Author:
Ellen Moore
Date Of Creation:
15 January 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 4: Square, Rectangle, and Other Parallelograms
- Method 2 of 4: Trapezoid
- Method 3 of 4: Deltoid
- Method 4 of 4: Freeform Quadrangle
- Tips
You've been given a problem in which you need to find the area of a quadrilateral, and you don't even know what a quadrangle is? Don't worry, this article will help you! A quadrilateral is any shape with four sides. To calculate the area of a quadrangle, you need to determine the type of quadrilateral that is given to you and use the appropriate formula.
Steps
Method 1 of 4: Square, Rectangle, and Other Parallelograms
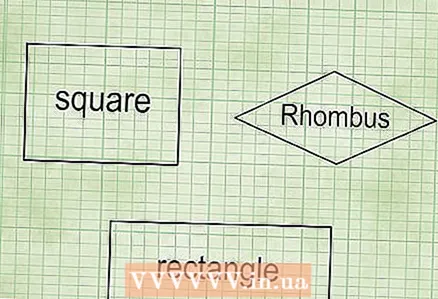 1 Definition of a parallelogram. A parallelogram is a quadrilateral in which opposite sides are equal and parallel to each other. Squares, rectangles and rhombuses are parallelograms.
1 Definition of a parallelogram. A parallelogram is a quadrilateral in which opposite sides are equal and parallel to each other. Squares, rectangles and rhombuses are parallelograms. - Square is a parallelogram in which all sides are equal and intersect at right angles.
- Rectangle is a parallelogram in which all sides intersect at right angles.
- Rhombus is a parallelogram with all sides equal.
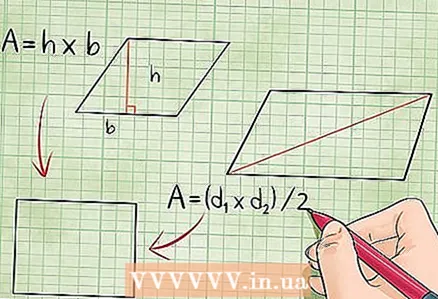
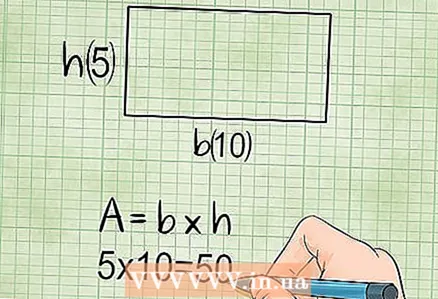 2 The area of the rectangle. To calculate the area of a rectangle, you need to know its width (short side; think of it as height) and length (long side; think of it as the side to which the height is drawn). The area of the rectangle is equal to the product of the length and the width.
2 The area of the rectangle. To calculate the area of a rectangle, you need to know its width (short side; think of it as height) and length (long side; think of it as the side to which the height is drawn). The area of the rectangle is equal to the product of the length and the width. - ’Area = length x height, or S = a x h.
- Example: if the length of the rectangle is 10 cm and the width is 5 cm, then the area of this rectangle is: S = 10 x 5 = 50 square centimeters.
- Remember that area is measured in square units (square meters, square centimeters, and so on).
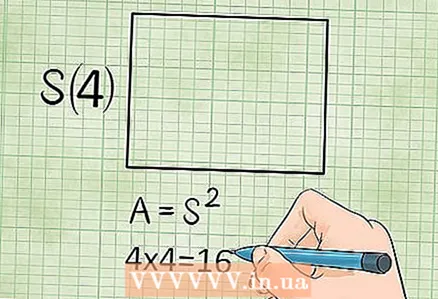 3 Square area. A square is a special case of a rectangle, so use the same formula as for finding the area of a rectangle. But in a square, all sides are equal, so the area of a square is equal to any of its sides squared (that is, multiplied by itself).
3 Square area. A square is a special case of a rectangle, so use the same formula as for finding the area of a rectangle. But in a square, all sides are equal, so the area of a square is equal to any of its sides squared (that is, multiplied by itself). - Area = side x side, or S = a.
