Author:
Peter Berry
Date Of Creation:
15 February 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
This wikiHow teaches you how to activate, create, execute, and save macros in Microsoft Excel. Macros are small programs that allow users to perform complex tasks like calculating formulas or creating charts in Excel. Macros can save you considerable time doing repetitive operations, and thanks to the "Record Macro" feature, you can still create macros even though you know nothing about programming.
Steps
Part 1 of 4: Enabling macros
Open Excel. Double-click the Excel app icon with a white "X" in the green box, then click Blank workbook (New spreadsheet set).
- If you want to open a specific file in Excel, double-click it.
Click the card File (File) in the upper left of the Excel window.- On a Mac computer, click the card Excel in the upper left corner of the screen to open a drop-down menu.
Click Options (Option). This item is on the left side of the Excel window.
- On a Mac computer, click Preferences ... (Custom) in the drop-down menu.
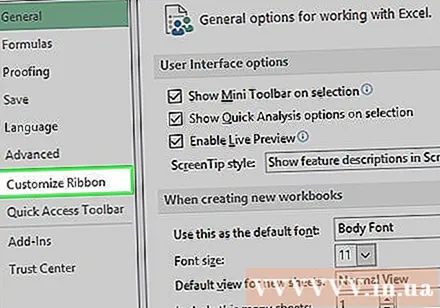
Click Customize Ribbon (Customize the ribbon). The option is on the left side of Excel's Options window.- On a Mac computer, click Ribbon & Toolbar (Toolbars & ribbons) in the Preferences window.
Check the "Developer" box. This box is near the bottom of the "Main Tabs" drop-down list.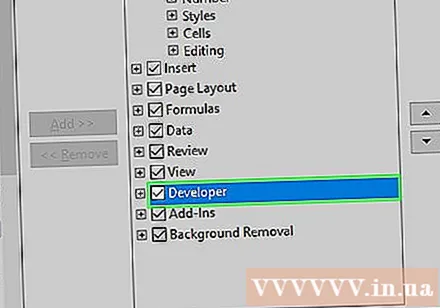
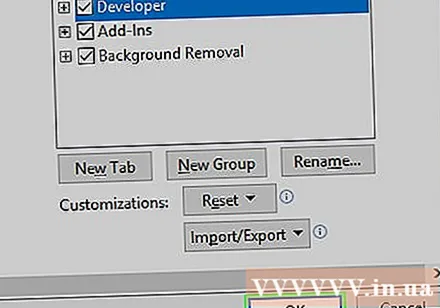
Click OK near the bottom of the window. Now you can use macro commands in Excel.- On a Mac computer, click Save (Save) here.
Part 2 of 4: Recording macros
Enter the required data. If you have a blank set of workbooks open, enter all of the data you want to use before proceeding.
- You can also close Excel and double-click the file to open the specific workbook.
Click the card Developer at the top of the Excel window. A toolbar will open here.
Click an option Record Macro located in the toolbar. A window will pop up.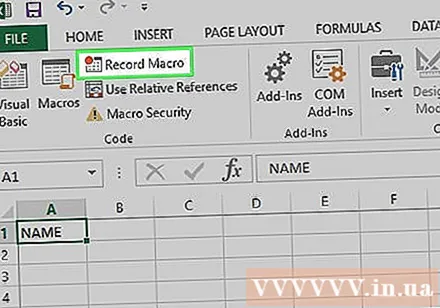
Enter a name for the macro command. In the "Macro name" text box, enter a name for the macro command. This will help you to recognize the macro command later.
Create keyboard shortcuts (if you like). Press ⇧ Shift along with certain character keys (for example: E) to create keyboard shortcuts. You can use this key combination to execute macro commands later.
- On a Mac, the keyboard shortcut will contain keys ⌥ Option+⌘ Command and character (for example: ⌥ Option+⌘ Command+T).
