Author:
Laura McKinney
Date Of Creation:
2 August 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
In algebra, the two-dimensional coordinate graph has the horizontal horizontal axis, also known as the x-axis, and the vertical vertical axis, also known as the y-axis. Where the lines representing a series of values intersect these axes is called the intersection. The junction of the function with the vertical axis is the position where the line intersects the y-axis, and the point x of the function with the horizontal axis is where the line intersects the x-axis. For simple problems, it is easy to find the x intersection of the function with the horizontal axis by looking at the graph. You can find the exact intersection point by solving math problems using the equation of the line.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Use a straight line graph
Determine the x-axis. The coordinate graph will have both the x-axis and the y-vertical axis. The x-axis is the horizontal line (the line from left to right). The y-axis is the vertical line (the straight line going up and down). It is important that you look at the x-axis when determining the intersection x.

Find the position of a line that intersects the x-axis. This is the intersection point x. If you are asked to find the point of intersection x based on the graph, this will usually be the correct number (for example, at point 4). Usually, however, you will have to make an estimate using this method (for example, the point is somewhere between 4 and 5).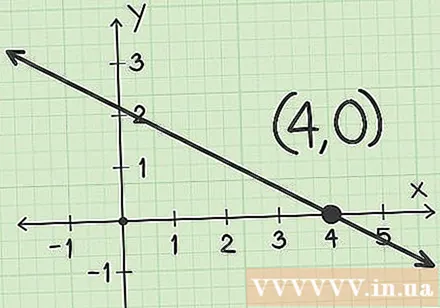
Write down pairs of values for intersection x. Value pairs are written in the form and give you the coordinates of the intersection. The first number of the pair is the intersection point where the line intersects the x-axis (the intersection of the function with the horizontal axis). The second number will always be 0, because on the x-axis there will be no y value.- For example, if the line intersects the x-axis at point 4, the pair of values for the x-intersection of the function with the horizontal axis is.
Method 2 of 3: Use the equation of the line

Determine that the equation of the line is the standard form. The standard form of linear equations is. In this form,,, and are integers, and are the coordinates of the intersection point on the line.- For example, you can have equations.
Set to 0. The intersection point of the function with the horizontal axis is the intersection point of the line and the horizontal axis x. At this point, the value of will be 0. So to be able to find the x intersection of the function with the horizontal axis, you need to set it to 0 and solve it.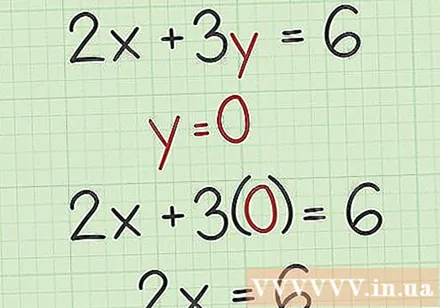
- For example, if you substitute 0 for, your equation will take the form:, the simplification would be.
Solve search. To do this, you need to isolate the variable x by dividing both sides of the equation by coefficients. This method will give you the value of when, and this is the intersection of the function's x with the horizontal axis.
- For example:
- For example:
Write down pairs of values. You should remember that value pairs are written as. For the x intersection, the value of will be the value you calculated earlier, and the value will be 0, since it will always be 0 at the intersection of the function with the horizontal axis.
- For a line, for example, the intersection point x would be at the point.
Method 3 of 3: Use the quadratic equation
Determine that the coordinates of the line are a quadratic equation. A quadratic equation is an equation of form. It has two solutions, which means that the line written in this form is a parabola and there will be two intersections with the horizontal axis.
- For example, the equation is a quadratic equation, so this line will have two intersections with the horizontal axis.
Set up the formula for the quadratic equation. The formula is, where it equals the coefficient of the quadratic root (), is equal to the variable of the first root (), and is the constant.
Plug all the values into the quadratic formula. Remember to make sure that you substitute the correct values for each variable of the equation of the line.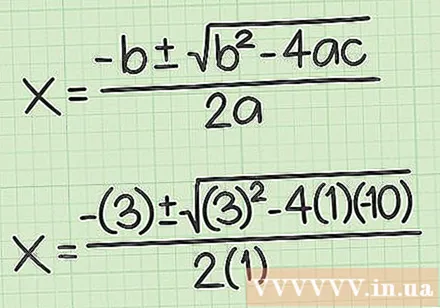
- For example, if the equation for the line is, your quadratic formula will take the form:.
Simplify the equation. To do this, you need to first complete all multiplication. Remember to pay attention to any positive and negative number signs.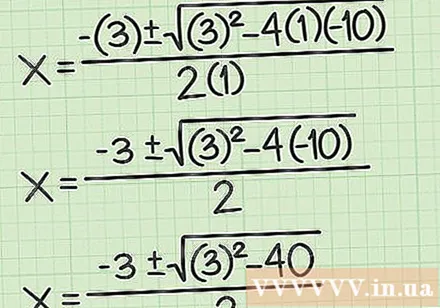
- For example:
- For example:
Exponentiate. Square the solution. Then add it to the remaining number below the square root sign.
- For example:
- For example:
Solve the addition formula. Because the square root formula does, you need to do an addition problem and a subtraction problem. Solving the addition problem will help you find the value.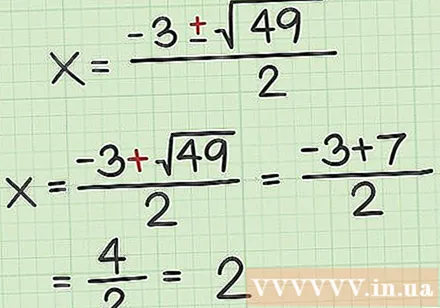
- For example:
- For example:
Solve the subtraction formula. It will give you the second value of. First, calculate the square root, then find the difference in the numerator. Finally, divide it by 2.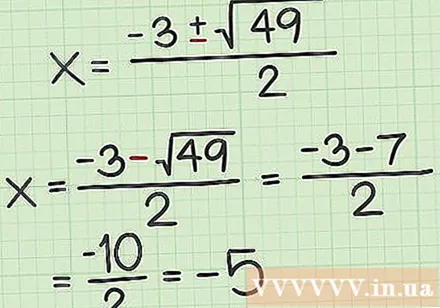
- For example:
- For example:
Find a pair of values for the x intersection of the function with the horizontal axis. You should remember that a pair of values will have the first x, followed by the y coordinate. The value will be the value that you calculated using the square root formula. The value will remain 0, because at the intersection of x with the horizontal axis, it will always be 0.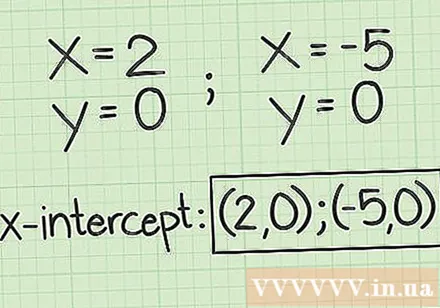
- For a line, for example, the x intersection of the function with the horizontal axis lies at and.
Advice
- If you are working with an equation, you need to know the slope of the line and the y intersection of the function with the vertical axis. In the equation, m = slope of the line and b = intersection of the function y with the vertical axis. Let y equal 0, and solve for x. You will find the x intersection of the function with the horizontal axis.



