Author:
Clyde Lopez
Date Of Creation:
17 June 2021
Update Date:
24 June 2024

Content
- Steps
- Part 1 of 3: Symptoms of the Disease
- Part 2 of 3: Understanding Causes and Risk Factors
- Part 3 of 3: Treating the Infection
- Tips
Labyrinthitis (internal otitis media) is a condition in which inflammation occurs in the inner part of the ear, particularly in the membranous labyrinth. The inner ear is responsible for hearing, balance and balance. Typically, this disease can be caused by a bacterial or viral infection. This condition can cause temporary and sometimes, in rare cases, permanent hearing loss. This disease is usually a complication of the disease, and may be due to a respiratory or ear infection that leads to inflammation in the labyrinth. See Step 1 to see if you have a labyrinthitis.
Steps
Part 1 of 3: Symptoms of the Disease
 1 Monitor your dizziness. Are you feeling unstable or out of balance? Moving your head, watching TV for a long time, reading books, focusing your gaze on an object for a long period of time, being among a large concentration of people, darkness and walking aggravate dizziness? This feeling is due to incorrect signals from the vestibular system, which is located in your ears.
1 Monitor your dizziness. Are you feeling unstable or out of balance? Moving your head, watching TV for a long time, reading books, focusing your gaze on an object for a long period of time, being among a large concentration of people, darkness and walking aggravate dizziness? This feeling is due to incorrect signals from the vestibular system, which is located in your ears. - The semicircular pipes of the labyrinth vestibule are filled with a special type of liquid. The movement of this fluid stimulates the nerve tissue in the tubes, which induces a sense of body position and balance. Labyrinthitis changes the usual composition of this fluid, which leads to incorrect reproduction of a signal, which is subsequently interpreted by the nervous system as dizziness.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness can occur with other illnesses. With anemia, low blood pressure, low blood glucose (hypoglycemia), blood loss, or dehydration, weakness is the main symptom. You may also faint at times.
- The semicircular pipes of the labyrinth vestibule are filled with a special type of liquid. The movement of this fluid stimulates the nerve tissue in the tubes, which induces a sense of body position and balance. Labyrinthitis changes the usual composition of this fluid, which leads to incorrect reproduction of a signal, which is subsequently interpreted by the nervous system as dizziness.
 2 Perhaps you have vertigo? Do you feel dizzy or the world revolves around you? It is also a sign of inflammation in the vestibular system. Head trauma, Meniere's disease, stroke, and some other illnesses can cause vertigo, but they will have specific features and other associated symptoms (which will be discussed later).
2 Perhaps you have vertigo? Do you feel dizzy or the world revolves around you? It is also a sign of inflammation in the vestibular system. Head trauma, Meniere's disease, stroke, and some other illnesses can cause vertigo, but they will have specific features and other associated symptoms (which will be discussed later). - The degree of vertigo disease varies greatly. You may feel mildly dizzy and imbalanced, or the sensation may be so severe that you simply cannot stay upright. You may also experience nausea and vomiting. In labyrinthitis, the most severe symptoms of vertigo occur in the first week. After that, you will feel better. The body will learn to deal with the symptoms.
 3 Understand if you have tinnitus. You may hear constant ringing, buzzing, whistling, or humming sounds in the affected ear. This is due to the formation of abnormal particles in the internal fluid that stimulate hair cells (nerve endings that transmit sound signals). This unusual stimulation is interpreted as tinnitus.
3 Understand if you have tinnitus. You may hear constant ringing, buzzing, whistling, or humming sounds in the affected ear. This is due to the formation of abnormal particles in the internal fluid that stimulate hair cells (nerve endings that transmit sound signals). This unusual stimulation is interpreted as tinnitus. - Diseases that cause vertigo can also cause tinnitus. Noisy environments can cause tinnitus. In this case, you usually will not experience other symptoms.
 4 Analyze your feelings - if you have hearing impairment. It happens when the cochlear nerve is damaged or blocked by inflammation. You may experience hearing loss or complete hearing loss. This is a more severe symptom of labyrinthitis and requires urgent medical attention because hearing loss can become permanent.
4 Analyze your feelings - if you have hearing impairment. It happens when the cochlear nerve is damaged or blocked by inflammation. You may experience hearing loss or complete hearing loss. This is a more severe symptom of labyrinthitis and requires urgent medical attention because hearing loss can become permanent. - If your hearing loss is accompanied by tinnitus, check your pinna for large amounts of earwax. You will be able to fully restore your hearing function after removing the earwax.