- Example: if the side of the square is 4 cm (a = 4), then the area of this square: S = a = 4 x 4 = 16 square centimeters.
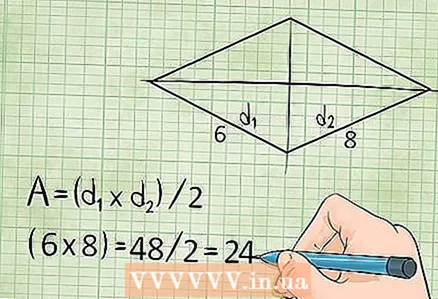 4 The area of a rhombus is equal to the product of its diagonals divided by two. Diagonals are line segments connecting opposite vertices of a rhombus.
4 The area of a rhombus is equal to the product of its diagonals divided by two. Diagonals are line segments connecting opposite vertices of a rhombus. - Area = (diagonal1 x diagonal2) / 2, or S = (d1 × d2)/2
- Example: if the diagonals of the rhombus are 6 cm and 8 cm, then the area of this rhombus is: S = (6 x 8) / 2 = 24 square centimeters.
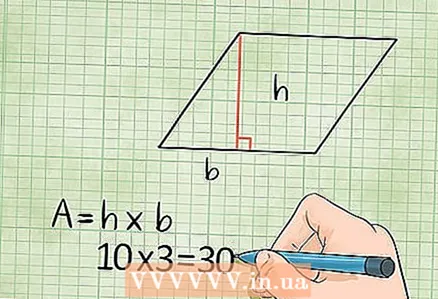 5 The area of a rhombus can also be found by multiplying its side by the height dropped on that side. But don't confuse the height with the adjacent side. Height is a straight line dropped from any vertex of the rhombus to the opposite side, and intersects the opposite side at a right angle.
5 The area of a rhombus can also be found by multiplying its side by the height dropped on that side. But don't confuse the height with the adjacent side. Height is a straight line dropped from any vertex of the rhombus to the opposite side, and intersects the opposite side at a right angle. - Example: if the length of a rhombus is 10 cm, and its height is 3 cm, then the area of such a rhombus is 10 x 3 = 30 square centimeters.
 6 Formulas for calculating the areas of a rhombus and a rectangle are applicable to squares, since a square is a special case of both a rectangle and a rhombus.
6 Formulas for calculating the areas of a rhombus and a rectangle are applicable to squares, since a square is a special case of both a rectangle and a rhombus.- Area = side x height, or S = a × h
- Area = (diagonal1 × diagonal2) / 2, or S = (d1 × d2)/2
- Example: if the side of the square is 4 cm, then its area is 4 x 4 = 16 square centimeters.
- Example: the diagonals of a square are 10 cm each.You can find the area of this square using the formula: (10 x 10) / 2 = 100/2 = 50 square centimeters.
Method 2 of 4: Trapezoid
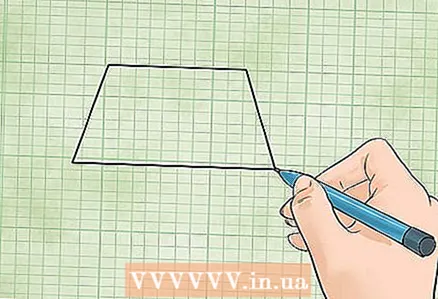 1 Definition of a trapezoid. A trapezoid is a rectangle with two opposite sides parallel to each other. Each of the four sides of the trapezoid can be of different lengths.
1 Definition of a trapezoid. A trapezoid is a rectangle with two opposite sides parallel to each other. Each of the four sides of the trapezoid can be of different lengths. - There are two ways to calculate the area of a trapezoid (depending on the given values).
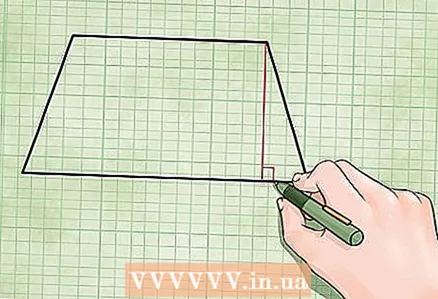 2 Find the height of the trapezoid. The height of a trapezoid is a segment connecting parallel sides (bases) and intersecting them at right angles (the height is not equal to the sides). Here's how to find the height of a trapezoid:
2 Find the height of the trapezoid. The height of a trapezoid is a segment connecting parallel sides (bases) and intersecting them at right angles (the height is not equal to the sides). Here's how to find the height of a trapezoid: - From the intersection of the smaller base and the side, draw a perpendicular to the larger base. This perpendicular is the height of the trapezoid.