Click the "Store macro in" drop-down box. This frame is in the middle of the window. A drop-down menu will appear.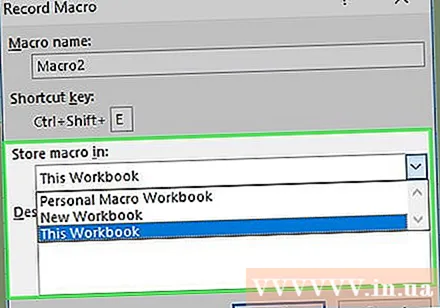
Click This Workbook (Gather this spreadsheet). This option is in the drop-down menu. The macro commands will be integrated into this spreadsheet, and anyone with the file will be able to use the macro.
Click OK at the bottom of the window. The settings of the macro command are saved, and recording starts.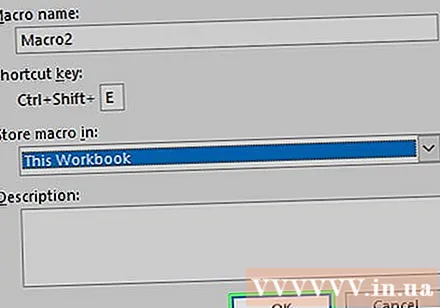
Follow the steps of the macro. Any action that you have performed since clicking OK until clicked Stop Recording (Stop recording) will all be added to the macro. For example, if you want to create a macro of manipulation of data values in two columns into a chart:
- Click and drag the mouse over the data to select it.
- Click Insert (Insert)
- Select a chart shape.
- Click the chart you want to use.
Click on the action Stop Recording located in the toolbar Developer. The macro command will be saved. advertisement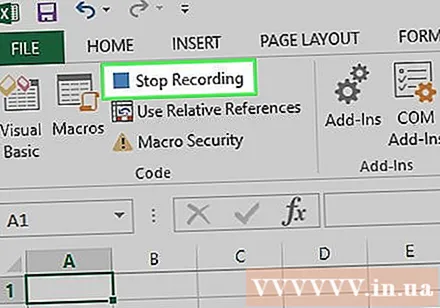
Part 3 of 4: Save the macro enabled workbook
- You need to understand why we need to save the workbook with the macro enabled. If you don't save as macro-activated workbook (XLSM format), the macro command will not be saved as part of the file, meaning users on another computer will not be able to use the macro command if you send the workbook to surname.
Click File in the upper-left corner of the Excel (Windows) window or the desktop (Mac). A drop-down menu will appear.
Click Save As (Save as). This option is on the left side of the window (Windows) or in the drop-down menu (Mac).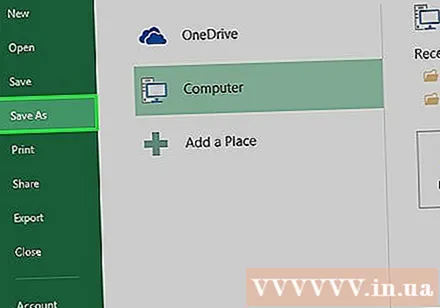
Double-click This PC (This computer). The option is in the location column to be saved near the left side of the window. The "Save As" window will open.
- Skip this step on a Mac computer.
Enter a name for the Excel file. Enter a name for the Excel spreadsheet in the "Name" text box.
Convert the file format to XLSM. Click the "Save as type" drop-down box then select Excel Macro-Enabled Workbook (Set of macro-enabled spreadsheets) in the drop-down menu that appears.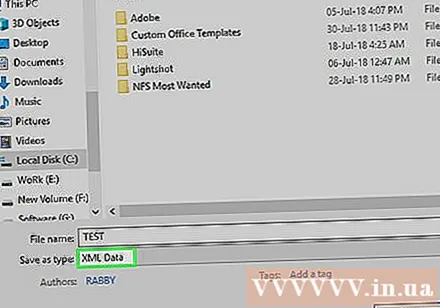
- On a Mac, you'll need to replace the "xlsx" extension at the end of the filename xlsm.