 5 Check for ear discharge. A discharge of pus or colorless fluid indicates a bacterial infection of the middle ear (otitis media) that has invaded the eardrum (the septum between the outer and middle ear). You should see your doctor right away to control the infection, because this can lead to permanent hearing impairment.
5 Check for ear discharge. A discharge of pus or colorless fluid indicates a bacterial infection of the middle ear (otitis media) that has invaded the eardrum (the septum between the outer and middle ear). You should see your doctor right away to control the infection, because this can lead to permanent hearing impairment. - Consider if you feel a heaviness in your ears. If you have a buildup of pus or fluid in your middle ear, you may feel heaviness or pressure in your sore ear. This usually occurs with bacterial infections.
 6 Determine if you have vomiting, ear pain, blurred vision, and fever. In fact, these are symptoms of symptoms. And here's how it works:
6 Determine if you have vomiting, ear pain, blurred vision, and fever. In fact, these are symptoms of symptoms. And here's how it works: - Ear pain is a sign of an infectious disease. It may be accompanied by ringing in the ears.
- Vertigo or dizziness that accompanies labyrinthitis can lead to nausea and vomiting.
- A temperature above 38 ° C indicates that there is an infection in the body.
- Defocused vision can result from a pinched nerve. You may find it difficult to read and view things from a distance.
 7 Find out what is not a maze. Some diseases are similar to labyrinthitis. To treat yourself effectively, it is important to be sure that you have this particular disease, and not something similar. Here are some diseases similar to labyrinthitis:
7 Find out what is not a maze. Some diseases are similar to labyrinthitis. To treat yourself effectively, it is important to be sure that you have this particular disease, and not something similar. Here are some diseases similar to labyrinthitis: - Meniere's disease... It is caused by an unusual buildup of fluid in the inner ear. A typical attack begins with a feeling of fluid filling in your ear, increased tinnitus and hearing loss, followed by severe vertigo. The attack is often accompanied by nausea and vomiting. The attack usually lasts 20-30 minutes.
- Migraine... This disease is completely unrelated to problems in the ear.Migraine occurs due to constriction and subsequent dilation of the blood vessels in the brain. Unilateral headache is the main symptom of migraine.
- Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo... The disease occurs due to the displacement of crystals from the uterus of the vestibular labyrinth and the spherical sac into the bony semicircular canals of the bone labyrinth. The displaced particles do not properly stimulate the semicircular canals, which leads to vertigo and dizziness.
- Transient ischemic attack (TIA) or mini stroke... If there is vascular insufficiency in the areas of the brain responsible for hearing and balance, you may experience dizziness, loss of balance, or temporary hearing loss. You should feel better within a few minutes and the symptom should not recur.
- A brain tumor... Typically, this disease has a very specific set of symptoms. It all depends on the location of the tumor. However, headaches and seizures are common symptoms with any brain tumor. Weakness in a specific part of the body may also be a symptom.
 8 See your doctor. Symptoms can last from 1 to 3 weeks. While this seems like a short time, it is best to see your doctor to avoid serious complications such as permanent hearing loss. There are laboratory tests that can confirm if you have a labyrinthitis.
8 See your doctor. Symptoms can last from 1 to 3 weeks. While this seems like a short time, it is best to see your doctor to avoid serious complications such as permanent hearing loss. There are laboratory tests that can confirm if you have a labyrinthitis.
Part 2 of 3: Understanding Causes and Risk Factors
 1 Be aware that a viral infection is the most common cause of illness. A viral infection usually affects people in their 30s and 60s. Mostly viruses that cause infections of the mouth, nose, sinuses, respiratory tract and lungs are the cause of this disease. In a viral infection, microbes reach the inner ear through the bloodstream. This type of disease can go away without treatment.
1 Be aware that a viral infection is the most common cause of illness. A viral infection usually affects people in their 30s and 60s. Mostly viruses that cause infections of the mouth, nose, sinuses, respiratory tract and lungs are the cause of this disease. In a viral infection, microbes reach the inner ear through the bloodstream. This type of disease can go away without treatment. - You most likely had a cold or flu about one week before the labyrinthitis. Cold and flu symptoms: runny nose, cough, sore throat.
- Other viral infections that are less likely to cause labyrinthitis are measles, mumps, herpes, and infectious mononucleosis.
- With measles, a skin rash usually appears. With mumps, the face swells near the ears. With infectious mononucleosis, there is a high fever, sore throat, and nodules on various parts of the body.
