Author:
Clyde Lopez
Date Of Creation:
23 June 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Part 1 of 3: Describe the physical characteristics of the ring
- Part 2 of 3: Describe the main characteristics of a gemstone
- Part 3 of 3: Describe the entire ring
Rings for any occasion come in different shapes and sizes, and it is not always clear where to start describing a particular ring if you are not familiar with the different options. You will need to describe both the bezel (shank) and the gems (when needed). Sometimes it is advisable to mention other details as well, such as the meaning that this ring carries.
Steps
Part 1 of 3: Describe the physical characteristics of the ring
 1 Find out what the different parts of the ring are called. When describing a ring, it is useful to know what professional jewelers call each part of it.
1 Find out what the different parts of the ring are called. When describing a ring, it is useful to know what professional jewelers call each part of it. - The rim is the part of the ring that actually goes around your finger.
- Shank can mean the bezel as a whole, but more often refers to the portions of the ring that are found on each side of the gem.
- A welt is a lower contour rim soldered to the caste or top.
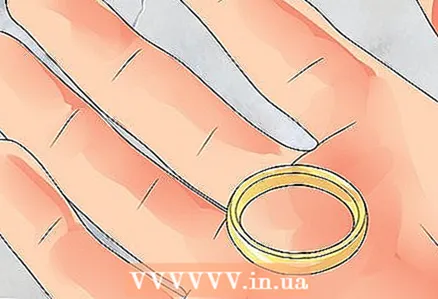 2 Identify the metal. Ring bezels can be made from a wide variety of base metals, but the most common options are gold, platinum, silver, tungsten carbide, titanium, and palladium.
2 Identify the metal. Ring bezels can be made from a wide variety of base metals, but the most common options are gold, platinum, silver, tungsten carbide, titanium, and palladium. - Gold bezels are classics and are available in a variety of colors.Yellow gold is the purest and most traditional. White gold is formed when yellow gold is plated with rhodium and rose gold when a copper alloy is added to the metal. Purity is determined by the number of carats. The more carats, the higher the purity of the stone.
- Platinum is almost always 95 percent pure. It is a white metal, very durable, heavy and naturally non-allergenic.
- Silver is a white-gray metal that is very soft and easily damaged, so it is usually inexpensive. More often silver is used for the production of decorative rather than wedding rings.
- Tungsten carbide is a gray metal made from tungsten and carbon. It is very durable, heavy and hard. Although it retains its luster, due to its strength, it cannot be cut or soldered, so the rings made from it cannot be resized.
- Titanium has a natural gray finish but is sometimes polished to black. It is as strong as steel, yet light as aluminum and is considered a popular choice for men's rings. This metal also does not cause allergic reactions.
- Palladium is silvery white in color. It does not fade, it is quite plastic and hypoallergenic.
- Recycled materials can also be used to make rings. Recycled metals come from a wide variety of sources and take on dominant metal properties.
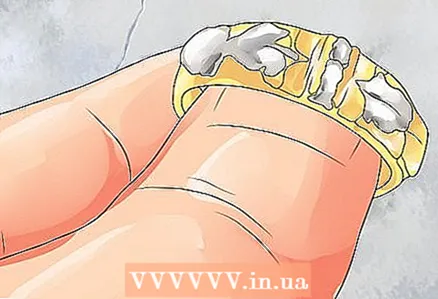 3 Note any distinguishing characteristics. The ring may include special performance or other characteristics that are not common enough to create a category for them. Even though there is no way to categorize such characteristics, you should still mention them when describing the ring.
3 Note any distinguishing characteristics. The ring may include special performance or other characteristics that are not common enough to create a category for them. Even though there is no way to categorize such characteristics, you should still mention them when describing the ring. - Metal artwork is a common example of these characteristics. For example, the headband can be in the shape of a leaf, or there can be an elaborate metal twisted flower in the center of an otherwise simple headband.
- Another special feature worth mentioning is engraving. Most engravings are very personal in nature. They can be located either on the inside of the rim or on its top.
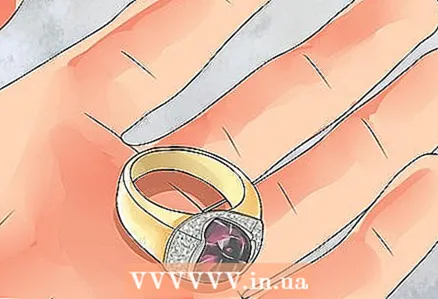 4 Indicate the presence of precious stones. Some rings only consist of a solid metal rim. Others include one or more gems. The last option should be described in more detail, as you should focus on the type, quality and placement of the stone.
4 Indicate the presence of precious stones. Some rings only consist of a solid metal rim. Others include one or more gems. The last option should be described in more detail, as you should focus on the type, quality and placement of the stone.  5 Describe the bartack style. Setting style refers to placing stones along the ring. There are many different bartacks to choose from.
