Author:
Louise Ward
Date Of Creation:
10 February 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024
Content
Modern versions of Word contain most of the symbols and structures that a math professor needs. You can type quickly with keyboard shortcuts or look in an equation menu of your choice. The operation is a bit different if you use a Mac, or Word 2003 or earlier. Note that the old "Add Object" method from Word 2003 doesn't have new icons, you can purchase the MathType extension if you prefer.
Steps
Method 1 of 4: Use the keyboard: Microsoft Word 2007 to type equations
Press Alt and "=". This will insert an equation at the position of your cursor and open the editor.

Insert letters by typing. The English letters correspond to the variables, you just need to tap the keyboard to insert the text.
Insert symbols by typing symbolic name. If you know the name of the symbol, simply type the symbol name after the . For example, for the Greek letter theta, type theta and press the spacebar to convert the character.

Use the SPACEBAR to switch equations just typed. Note in the previous step, only when you press the spacebar will the symbol be converted, similar to when processing the equation.
Insert fractions with /. For example, typing a / b (press the spacebar) will have the fraction a above b.

Expression groups use parentheses (). Parentheses (), are used to group parts of an equation in the editor. For example, when you type (a + b) / c and press the spacebar, you will have the fraction a + b over c, without the parentheses displayed.
Use _ and ^ to insert subscript and superscript. For example a_b turns b into the subscript of a, whereas a ^ b turns b into the exponent of a. The indexes above and below can be used at the same time, which is how to add an integral limit, for example type int_a ^ b and press the spacebar, we get an integral equation from a to b.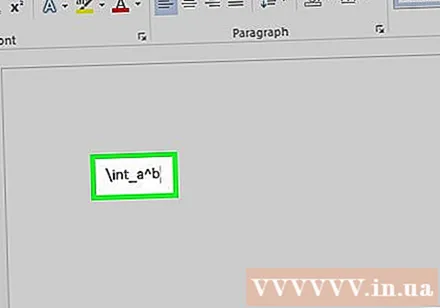
Insert a function by pressing the spacebar after the function name. You can type the trigonometric functions sine, arctan, log, and exp, but press the spacebar after the function name for the editor to recognize it as a function.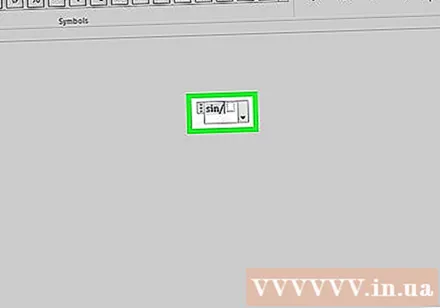
Change the font. You can change the font. To use bold or italic, press the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+B or Ctrl+I. To make the word in the equation normal, enclose it in quotes. To turn a character into an index, you use script, for example, scriptF will turn F into index.
Find other keyboard shortcuts. Typing equations is much faster than selecting symbols and structures from a menu, but you need to know the keyboard shortcut. With the steps above, you can guess most of the shortcuts to use. advertisement
Method 2 of 4: Microsoft Word 2016, 2013, 2010, or 2007
Select the Insert tab on the control menu. A driver is a horizontal menu between the document name and the text. Find the Insert tab in the first row and click on it.
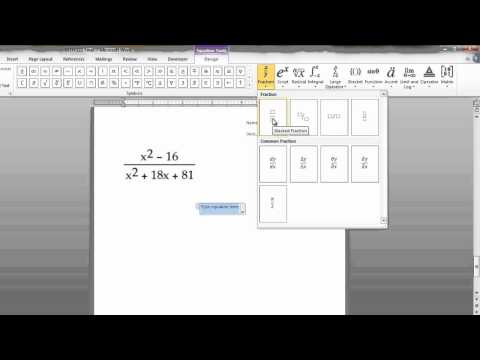
Find the Equation button in the right corner. The Insert menu has many options, but we only need to consider the Equations section with the big π (pi) symbol on the right, in the "Symbols" group.
Click on the icon to insert the equation. A dialog box will appear at the cursor position. You can always type to start the equation, or go to the next step to see more options.
Insert special format. When you click the Equations icon, the driver will display a large panel of new options. Go through the options to find the symbol you want, then complete the equation. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Click the Script icon to open the drop-down menu. Hover your mouse over each button and you will see tooltip text.
- Select the basic indicator option, the equation will appear 2 squares, one on one below: □□
- Click the first square and type in the value you want to display: 5□
