Content
Rounding makes numbers look shorter. Although rounded numbers are less precise than the original numbers, rounding is imperative in many situations. Depending on the situation, you may need to round up to decimal or whole numbers. Here are the steps to guide you through.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Round a decimal
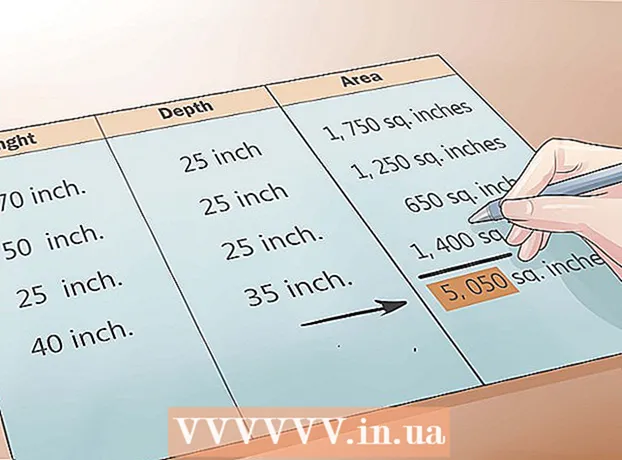
Determines the value of the row of digits to be rounded. This can be ordered by your teacher if you are doing a math exercise, or you can define it based on the context and the units you are using. For example, when rounding money, you will usually round to the nearest thousand. When rounding off a weight, round it up to the nearest kilo.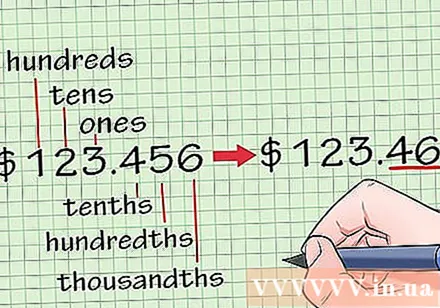
- The less precision a number requires, the more rounding you can round (to higher digit rows).
- The more exact number will be rounded to the lower digit rows.

Determine the value of the row of digits that you will round. Let's say you have numbers 10,7659, and you want to round to a digit in the thousandth place, that is, a number 5, third digit to the right of the decimal point.
Specifies the number to the right of the rounding number. Consider only one digit to the right. In this case, you will consider the number 9 next to the number 5. This number will decide 5 will be rounded up or down.
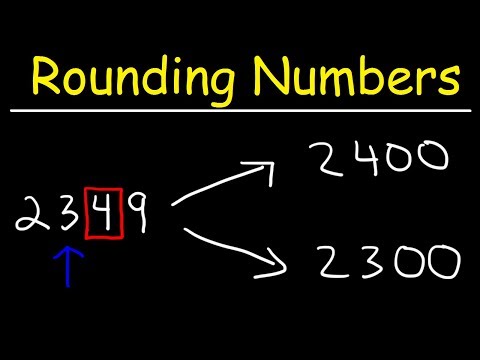
- Round up if the right digit is greater than or equal to 5. The rounded digit will be larger than the original. Your initial digit is 5 will become 6. All numbers to the left of the number 5 the original will remain the same, and the numbers to the right will be discarded. So number 10,7659will be rounded to 10,766’.

- Although 5 is the number between the digits 1 through 9, it is a convention that the number before it must be rounded up. However, this may not apply to year-end school scores!
- When the rounded digit is 5, look at the digits to the right of it. If the next digit is nonzero, round up. If all subsequent digits are 0 or no additional digits are added, round up if the rounded digit is an odd number, and round down if the rounding digit is an even number.