- Use trigonometry to calculate the height. For example, if you know the side and the adjacent angle, then the height is equal to the product of the side and the sine of the adjacent angle.
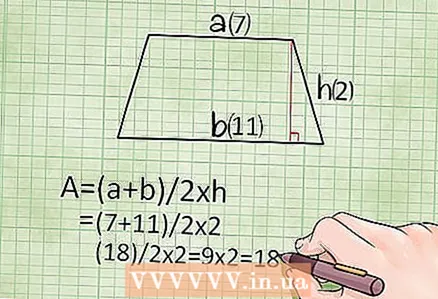 3 Find the area of the trapezoid using the height. If you know the height of the trapezoid and both bases, use the following formula to calculate the area of the trapezoid:
3 Find the area of the trapezoid using the height. If you know the height of the trapezoid and both bases, use the following formula to calculate the area of the trapezoid: - Area = (base1 + base2) / 2 × height, or S = (a + b) / 2 × h
- Example: if the height of the trapezoid is 2 cm, and the bases of the trapezoid are 7 cm and 11 cm, then the area of this trapezoid is: S = (a + b) / 2 * h = (7 + 11) / 2 * 2 = 18 square centimeters.
- If the height of the trapezoid is 10, and the bases of the trapezoid are 7 and 9, then the area of this trapezoid is: S = (a + b) / 2 * h = (7 + 9) / 2 * 10 = (16/2) * 10 = 8 * 10 = 80.
 4 Find the area of the trapezoid using the midline. The middle line is a segment parallel to the bases and dividing the sides in half. The middle line is equal to the average of both bases (a and b): middle line = (a + b) / 2.
4 Find the area of the trapezoid using the midline. The middle line is a segment parallel to the bases and dividing the sides in half. The middle line is equal to the average of both bases (a and b): middle line = (a + b) / 2. - Area = midline x height, or S = m × h
- Basically, here you are using a formula to find the area of a trapezoid from two bases, but instead of (a + b) / 2, m (middle line) is substituted.
- Example: if the middle line of a trapezoid is 9 cm, then the area of this trapezoid is: S = m * h = 9 x 2 = 18 square centimeters (you got the same answer as in the previous step).
Method 3 of 4: Deltoid
 1 Determination of the deltoid. A deltoid is a quadrangle with two pairs of sides of the same length.
1 Determination of the deltoid. A deltoid is a quadrangle with two pairs of sides of the same length. - There are two ways to calculate the area of the deltoid (depending on the given values).
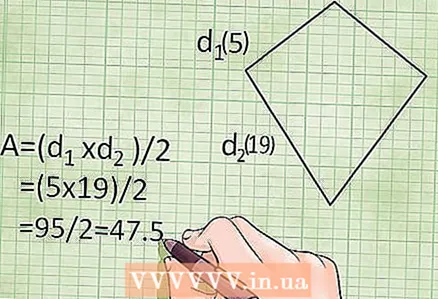 2 Find the area of a deltoid using the formula for finding the area of a rhombus (using the diagonals), since a rhombus is a special case of a deltoid in which all sides are equal. Recall that a diagonal is a line segment connecting opposite vertices.
2 Find the area of a deltoid using the formula for finding the area of a rhombus (using the diagonals), since a rhombus is a special case of a deltoid in which all sides are equal. Recall that a diagonal is a line segment connecting opposite vertices. - Area = (diagonal1 x diagonal2) / 2, or S = (d1 × d2)/2
- Example: if the diagonals of the deltoid are 19 cm and 5 cm, then the area of this deltoid is: S = (19 x 5) / 2 = 47.5 square centimeters.
- If you don't know the length of the diagonals and cannot measure them, use trigonometry to calculate them. Read this article for more information.