 2 A bacterial infection can also be the cause of the disease. This happens less often, but the condition is much more serious. Usually children get sick with it. Pneumococcus, haemophilus influenzae and moraxella catarralis - these types of infections need treatment and should be taken very seriously as they can lead to permanent hearing loss.
2 A bacterial infection can also be the cause of the disease. This happens less often, but the condition is much more serious. Usually children get sick with it. Pneumococcus, haemophilus influenzae and moraxella catarralis - these types of infections need treatment and should be taken very seriously as they can lead to permanent hearing loss. - The infection usually spreads from the middle ear or lining of the brain through the bloodstream or through an opening caused by a head injury.
 3 Autoimmune diseases can also be the cause. In some autoimmune diseases, such as Wegener's granulomatosis or Kogan's syndrome, the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues. The formation of antibodies is formed, which attack the labyrinth, thinking that these are tissues foreign to the body.
3 Autoimmune diseases can also be the cause. In some autoimmune diseases, such as Wegener's granulomatosis or Kogan's syndrome, the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues. The formation of antibodies is formed, which attack the labyrinth, thinking that these are tissues foreign to the body.  4 Please note that some of your medications may also put you at risk. Some drugs are especially toxic to the ears. For example, gentamicin, diuretics, anticancer drugs, etc. The substances in these drugs can concentrate in the inner ear, causing damage.
4 Please note that some of your medications may also put you at risk. Some drugs are especially toxic to the ears. For example, gentamicin, diuretics, anticancer drugs, etc. The substances in these drugs can concentrate in the inner ear, causing damage. - Certain medications such as aspirin, anticonvulsants, diuretics, and antihypertensive drugs can cause side effects such as inflammation and irritation of the inner ear. Some of them are thought to be harmful to hearing, causing dizziness and vertigo.
 5 Also, your age and health condition can be negative factors. This condition usually affects people between the ages of 30 and 50. However, bacterial labyrinthitis is also common in children.
5 Also, your age and health condition can be negative factors. This condition usually affects people between the ages of 30 and 50. However, bacterial labyrinthitis is also common in children. - During illness, certain illnesses such as mumps, respiratory infections, colds and coughs can spread to the inner ear. Bacterial and viral infections can cause inflammation and spread to other parts of the body.
- Allergies such as hay fever, rhinitis and cough increase the risk of labyrinthitis. This is due to the appearance of swelling and inflammation in the nasal canal, which can lead to labyrinthitis. The presence of an infectious respiratory irritation can cause subsequent infection of the lungs and inner ear.
Part 3 of 3: Treating the Infection
 1 Drink plenty of fluids. This will help prevent dehydration. Feeling dizzy all the time can disrupt your daily life and cause anxiety. You can stop monitoring your food and fluid intake. Due to dehydration, purulent inflammation can begin to concentrate in the inner ear, which will only aggravate the disease.
1 Drink plenty of fluids. This will help prevent dehydration. Feeling dizzy all the time can disrupt your daily life and cause anxiety. You can stop monitoring your food and fluid intake. Due to dehydration, purulent inflammation can begin to concentrate in the inner ear, which will only aggravate the disease.  2 Relax. In the first few days of illness, you may feel severe dizziness and bouts of vertigo. You need to rest during this time to avoid falls and injuries. You should feel better in about a week.
2 Relax. In the first few days of illness, you may feel severe dizziness and bouts of vertigo. You need to rest during this time to avoid falls and injuries. You should feel better in about a week. - You should not drive or work with sharp objects during this time. Sudden flare-ups of dizziness can lead to an accident or serious injury.
- You shouldn't watch TV or read books for a long time. This can lead to eye fatigue, which in turn can create balance problems.
 3 Take vitamins. They can help you boost your immunity, which will help you fight any viral or bacterial infections. Take these vitamins:
3 Take vitamins. They can help you boost your immunity, which will help you fight any viral or bacterial infections. Take these vitamins: - Vitamin A helps the body by reducing inflammation in the ear and fighting viral or bacterial infections.
- Vitamin C is known as an antioxidant that promotes healing and recovery. It also strengthens the immune system.
- Vitamin B6. It is believed to prevent or reduce dizziness.
- Vitamin E also helps speed up the healing process and also strengthens the immune system.
 4 Lie down during seizures. If you experience a bout of vertigo or dizziness when walking or when standing, try to go to bed to rest. You must find a position that relieves your symptoms. People often feel better lying on their side rather than on their back.
4 Lie down during seizures. If you experience a bout of vertigo or dizziness when walking or when standing, try to go to bed to rest. You must find a position that relieves your symptoms. People often feel better lying on their side rather than on their back. - Change your posture slowly. Sudden head movements shake the fluid in the inner ear, which in turn stimulates the nerves in the wrong way. If you need to get out of bed, do it slowly. Lie down also slowly.
