Author:
John Stephens
Date Of Creation:
28 January 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
Some plants like camellia, lupine, lily and primrose are acid-loving plants. If your garden soil is not acidic enough or has been over-applied with lime, here are some ways to slightly increase the acidity of your soil to help acid-loving plants grow well.
Steps
Part 1 of 3: Testing soil and water pH
Take the sample to a specialized agency for testing for the most accurate results. If you are serious about growing plants or want to increase soil acidity for some reason, you will find that taking soil samples to a specialist for testing is more accurate than doing it yourself at home. You probably don't think so, but the difference between 5.5 and 6.5 on the pH scale is pretty big!
- If you are in the US, contact the nearest rural development department in the county. They will help you with basic soil tests including free or very small pH measurements.

Try using a home pH meter. If you don't want to take your soil for a professional test, you can easily measure the pH of your soil at home, but note that the results will not be as accurate as the professional test results. There are several ways to get relatively accurate results at home:- Use paper tape to test the pH. This will only tell if the soil is acidic or alkaline, but it's also an interesting way that you can apply it to a variety of plants, vegetables, and herbs.
- Use vinegar and baking soda to test your pH. This method is another rudimentary way to test whether the soil is acidic or alkaline. You will take about 1 cup of soil and divide it into two containers, then add vinegar to one side and baking soda and water on the other. Observe which side is bubbling up. If the side adds effervescent vinegar, the soil is alkaline; If the side for the baking soda is bubbly, the soil is acidic.
- Buy a home pH test kit. Your home pH tester will tell you the pH of your soil in numbers. This number gives more information than the "acidic" or "alkaline" results of the above methods.
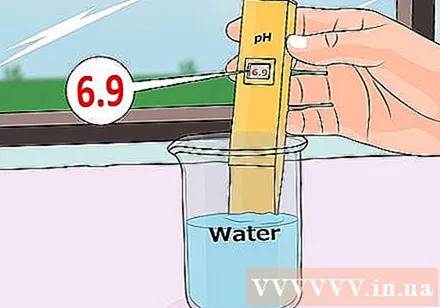
Remember to also test the pH of the water. The pH of the groundwater that you can use to water your plants is usually between 6.5 and 8.5, but is usually more alkaline so it won't corrode the pipes. If the water used to water the plants is initially alkaline and so is the soil, you will need a bit of action to give the desired acidic effect to the plant.- One way to deal with this problem is to use purified water. Pure water has a pH of 7, which is almost absolutely neutral. Using purified water is an effective way, but soon you will find it very expensive.

Know how to read the pH measurement results of the test kits you use. PH is an indicator of how acidic or alkaline a substance is. This measurement ranges from 0 to 14, where 0 is the acid pole (like the acid in the batteries) and 14 is the alkaline polarity (like drain water). PH 7 is considered "neutral" on the pH scale.- For example, if you measure a pH of 8.5, the soil is slightly alkaline. You will need to add a little acidic material to the soil to reduce the alkalinity. An index of 6.5 on the pH scale indicates that the soil is slightly acidic. If you want to add acidity, you need to add acidic material to the soil.
- If you want more detailed information, you can calculate the pH on a logarithmic scale, which means that each degree increases by 10 times. Thus, pH 8 will be 10 times more alkaline than pH 7, pH 8.5 is 15 times more alkaline, and so on.
Part 2 of 3: Increasing acidity in soil
Determine the soil type. This step is different from the step of determining the pH of the soil, and is a very important one. The method of increasing the acidity of the soil will depend on the type of soil to be treated.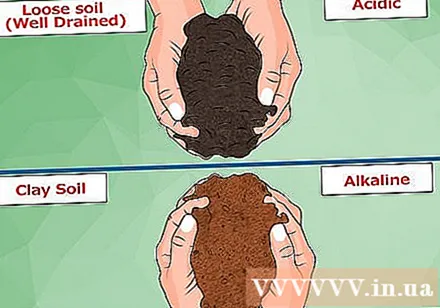
- A well drained, relatively loose soil will make it much easier to increase acidity. With these soils, you can use the vast amount of organic compounds that increase acidity as they break down.
- Clumping and compaction of clay makes the acidification much more difficult. The addition of organic matter to this soil will only do increase alkalinity, not reduced.
Apply organic materials to loose, well-drained soil. Adding organic material is the best way to increase acidity in this soil type. Organic materials increase soil acidity as they decompose, but you need to use large amounts to lower soil pH. Here are some very good organic materials that you should consider:
- Sphagnum peat moss
- Oak leaves have been aged
- Compost and manure
Apply elemental sulfur to soils of compactness or with a lot of clay. As noted above, the addition of organic material to compacted soil can worsen the situation as the soil will retain more moisture resulting in increased alkalinity. Therefore, the surest way to increase the acidity of a heavy clay soils is to apply elemental sulfur or iron sulfate to the soil.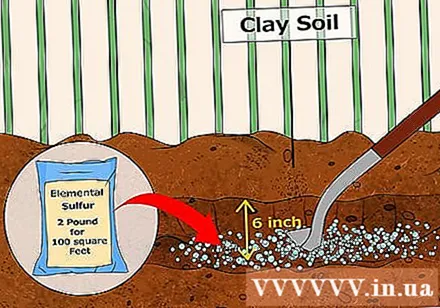
- Elemental sulfur increases soil acidity when the bacteria convert the chemical into sulfuric acid. You will need about 1kg of elemental sulfur for every 10 m2 of soil to decrease the soil pH from 7 to 4.5.
