Author:
Lewis Jackson
Date Of Creation:
6 May 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024
Content
Also known as otomycosis or "swimming ears", fungal ear infections mainly affect the ear canal. Ringworm of the ear canal accounts for 7% of all diagnosed cases otitis externa, that is, inflammation and infection of the ear canal. The most common cause of this disease is a fungal infection Candida and Aspergillus. Fungal ear infections are often confused with bacterial ear infections. Doctors often prescribe antibiotics, but antibiotics do not cure the fungus, so the disease does not change. Your doctor can then teach you a few home remedies and prescribe some antifungal medications.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Recognize the symptoms of fungal ear infections

Recognize unusual itching (pruritis). Itchy ears are also quite common. Hundreds of tiny hairs on the ear and inside the ear can be easily stimulated. However, if the itching continues and doesn't get better with scratching or rubbing, you may have a fungal ear infection. This is the main symptom of ear fungus.
Recognize ear pain (otalgia). You will most likely have pain in one ear - not in both ears, as the fungus is often infected locally. Sometimes the patient describes it as being "angry" or "full". The pain can be mild or severe, and usually intensifies when touched.
Check for ear discharge (otorrhea). Fungal ear discharge is usually thick, can be clear or white, yellow, and sometimes blood / foul-smelling. Do not be confused with earwax. Take a cotton swab and wipe the inside of the ear (be careful not to stick the tip of the cotton swab into the ear canal). Earwax usually builds up inside, but if the amount and color seems abnormal, you may have a fungal infection in the ear.
Check for hearing loss. Fungal ear infections can manifest through hearing muffled sounds or voices, difficulty understanding what others say, and hearing consonants. Sometimes people recognize hearing loss through a change in behavior. Chronic disappointment is the result of impaired hearing, withdrawing the person from conversation and social interaction. advertisement
Method 2 of 3: Use of drugs
Know when to see a doctor. When you have ear infections, it's best to see your doctor for an accurate diagnosis and to find the optimal treatment. If you experience severe pain, loss of hearing ability or any other unusual symptoms, you should seek professional help.
- Your doctor can help clean your ear canal with a suction device and prescribe medication for ear infections.
- Your doctor may also suggest you buy over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribe pain relievers if you have severe pain.
Use clotrimazole to treat fungal infections in the ear. Clotrimazole 1% solution is the most commonly used antifungal medication that doctors prescribe to treat fungal ear infections. This drug kills both fungi Candida and Aspergillus. Clotrimazole works by inhibiting the enzymes that have an ergosterol-converting effect. Ergosterol is essential for the maintenance of the integrity of fungal cell membranes. Fungal growth will be inhibited by an ergosterol deficiency.
- Watch for clotrimazole side effects. These side effects include irritation, burning, or discomfort. However, the topical clomatrizole is not as likely to cause side effects as the oral form.
- To use clotrimazole, wash your hands under running water with mild soap. Wash the ears with warm water until all any visible fluid is gone. Gently pat your ears dry with a clean towel. Do not wipe too hard, as doing so may worsen the condition.
- Lie down or tilt your head to the side to expose the ear canal. Straighten your ear canal by pulling your earlobe down, then back. Put two or three drops of clotrimazole in the ear. Tilt the ear for 2-3 minutes to let the solution run into the affected area. Then tilt your head to let the medicine drain.
- Cover the medicine vial and store it out of the reach of children. Store in a cool, dry place. Avoid direct sunlight and high temperatures.
- If clotrimazole doesn't work, your doctor may prescribe another antifungal medicine, such as miconazole.
Use the medicine fluconazole (Diflucan) prescribed by your doctor. If your fungal infection is more severe, your doctor may prescribe fluconazole. This drug also works similarly to clotrimazole. The most common side effects are headache, nausea, dizziness, change in taste, loose stools, abdominal pain, skin rash, and elevated liver enzymes.
- Fluconazole comes in the form of tablets. Doctors usually prescribe a dose of 200 mg for one day, then 100 mg per day for 3 to 5 days.
Avoid antibiotics. Antibiotics are only effective in treating bacterial infections, so they are ineffective against fungi.
- Antibiotics can even aggravate fungal ear infections because they can kill beneficial bacteria in the ear or other parts of the body - the bacteria that help you fight off a fungal infection.
Seek re-examination. You will have to see your doctor again in about a week to see if the treatment is working. If not, your doctor may try another option.
- Also, make sure to contact your doctor if your symptoms get worse or don't get better.