Rounds down if the right digit is less than 5. If the number to the right of the row to be rounded is less than 5, the number in the rounding row will remain. Although this is called rounding down, it just means that the number in the rounded row will stay the same; you must not transfer it to a lower gear. In the case of numbers need to be rounded 10,7653You will round down as well 10,765 because of the number 3 to the right of 5 less than 5.- By keeping the number in the rounding row and converting all numbers to its right to 0, the final rounded number is smaller than the original number. Thus, considering the overall number is smaller.
- The above two steps are shown on most desktop computers as 5/4 rounding. You can use the slide-switch button to switch to the 5/4 rounding position to get these results.
Method 2 of 3: Round an integer
Round to the nearest tens digit. To do this, simply consider the digit to the right of the tens digit of the rounding digit. The tens is the second digit from the last digit in a number, before the unit digit. (If you have 12, consider number 2). Then, if the number is less than 5, keep the number rounded; If it is greater than or equal to 5 round up one digit. Here are some examples: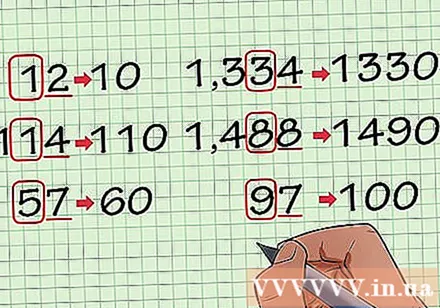
- 12 -> 10
- 114 -> 110
- 57 -> 60
- 1334 -> 1330
- 1488 -> 1490
- 97-> 100
Round to the nearest hundred digit. Follow the same steps as for rounding to the nearest hundred digit. Consider the hundreds digit, which is the third digit from the last number in a number, immediately before the tens digit. (In the number 1234, 2 is the hundreds digit). Then, use the number to the right of the hundreds digit, that is, the tens digit, to see if you're going to round up or down, converting the numbers after it to 00. Here are some examples. :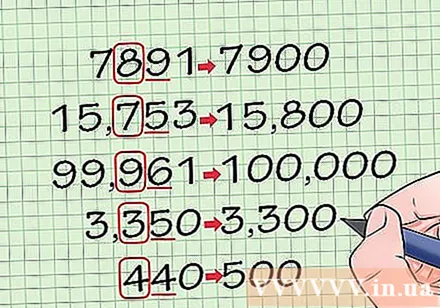
- 7 891 - > 7 900
- 15 753 -> 15 800
- 99 961 -> 100 000
- 3 350 -> 3 300
- 450 -> 500
Round to the nearest thousands digit. Same rule as above applies. Just know how to determine the thousands, which is the fourth digit from the bottom up, and then look at the number in the hundreds, that is, the number to the right of the number. If the digit is less than 5, round it down, and if it is greater than or equal to 5, round up. Below are a few examples:
- 8 800 -> 9 000
- 1 015 -> 1 000
- 12 450 -> 12 000
- 333 878 -> 334 000
- 400 400 -> 400 000
Method 3 of 3: Round by the number of significant digits
Understand what a "significant digit" is. Simply think digit means "interesting" or "important" digit that gives you useful information about a number. This means that any zeros to the right of the integer or to the left of the decimal number do not count as significant digits. To find the number of significant digits in a number, simply count the number of digits from left to right. Here are some examples:
- 1,239 has 4 significant digits
- 134.9 has 4 significant digits
- 0.0165 has 3 significant digits
Rounds a number according to the number of significant digits. This depends on the problem you are considering. If you want to round a number down to two significant digits, then you will need to identify the second significant digit of that number and then use its right digit to see if you will round it. down or up. Here are some examples:
- 1.239 rounded to 3 significant digits 1.24. This is because the number to the right of the third digit (3), 9, is greater than 5.
- 134.9 rounded to 1 significant digit 100. This is because the right-hand digit of the hundreds (1) number is 3 less than 5.
- 0.0165 rounded to 2 significant digits 0.017. This is because the second significant figure is 6, and the number to the right of it is 5 making it rounded up.
Round to the exact number of significant digits in addition. To do this, you will first have to add up the numbers given. You will then have to find the number with the smallest number of significant digits and then round the entire answer down to that number of significant digits. Here's how to do it:
- 13,214 + 234,6 + 7,0350 + 6,38 = 261,2290
- See that the second number, 234.6, is only accurate to the tenth, or four significant digits.
- Round off your answer so that it is correct to the tenth. 261,2290 becomes 261.2.
Round to the exact number of significant digits in the multiplication. First, multiply all the numbers given. Then check which number is rounded to the least significant number of digits. Finally, round up your final answer to match that number's precision. Here's how to do it: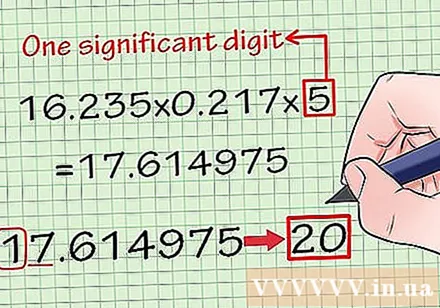
- 16,235 × 0,217 × 5 = 17,614975
- Note that the number 5 has only one significant digit. That means that your final answer will also have only one significant number.
- 17.614975 rounded to one significant digit becomes 20.
Advice
- You can omit trailing zeros after rounding up the values of the row of digits to the right of the decimal point. Zeros after the decimal do not change the value of the number so they can be deleted. However, this is not true for the zeros to the left, or before the decimal point.
- After finding the value of the row of digits that you will round, underline it. This helps to minimize confusion between the number you are about to round with the number to the right of it. The right digit plays a role in determining the fate of the rounded digit.
- One most recent method of rounding a number is to round up if the value that preceded it was greater than 5. Rounds down if the number that preceded it was less than 5. If the number that preceded it was 5, round up ONLY if the number is becomes an even number, NOT an odd number.
The importance of rounding
The rounding method becomes important in problems / computations where error plays an important part, such as calculations involving measurements performed by screw or caliper rulers, etc. Under such circumstances error is inevitable due to the method of measurement being carried out by different users. Values with tolerance result in greater error when performing calculations. Some errors are exponential and others exponential. Thus the error should be minimized as much as possible, otherwise it will lead to unwanted confusion and meaningless accuracy. For example, if a calculation is performed between two numbers with an error range of +/- 0.003 then the third point after the decimal point is uncertain, so the third point after the decimal point in the result becomes. meaningless. This can be avoided by rounding the result.
Warning
- Be cautious when reading the numerical values in decimal numbers. The spelling of the digits to the right and left of the decimal point is the same, but the reading is different. To the left of the decimal point we read is the row of units, tens, hundreds, and so on, but to the right of the decimal point we read is the tenth position, the percent position, and so on.