- If you notice symptoms while lying down, try sitting in a chair.
 5 Avoid bright light and strong noise. You will feel uncomfortable with them. Bright light and absolute darkness exacerbate the feeling of imbalance. Use soft light in your room. Likewise, very loud noises will aggravate the noise in your ears.
5 Avoid bright light and strong noise. You will feel uncomfortable with them. Bright light and absolute darkness exacerbate the feeling of imbalance. Use soft light in your room. Likewise, very loud noises will aggravate the noise in your ears. - The goal is to rest the vestibular and hearing aids. You will gradually be able to overcome the change in the functions of these systems if there is no unnecessary external interference.
 6 Avoid drinking coffee, alcohol, and smoking. These natural stimulants make the nerves of the inner ear very excitable. As a result of their use, you will experience a much more acute reaction to minor stimuli, such as simple movements.
6 Avoid drinking coffee, alcohol, and smoking. These natural stimulants make the nerves of the inner ear very excitable. As a result of their use, you will experience a much more acute reaction to minor stimuli, such as simple movements. - Alcohol and coffee also cause dehydration, which is detrimental to the health of the inner ear.
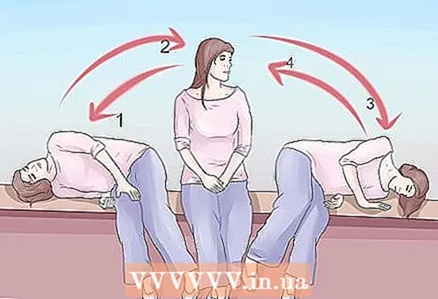 7 Begin vestibular rehabilitation therapy. This is a range of movements performed under the guidance of a physiotherapist. The therapy trains your brain to adapt to abnormal signals from the vestibular system. Your brain learns to identify the wrong signals and ignore them. It is very effective, especially in chronic labyrinthitis.
7 Begin vestibular rehabilitation therapy. This is a range of movements performed under the guidance of a physiotherapist. The therapy trains your brain to adapt to abnormal signals from the vestibular system. Your brain learns to identify the wrong signals and ignore them. It is very effective, especially in chronic labyrinthitis. - Exercise to stabilize your gaze.Try moving your head from side to side while looking at a stationary object. Your head will move, but your gaze should remain fixed.
- Do addictive exercises. Their goal is to deliberately provoke symptoms and train the brain to get used to the symptoms. One example is the Brant-Darov exercise. You need to lie down quickly from a seated position with your head turned at a 45-degree angle. Lie still for 30 seconds, or until the dizziness subsides. Then sit down again. Repeat the procedure with your head turned in the opposite direction. Do the exercise 3 times a day.
 8 Take your medicine. They are intended to relieve symptoms, not cure the infection. Vertigo, dizziness, nausea, or vomiting can be severe enough to make your life worse. Thus, medications are essential for you. There are such options:
8 Take your medicine. They are intended to relieve symptoms, not cure the infection. Vertigo, dizziness, nausea, or vomiting can be severe enough to make your life worse. Thus, medications are essential for you. There are such options: - Antihistamine helps to alleviate an allergic reaction, minimizing the chances of developing labyrinthitis. You can take diphenhydramine (Benadryl) 25 g and 50 mg. You can take 25 mg of the medication twice a day to relieve symptoms.
- Antiemetic... You can take meclizine hydrochloride to prevent or reduce dizziness and vomiting. It is also effective for vertigo. The medication is available in 25 mg and 50 mg sizes and can be taken with or without food. Do not exceed 2 tablets in a 24 hour period.
- Steroids... This medication is intended to treat inflammation. It is an anti-inflammatory agent that helps reduce inflammation in the affected area. Prednisolone is a first-line drug. It is available in a 20mg size. You can take it 3 times a day at intervals of 6-8 hours.
- Antibiotic taken when a bacterial infection is the cause of your labyrinthitis. It must be taken right away to prevent hearing loss. Your doctor should prescribe an antibiotic that is appropriate for your condition.
- Antiviral drug used to treat various infections caused by the virus. Acyclovir 400 mg or 800 mg is the first-line drug. However, your doctor must prescribe the correct dose for you.
Tips
- Please note that you should only use the medications mentioned in this article after consulting your doctor.
- You can also eat one or two cloves of garlic daily. There are studies that show that garlic can help fight any bacteria and infection.