Author:
Robert Simon
Date Of Creation:
21 June 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
We can avoid it, but sooner or later most of us will be stung or bitten by an insect. An insect bite can be quite painful and uncomfortable. Find out how to treat the bite or sting that can help ease the pain and heal the wound.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Treating Insect Bites
Leave the place of attack. Before treating the sting, go to a safe place, away from where it was stung. Determine where and how many were stung.
- Quickly and calmly leave the area.
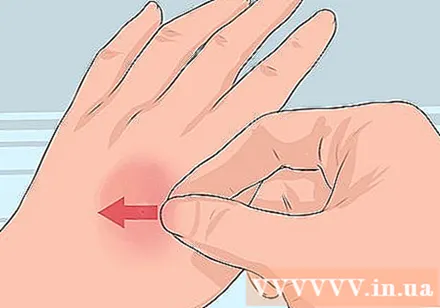
Take out the stinger. Use your fingernail or credit card to carefully pry the stinger out of your skin. Avoid taking the stinger with tweezers, as this can spread the venom.- The stinger is often spiny, which is why it can attach to the skin.
- The wasps will not leave a stinger on your skin.

Sponge. Gently wipe the wound with soap and water. Doing this will remove any potential bacteria and lower the risk of infection.- Wash the sting gently to avoid future damage.
Treat the wound. Use an over-the-counter antihistamine cream over the affected area. Use a cold compress or place an ice pack on it to ease the wound.
- Avoid scratching the injured area, even if it itches. Scratching will only further irritate the sting.
- Rub an over-the-counter hidrococtizon cream or ointment onto the wound twice a day for several days. If the wound is too itchy or swollen, take an antihistamine such as Benadry or Zyrtec. Do not take both oral medications and antihistamines together.
- For pain, try a pain reliever like ibuprofen, aspirin, or acetaminophen.
- Soak in cool water. Add 14 g of baking soda to 1 liter of water.
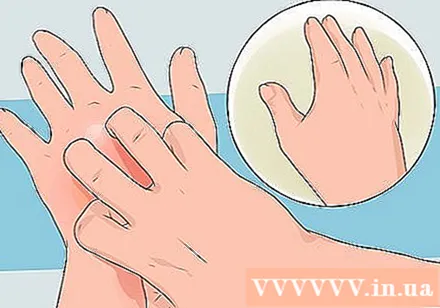
Know the symptoms of the sting. Recognize that swelling, itching, or pain are common reactions to an insect bite. Severe reactions will have symptoms such as wheezing, nausea, hives, or indigestion or difficulty breathing.- The reaction would normally be unpleasant, but not life-threatening.
- Serious reactions require emergency medical attention.
Keep track of the sting regularly. Watch for the sting if there are any negative signs. Tell your doctor right away if you experience any worse symptoms or if you think the wound is beginning to become infected.
- Signs of infection include: severe redness, swelling or pain, blistering or discharge of pus, or an extensive or streaked rash from the sting.
- Pay special attention to stings on the neck and mouth. If it swells up it can cause choking. Get immediate medical attention if this occurs.
Method 2 of 3: Handling Allergies
Find a drug or an allergist. Check with your doctor for any allergies to insect stings. Knowing the bite diagnoses will help you track and deal with the insect bites in the future.
Use an epinephrine pen if you have a severe allergy. Timely use of the epinephrine pen will help stop the life-threatening symptoms. Make sure you follow your doctor's instructions exactly when taking epinephrine.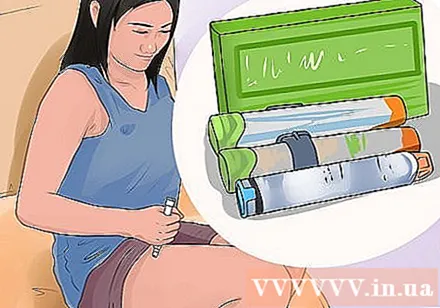
- Only a doctor can prescribe an injection pen for epinephrine.
- Ask your doctor when you should use the epinephrine pen.
- People with severe allergies should always carry the epinephrine pen when outside.
- If you begin to feel the following: chest tightness, swelling of the lips, eyelids, or throat, wheezing, hives, vomiting, dizziness or fainting, confusion, or a fast heartbeat, trouble breathing , Use a pen to inject epinephrine as soon as possible and get it to the emergency immediately.
Take antihistamines if you have a mild allergy. Take an antihistamine to reduce life-threatening reactions from an insect sting, such as swelling, itching, or redness.
- Use only according to instructions.
Give first aid to people with severe reactions. If you come across a person who has serious reactions to insect bites, take action immediately. Take first aid by following these steps:
- Ask if the person has an epinephrine pen, and if needed, also how to use it.
- Remove clothing if too tight.
- Turn the sick person upside down if they are vomiting or bleeding from their mouth.
- Keep the affected area and lower than the heart to reduce the spread of the venom.
- Call 911 and initiate CPR if the person stops breathing or is unresponsive if you have CPR training.
Method 3 of 3: Prevent Insect Stings
Wear long sleeves. Wear clothing that covers your legs and hands to limit contact with the sting. Although you can get bitten through clothing, it will protect you better than nothing.
Avoid wearing bright colors and with strong scents. Wearing clothes that are light in color or with strong scents can attract insects. Wear neutral colors and wear no perfumes when walking outside.
- Insect sprays will not work by preventing the whole nest from attacking you. However, spraying with insect repellent on your body when you have the potential to be bitten is a good idea.
Be careful. Find the nest when you go for a walk outside. Insect nests can be hung from trees or burrows emerging from the ground. Pay attention to areas on the ground where you see insects moving or flying around.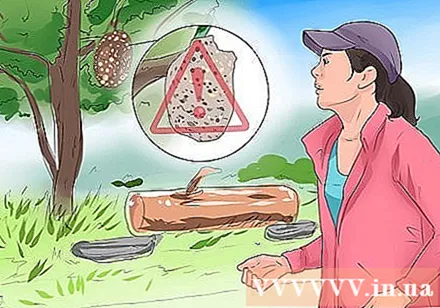
- If you see a threat, avoid it.
- Destroying the nest will be attacked by insects.
- Call a professional to get rid of wasps, wasps, or other stinging insects.
Advice
- If you know you are allergic to insect bites or stings, carry an epinephrine pen with you.
Warning
- Any unusual reaction (besides the usual itching, slightly swollen sting or pain) should be reported to your doctor immediately.
- Call emergency and use an epinephrine pen if you have one, if you know you have a history of serious allergic symptoms such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the lips, eyelids or throat, dizziness, fainting or confusion, heart beating rapid, rash, nausea, convulsions or vomiting, or if it is a minor sting by a scorpion.
- Children under 16 years of age should not take aspirin.
What you need
- Ice or cold water.
- Baking soda.
- Antihistamines.
- Ibuprofen, aspirin, or acetaminophen.