Method 3 of 3: Use home remedies
Use hydrogen peroxide. Use a medical dropper to place 2-3 drops of hydrogen peroxide in the inflamed ear. Leave in the ear canal for 5-10 minutes, then tilt your head to let it drain. This therapy will help soften scales or debris that hardens in the ear canal, thereby helping to wash the fungus out of the ear.
Use a hair dryer. Turn on the hair dryer on the lowest setting and keep at least 25 cm away from the inflamed ear. This method helps dry the moisture in the ear canal, which hinders the growth of fungus.
- Be careful not to burn your ears.
Apply a warm compress to the affected ear. Use a clean towel and soak it in warm water. Make sure the towel is not too hot. Place a warm towel over the inflamed ear and wait until it cools down. This method helps relieve pain without using pain relievers, and at the same time stimulates blood circulation to the affected area, helping to heal.
Use rubbing alcohol and apple cider vinegar. Mix the mixture with a ratio of 1: 1. Use a medical dropper to place a few drops in the inflamed ear. Leave the solution in your ear for 10 minutes, then tilt your head to let it drain. You can use this therapy every 4 hours, up to 2 weeks.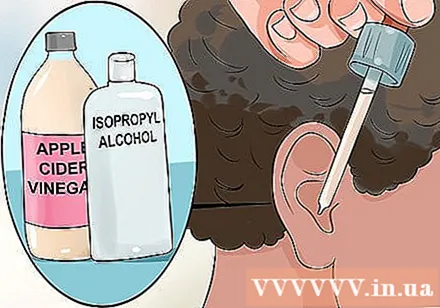
- Rubbing alcohol is a volatile substance that can help remove the warmth in the ear canal that is the cause of a fungal infection. Alcohol also disinfects the skin in the ear canal. The acidity of the vinegar slows down the growth of fungi, because of both fungi Candida and Aspergillus all grow better in "alkaline" environments.
- This mixture has an antiseptic and drying effect on the ears, reducing the time spent on infections.
Eat foods rich in vitamin C. Vitamin C is essential for the growth and repair of tissues damaged by a fungal infection. Vitamin C also helps the body produce collagen, a protein that makes up tissues such as skin, cartilage and blood vessels. Doctors recommend taking a vitamin C supplement in doses of 500 to 1,000 mg per day with food.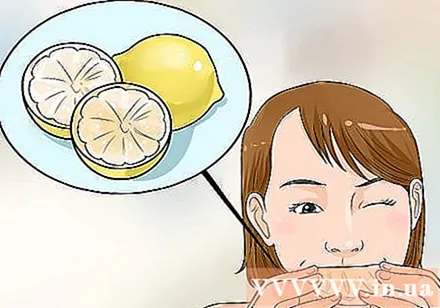
- Good food sources of vitamins include citrus fruits (oranges, lemons, lemons), berries (blueberries, cranberries, strawberries, raspberries), pineapple, watermelon, papaya, and broccoli. greens, spinach, baby cabbage (Brussel sprouts), cabbage, and cauliflower.
Use garlic oil. Take a capsule of garlic oil, puncture it and drop it into the inflamed ear. Leave on for 10 minutes, then tilt your head to let it drain. This therapy can be used daily for up to 2 weeks. Studies show that garlic oil has anti-fungal effects Aspergillus (one of the two main fungi that cause ear infections).
- What's more, garlic oil is also said to have equal or better effects than prescription medications for fungal ear infections.
Use olive oil to clean the ears. If you have a yeast infection, a white or yellow discharge will appear in your ear. In addition, more earwax will form. Those factors can clog the eardrum. Olive oil is a perfect wax emollient.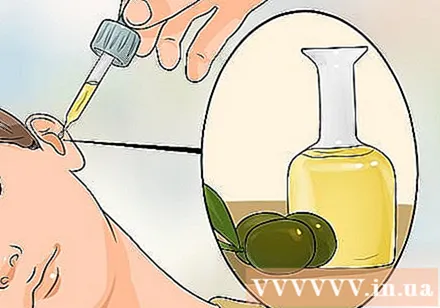
- Use a medical dropper to place 3 drops into the infected ear. Leave it on for 5-10 minutes, then tilt your head to let the oil drain. Olive oil will soften earwax (cerumen) and other solid residue, making it easy to remove (similar to hydrogen peroxide).Olive oil also works to reduce ear infections associated with fungal infections. Olive oil's anti-inflammatory properties are due to its high content of polyphenols.