- Because elemental sulfur is slow-acting, it's best to add it to the soil about 1 year before planting for best results.
- Add elemental sulfur to the soil and dig 15 cm deep.
Add iron sulfate to compact or clay-rich soils. Iron sulfate relies on chemical reactions to form acids. Consequently, this chemical is less dependent on temperature conditions than elemental sulfur, which relies on bacteria for biological reactions.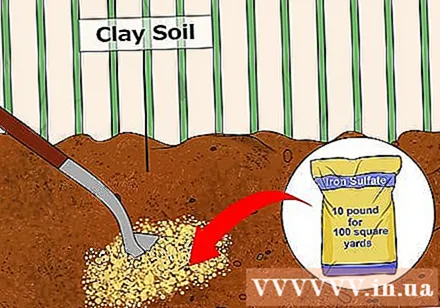
- You may need up to 5 kg of iron sulfate for every 10 m2 of soil to bring the pH down to one unit.
- If you intend to add more than 5 kg of iron sulfate for every 10 m2, you will have to divide it into two, each time spaced 1 or 2 months apart so that the soil will have time to absorb the iron sulfate.
- Iron sulfate acts much faster than elemental sulfur. This chemical can significantly lower the pH within 3-4 weeks instead of months. This means that iron sulfate has the added advantage of being able to be used in pre-planting season.
- Be careful when using iron sulfate. This chemical can stain clothing, sidewalks and yards. It is best to separate the iron sulfate-contaminated clothing and wash them separately to avoid spreading them to other items.
Use fertilizers that contain ammonia. In many cases, you just need to use fertilizers that contain ammonia. Many acid-loving plant fertilizers contain ammonium sulfate or sulfur-coated urea.
- Calcium nitrate and potassium nitrate should not be used as fertilizers, even if they do not contain ammonia. These fertilizers will actually increase the pH of the soil.
Part 3 of 3: Maintain the right pH for your plants
If you have planted plants and flowers, use elemental sulfur. This chemical works slowly so you are not afraid of taking the wrong dose. Apply elemental sulfur as much as possible to moist soil, trying not to disturb the plant's roots. Continue monitoring soil pH after a few months.
Do not follow your feelings, but put vinegar in the soil. Vinegar will reduce the pH of the soil, but in this case that's not good. The change is too sudden, disappears quickly and this will kill beneficial microorganisms in the soil. Stay away from vinegar, unless you accept the risk of lethal.
Use cottonseed residue as a fertilizer to increase acidity over a one year period. As such, assuming you've treated the soil with iron sulfate and just planted blueberries, you can maintain a low pH by adding large amounts of natural fertilizers like cottonseed residue. Cottonseed residue, a byproduct of the cotton production process, is especially beneficial for acid-loving crops such as azaleas and camellia.
Test the pH at least once a year. Check the pH of the soil near the base of the plant, add fertilizers like aluminum sulfate (especially hydrangeas) and avoid damaging the roots. For best results, use a commercial pH test kit or submit a soil sample for expert testing.
- Most vegetables and ornamental plants prefer a mildly acidic environment between 6.5 and 6.8.
- Hydrangeas, azaleas, and blueberries prefer a more acidic environment - about 5 -5.5.
Increase soil pH with lime if necessary. In some cases, your efforts to increase soil acidity have proved so effective that the acidity is too high for vegetables and plants. You will then need to increase soil alkalinity by adding lime. Lime comes in three basic types - limestone, quick lime / hydrated lime, also known as hydrated lime - and the dosage to be used will depend on the type of soil as well as the type of lime you choose. You can read the instructions on the packaging or talk to the gardeners for more information. advertisement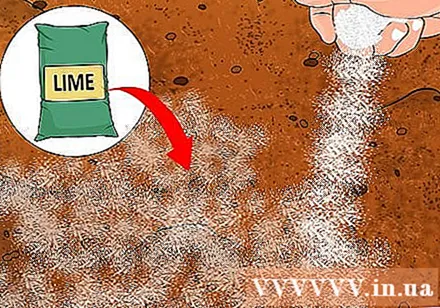
Advice
- Sulfur flower is a pure and fine sulfur powder. These chemicals can be purchased at gardening centers or online.
- Iron salts are also helpful; Soils that are too alkaline can "lock down" iron, preventing iron from reaching plants in need. You should also wait for the results of your first treatment before adding more iron.