5 Describe the bartack style. Setting style refers to placing stones along the ring. There are many different bartacks to choose from. - Rail setting is when a row of small stones are placed in a metal channel.
- Blind (nest) setting - one stone is located inside a thin and flat "nest" made of protective metal.
- In pavé setting, one large stone is in the center of the bezel, while the rest of the bezel is covered with a large number of small pebbles.
- In claw setting, thin metal "claws" extend upward from the rim to hold the center stone in place. Usually there are from four to six such metal claws.
- There may also be common prong settings where small adjacent stones share prongs with a large center stone.
- The raspberry fastener places one large gem in the center of the bezel, with smaller stones facing outward on all sides.
- In gypsy setting, the stone or stones are immersed in holes along the rim of the ring. As a result, the stone is embedded on the surface of the rim. For this reason, this bartack is also called "built-in".
- The spring setting is similar to the gypsy setting, but the holes are not so deep, and the stones rise above the surface of the rim. Only by spring tension, each stone is held in place.
- With a setting between the plates, small stones encircle the entire ring, and small metal plates separate one pebble from the next.
- With the "invisible" setting, special grooves are cut in the rim, which allow the stones to be securely fixed without metal plates or claws that would support them.
 6 What are the gems? Indicate the center gem. If the ring contains more than one gem, you will have to name each one.
6 What are the gems? Indicate the center gem. If the ring contains more than one gem, you will have to name each one. - Diamonds are very popular especially for engagement rings. They also correspond to one of the birth months - April. Cubic Fionite looks similar, but it does not shine as much and is nowhere near that expensive.
- Other popular birthstones include garnet (January), amethyst (February), aquamarine (March), emerald (May), alexandrite (June), pearl (also June), ruby (July), chrysolite (August), sapphire (September ), opal (October), tourmaline (also October), topaz (November), tanzanite (December), turquoise (also December) and zircon (also December).
- You can also find citrine (ranging in color from yellow to orange-brown), jade (bright green), lapis lazuli (blue), moonstone (usually colorless), morganite (soft pink and peach shades), onyx (black ), tourmaline (electric blue and tones of green) and a kind of corundum, spinel (bright red).
Part 2 of 3: Describe the main characteristics of a gemstone
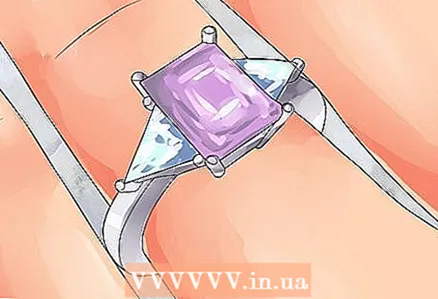 1 Indicate the cut of the center stone. Simply put, the cut of a stone means the shape of the stone. Cutting stones are usually square or round, but the center stone can appear in a wide variety of cuts.
1 Indicate the cut of the center stone. Simply put, the cut of a stone means the shape of the stone. Cutting stones are usually square or round, but the center stone can appear in a wide variety of cuts. - The most popular shape is the round or brilliant cut. The front side (crown) in it is of a round shape, a "belt" with a smaller conical base.
- The oval cut has a symmetrical oval crown.
- The princess cut is a square cut.
- The banquette cut resembles a narrow triangle.
- The triangular cut has a triangular crown.
- Marquis cut stones are shaped like an almond or a rugby ball.
- The pear cut is also called teardrop-shaped. The top of the crown is pointed and the base is rounded.
- The heart cut is shaped like a heart, as its name suggests.
- An emerald cut looks like a tall rectangle with cut edges.
- The radiant cut is a combination of emerald and brilliant cut. The outer shape is more like an emerald cut, but the facets are positioned to reflect light, like a brilliant cut.
- The "triangle" cut (also called "trillion" or "trillian") looks like triangles with curved edges.
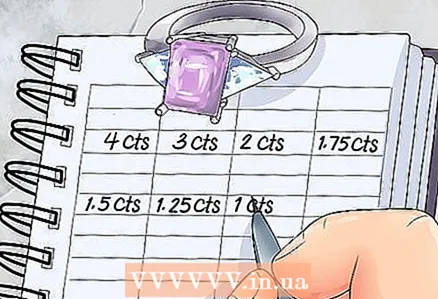 2 Note the carat weight. Carat is the standard unit of measure used to weigh gemstones. More carat weight means a larger stone.
2 Note the carat weight. Carat is the standard unit of measure used to weigh gemstones. More carat weight means a larger stone. - One carat equals 200 milligrams.
- Gemstones can also be measured by size, but carat weight is usually mentioned when describing a stone.
 3 Indicate the color of the gem. Naming the type of gem is not enough to describe the color of the stone. Color is further broken down into three distinct characteristics: hue, hue, and saturation.