 3 Find the area of the deltoid using unequal sides and the angle between them. If you know the unequal sides and the angle between these sides (θ), then the area of the deltoid is calculated using trigonometry using the formula:
3 Find the area of the deltoid using unequal sides and the angle between them. If you know the unequal sides and the angle between these sides (θ), then the area of the deltoid is calculated using trigonometry using the formula: - Area = (side1 x side2) x sin (angle), or S = (a × b) × sin (θ), where θ is the angle between unequal sides.
- Example: If the sides of the deltoid are 4 cm and 6 cm, and the angle between them is 120 degrees, then the area of the deltoid is (6 x 4) x sin120 = 24 x 0.866 = 20.78 square centimeters.
- Note that you must use two unequal sides and an angle between them; if you use two equal sides and an angle between them, you get the wrong answer.
Method 4 of 4: Freeform Quadrangle
 1 If you are given a quadrilateral of arbitrary shape, then even for such quadrangles there are formulas for calculating their areas. Please note that such formulas require knowledge of trigonometry.
1 If you are given a quadrilateral of arbitrary shape, then even for such quadrangles there are formulas for calculating their areas. Please note that such formulas require knowledge of trigonometry. - First, find the lengths of all four sides. Let us denote them by a, b, c, d (but against with, but b against d).
- Example: a quadrangle of arbitrary shape with sides of 12 cm, 9 cm, 5 cm and 14 cm is given.
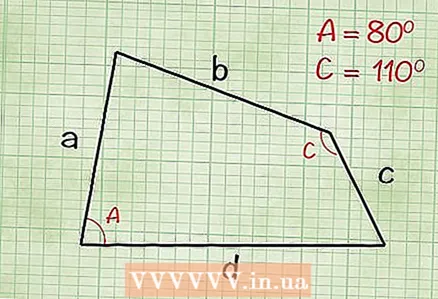 2 Find the angle A between sides a and d and the angle C between sides b and c (you can find any two opposite angles).
2 Find the angle A between sides a and d and the angle C between sides b and c (you can find any two opposite angles).- Example: in our quadrilateral A = 80 degrees and C = 110 degrees.
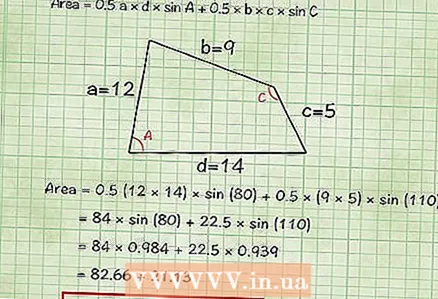 3 Imagine that there is a line segment connecting the vertices formed by sides a and b and sides c and d. This line will divide the quadrilateral into two triangles. Since the area of a triangle is 1 / 2absinC, where C is the angle between sides a and b, you can find the areas of two triangles and add them up to calculate the area of a square.
3 Imagine that there is a line segment connecting the vertices formed by sides a and b and sides c and d. This line will divide the quadrilateral into two triangles. Since the area of a triangle is 1 / 2absinC, where C is the angle between sides a and b, you can find the areas of two triangles and add them up to calculate the area of a square. - Area = 0.5 x side1 x side4 x sin (angle between side1 and side4) + 0.5 x side2 x side3 x sin (angle between side2 and side3), or
- Area = 0.5 a × d × sin A + 0.5 × b × c × sin C
- Example: you've found the sides and angles, so just plug them into the formula.
- = 0.5 (12 × 14) × sin (80) + 0.5 × (9 × 5) × sin (110)
- = 84 × sin (80) + 22.5 × sin (110)
- = 84 × 0,984 + 22,5 × 0,939
- = 82,66 + 21,13 = 103.79 square centimeters.
- Please note that if you are trying to find the area of a parallelogram (whose opposite angles are equal), then the formula will take the form: area = 0.5 * (ad + bc) * sin A
Tips
- This triangle area calculator comes in handy when calculating the area of a freeform quadrangle.
- For more information, read the articles on calculating area of a square, area of a rectangle, area of a rhombus, area of a trapezoid, and area of a deltoid.