- Click in the 2nd square and type the metric value: 53
Continue typing to complete the equation. If you don't need any special formatting, just enter a number to expand the equation. Word automatically inserts spaces and italics.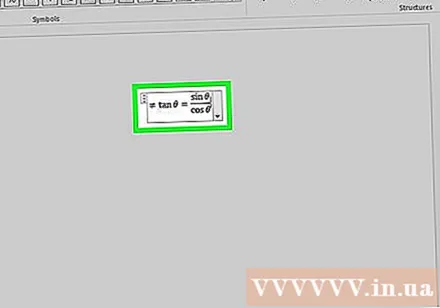
Change the position of the equation. Select the equation dialog and you will see a tab with an arrow to the right. Click the arrow to display display options, including centering, left alignment, and right alignment of the equation.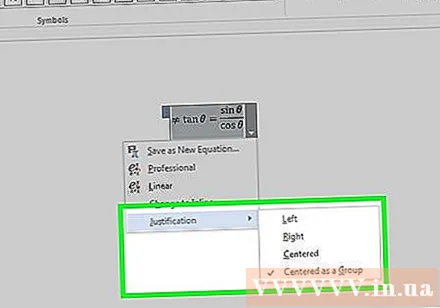
- You can bold the equation text and change the font and style as usual.
Enter equations manually (Word 2016 only). If you're using Word 2016, you can create "equations" by drawing with the mouse or the touchscreen tool. Select Ink Equation in the Equations menu to get started. advertisement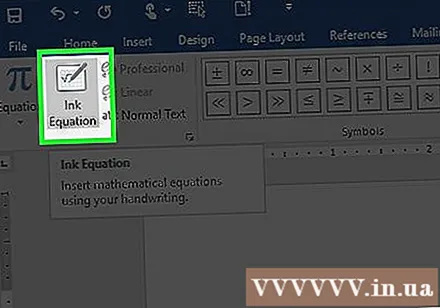
Method 3 of 4: Office for Mac 2016 or 2011
Select the Document Elements tab. This tab is on the controls menu, just below the top row of icons.
Select Equations in the right corner. When you select Document Elements, the Equation option will be in the right corner with the π icon. There are 3 options as follows:
- Click the arrow next to the Equations icon to open a menu of common equations.
- Click the arrow> New Equation to type it yourself.
- Click on the icon to open a larger menu containing the driver's equation options.
Use the top menu. If you like the top menu, select "Insert", scroll down and choose "Equation".
- The right mouse pointer is placed in an empty position in the text before you can access this command. (For example, if an object is selected, the command will be greyed out.)
Choose display options. Click the down arrow to the right of the Equation dialog. You will see a new menu with options for displaying equations.
- This menu includes the "save as new equation" command, handy if you use it frequently. This command will add the selected equation to the drop-down menu when you click the arrow next to the Equations icon.
Method 4 of 4: Microsoft Word 2003
Learn the limit. You cannot edit equations in Word 2003 or earlier. If you collaborate with other Word users, it's best to upgrade to the recent version.
Insert an equation. From the top menu, select Insert → Object → Create New. If you see "Microsoft Equation 3.0" or "Math Type" in the Objects list, click to insert a symbol. If you don't see it then go to the next step.
- After inserting an equation, a small window with many symbols will appear. Click and select the symbol to add to the equation.
- Word 2003 does not have the same formatting options as later versions. Some of the equations displayed are not very professional.
Install extensions if necessary. If the Word 2003 version does not have the utilities mentioned above, you should install it. It's not easy to find this utility, but with luck, the installation package is already on your computer:
- Close all Microsoft Office programs.
- Go to Start → Control Panel → Add or Remove Programs.
- Select Microsoft Office → Change → Add or Remove Features → Next.
- Click the + icon next to Office Tools.
- Select Equation Editor, then select Run, then click Update.
- Follow the instructions on the screen. If you're out of luck, you may have to use the Word 2003 installation disc.
Advice
- To type the second line of the equation, press Shift + Enter. Pressing Enter will exit the equation or create a new equation, depending on which version of Word you're using.
- Office 365 subscription services typically include the latest version of Word. Follow the instructions for the new versions that are compatible with your operating system.
- If using Word 2007 or a later version and want to edit text created in Word 2003 or earlier, use the File → Convert command to unlock equations and editing functions. other.
Warning
- If you save text in .docx format, users of Word 2003 or earlier cannot edit the equation.