3 Indicate the color of the gem. Naming the type of gem is not enough to describe the color of the stone. Color is further broken down into three distinct characteristics: hue, hue, and saturation. - Hue refers to the primary color of the stone. Some stones only exist in one shade, but others are available in a variety of colors. For example, jet is always green, but moonstone can be colorless, gray, brown, yellow, green, or pink.
- The tone simply indicates how light or dark the stone appears to be.
- Saturation is the intensity of a color. Stones with vibrant, vibrant colors are richer than stones with a light shade or color.
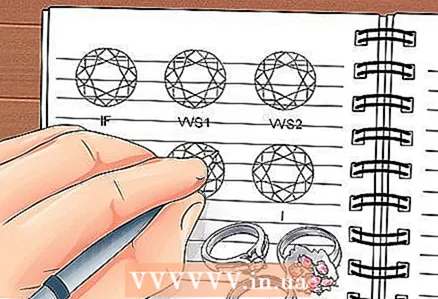 4 Describe the purity of the gemstones. The clarity of stones mainly refers to the amount of inclusions that are contained in the stone. The fewer inclusions in the stones, the greater their purity.
4 Describe the purity of the gemstones. The clarity of stones mainly refers to the amount of inclusions that are contained in the stone. The fewer inclusions in the stones, the greater their purity. - Inclusions are cracks and pieces of rock that are visible inside the stone.
- Accidental inclusions reduce the value of a stone, while elaborate artificial inclusions can even increase its value. Certain types of gemstones are more prone to inclusions than others.
Part 3 of 3: Describe the entire ring
 1 Mark your goal. Often the purchase of a ring is of particular importance or has a specific purpose. Usually you designate such a ring according to its purpose, without even thinking.
1 Mark your goal. Often the purchase of a ring is of particular importance or has a specific purpose. Usually you designate such a ring according to its purpose, without even thinking. - Engagement and wedding rings are the most obvious examples.
- Birthstone rings can be given as a special birthday present.
- Graduation rings are commonly worn to mark and celebrate graduation from high school or college.
 2 Please indicate the size. When describing the ring, you can also indicate the size. Dimensions are based on the diameter of the bezel of the ring.
2 Please indicate the size. When describing the ring, you can also indicate the size. Dimensions are based on the diameter of the bezel of the ring. - Ring sizes for adults range from 15 to 24.5.
- The range of the diameter of the ring number 15 - from 15 to 15.5 mm
- The range of the diameter of the ring number 15.5 - from 15.5 to 16 mm
- Diameter range of ring number 16 - from 16 to 16.5 mm
- The range of the diameter of the ring number 16.5 - from 16.5 to 17 mm
- Diameter range of ring number 17 - from 17 to 17.5 mm
- The range of the diameter of the ring number 17.5 - from 17.5 to 18 mm
- Diameter range of ring number 18 - from 18 to 18.5 mm
- The range of the diameter of the ring number 18.5 - from 18.5 to 19 mm
- The range of the diameter of the ring number 19 - from 19 to 19.5 mm
- The range of the diameter of the ring number 19.5 - from 19.5 to 20 mm
- The range of the diameter of the ring number 20 - from 20 to 20.5 mm
- The range of the diameter of the ring number 20.5 - from 20.5 to 21 mm
- The range of the diameter of the ring number 21 - from 21 to 21.5 mm
- The range of the diameter of the ring number 21.5 - from 21.5 to 22 mm
- Diameter range of ring number 22 - from 22 to 22.5 mm
- The range of the diameter of the ring number 22.5 - from 22.5 to 23 mm
- The range of the diameter of the ring number 23 - from 23 to 23.5 mm
- The range of the diameter of the ring number 23.5 - from 23.5 to 24 mm
- Diameter range of ring number 24 - from 24 to 24.5 mm
- The range of the diameter of the ring number 24.5 - from 24.5 to 25 mm
 3 Indicate whether the ring is included in the set or not. Most rings are sold separately, but some rings are sold in sets. Each ring in the set may look slightly different, but the overall design of all rings will have some similarities.
3 Indicate whether the ring is included in the set or not. Most rings are sold separately, but some rings are sold in sets. Each ring in the set may look slightly different, but the overall design of all rings will have some similarities. - Engagement rings are sometimes sold with wedding bands.
- Simple rings used as jewelry can also be purchased in a set, but this is a little less common.
 4 Consider whether you need to include a price. It is not always necessary to include the price of the ring in your description, but in some cases it is warranted.
4 Consider whether you need to include a price. It is not always necessary to include the price of the ring in your description, but in some cases it is warranted. - Always state the price clearly and clearly if your description is for the sale of the ring.
- Mention the price if you are discussing whether or not to buy the ring and describe it to someone who helps you make that decision.
- It is usually not worth mentioning the price of a ring that you have already purchased when you describe it to your friends and acquaintances.