that the baby can start eating on its own if necessary.
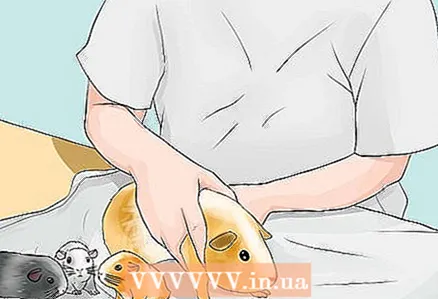 5 Examine the cubs and mother regularly. One day after giving birth, and periodically from that moment on, examine the mother with her cubs. This will allow them to identify deadly conditions and other problems. If you notice problems or have questions, please contact your veterinarian.
5 Examine the cubs and mother regularly. One day after giving birth, and periodically from that moment on, examine the mother with her cubs. This will allow them to identify deadly conditions and other problems. If you notice problems or have questions, please contact your veterinarian. - The size of the cubs can vary, they can weigh 70-100 g and be 7.5-10 cm long. In the first two days, the weight of the cubs may decrease, but on the third day it should begin to increase.
- The smallest calf in the litter can benefit from one or two fifteen-minute feedings per day alone with the mother.
Tips
- If you need to hand feed the pups, use kitten formula and a syringe.
- If the mother abandons her babies, you can hand feed them until they are old enough to start feeding on their own.
Warnings
- The female will be ready to mate again immediately after giving birth. If the male is still in the cage with her, he can fertilize her again. It would be better to plant the male to prevent an early re-pregnancy. This will allow the female to recover from birth.
What do you need
- At least two cells.
- Additional consumables including food and bedding.
- Two healthy heterosexual guinea pigs.
- Records of the nearest pedigree of the breeding male and female.
Additional articles
 How to introduce two guinea pigs
How to introduce two guinea pigs  How to care for guinea pigs
How to care for guinea pigs  How to trim the claws of a guinea pig
How to trim the claws of a guinea pig  How to make your guinea pig trust you
How to make your guinea pig trust you  How to toilet train your guinea pigs
How to toilet train your guinea pigs  How to wash your guinea pig
How to wash your guinea pig  How to comfortably furnish a guinea pig cage
How to comfortably furnish a guinea pig cage  How to determine if your guinea pig is pregnant
How to determine if your guinea pig is pregnant  How to properly pick up a guinea pig
How to properly pick up a guinea pig  How to play with a guinea pig
How to play with a guinea pig  How to entertain your guinea pig
How to entertain your guinea pig  How to Determine the Gender of a Guinea Pig
How to Determine the Gender of a Guinea Pig  How to train a guinea pig
How to train a guinea pig  How to care for your guinea pig to avoid bad odor
How to care for your guinea pig to avoid bad odor