Select a save location. Click the folder where you want to save the Excel file (for example: Desktop).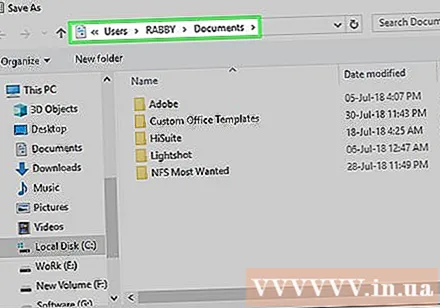
- On a Mac, you need to first click the "Where" drop-down box.
Click an option Save at the bottom of the window. The Excel spreadsheet with macro commands will be saved to the location of your choice. advertisement
Part 4 of 4: Executing macros
Open the spreadsheet that activates the macro. Double-click the integrated macro spreadsheet to open it in Excel.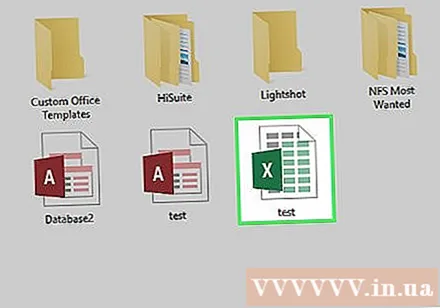
Click Enable Content (Activate content). Options are in the yellow bar at the top of the Excel window. The spreadsheet will unlock and allow you to use a macro command.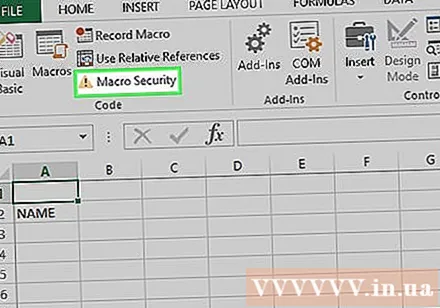
- If you don't see the option above, skip this step.
Click the card Developer at the top of the Excel window.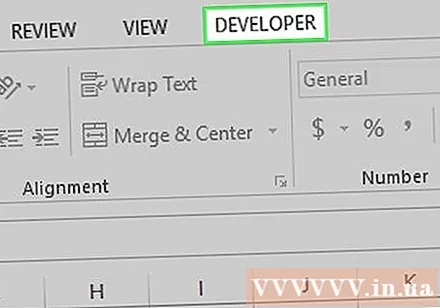
- Or you can press the key combination that is already set up for a macro command. If you choose this option, you can skip the rest of the method.
Click an option Macros in the toolbar of the card Developer. A window will pop up.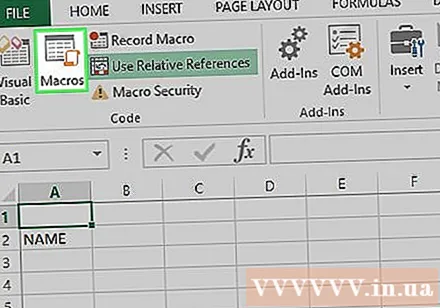
Select a macro command. Click the name of the macro command you want to execute.
Click on the action Tremor (Execute) is on the right side of the window. The macro command will start to execute.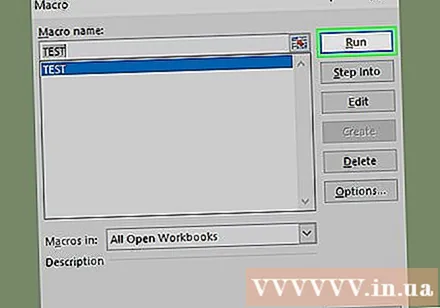
- Wait for the macro command to complete. Depending on the length of the macro command, this may take a few seconds. advertisement
Advice
- Macros are often useful for automating tasks that you must perform frequently, such as payroll calculation on weekends.
Warning
- While most macro commands are harmless, a few can make dangerous changes or erase information on a computer. Never open a macro from an untrusted source.



