Author:
Robert Simon
Date Of Creation:
15 June 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
Migraines are often described as one of the most terrible pain attacks a person ever experiences. Migraines prevent a person from thinking, working, resting and living a normal life. You can do acupressure yourself at home or ask a reflexologist to help ease migraines.
Steps
Method 1 of 5: Press acupressure points on the face
Third Eye Stimulation (Acupuncture Path). Each acupuncture point is called by many different names, traditional names or modern names (often consisting of letters and numbers). The An Duong acupuncture point, also known as GV 24.5 acupuncture point, is effective in reducing congestion and headache. This point is located between the eyebrows, at the point of the bridge of the nose adjacent to the forehead.
- Press firmly but gently on this point for 1 minute. You can simply press or round, notice which one is more effective.

Drilling Bamboo. Toan Truc acupuncture point, also known as Minh Quang acupuncture point or B2, is effective in soothing headache in front of forehead. These points are located at the inner corner of the eyes, just above the eyelids and on the bone around the eye.- Use the tips of two index fingers at the same time to press both points for 1 minute.
- You can press each side if you want. Just make sure to press each side for 1 minute.
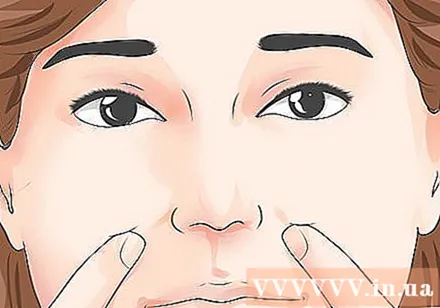
Welcome Fragrance (Welcome Fragrance). Huyet Nghinh Huong, also known as acupuncture point LI20, is effective in relieving migraine attacks and sinus pain. This point is located on the outside of the nose, near the end of the cheekbones.- Press deeply, hard and round. Done in 1 minute.
Method 2 of 5: Press the acupuncture points on the head
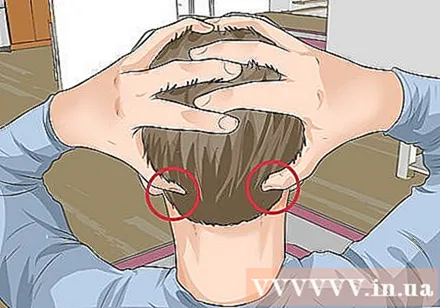
Feng Chi grave seal (Feng Chi). Phong Tri acupuncture point, also known as GB20 acupuncture point, is a acupuncture point commonly used to treat migraine headaches. This point is just below the ear. To find the Phong Tri acupuncture point, find two indents on the sides of the neck and the base of the skull. You can thread your fingers, gently embrace the back of your head with your hands, and place your thumbs in the indents at the base of the skull.- Use two thumbs to massage the acupuncture point with deep, strong pressure. Press 4-5 seconds. If you know where the two indentations are, you can try testing with your index or middle fingers, or use your knuckles to day.
- Relax and breathe deeply while doing the GB20 reflexology.
- You can day and press this point for up to 3 minutes.
Press the points along the temples. The temporal region has a series of points running around the ear above the skull. These points are located a distance from the earlobe about the width of a knuckle (a knot). The first is the Hairline Curve, located just above the tip of the ear. The next points are located at a distance from the front point, around the back and down around the ears.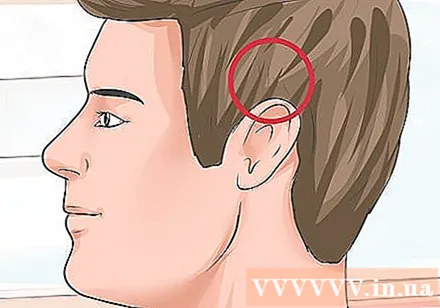
- Press into each of the points on both sides of the head. You can just press or round for 1 minute. Stimulate each acupuncture point right after pressing the first point for maximum results.
- The positions of these points are from front to back, including Hairline Curve, Valley Lead, Celestial Hub, Phu Bach (Floating White), and Head Portal Yin).
Wind Mansion's seal. Phong Phu acupuncture point, also known as GV16 acupuncture point, is effective in relieving migraine headaches, neck stiffness and nervous tension. This point is located in the center of the neck, below the skull. Find the depression under the base of the skull and press the midpoint.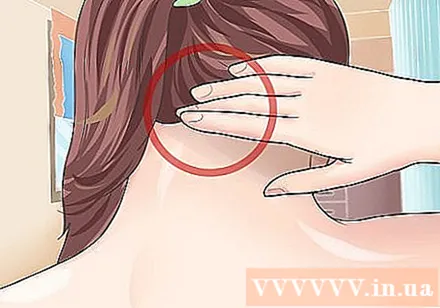
- Press deeply and vigorously into this point for at least 1 minute.
Method 3 of 5: Reflexology on other parts of the body
Heaven's Pillar (Heaven's Pillar). Thien Tru acupuncture point is located on the nape. You can find this point about two feet below the base of the skull. Slide your finger down from the base of the skull or from the depression. You can find these two points on the side muscles of the spine.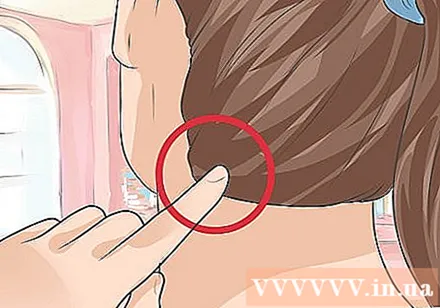
- You can press or squeeze in 1 minute.
Day stamping the grave of Hop Coc (Union Valley). The Hop Coc acupuncture point, also known as the LI4 acupuncture point, is located on both hands. This point is between your thumb and index finger. Use your left hand to press Hop Coc acupuncture point on your right hand and use your right hand to press Hop Coc acupuncture point on your left hand.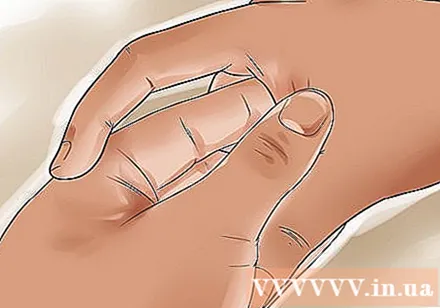
- Use strong, deep pressure to press the points for at least 1 minute.
Bigger Rushing (Bigger Rushing). The Tai Chong point is located on the instep, between the thumb and forefinger, and between the foot bones. Start with the skin between your toes and slide up about 2 inches (2.5 centimeters) up to feel the foot bones to find the point.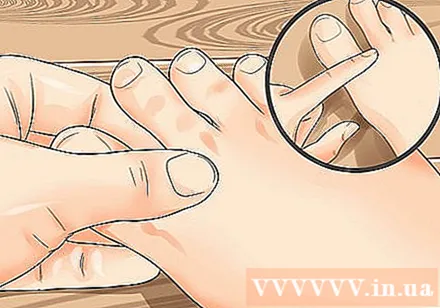
- You can press or squeeze in 1 minute.
- Some people find it easier to use their thumbs to do acupressure on their feet. This is a good way to stimulate these acupuncture points.
Method 4 of 5: Understand reflexology
Learn about reflexology. In traditional Chinese medicine, acupressure is the method of using points in the 12 main meridians. These channels are the energy currents carrying "qi", a term in oriental medicine for the energy of life. The basic concept of acupressure is that congestion leads to illness. Acupressure is a therapy that helps open up the meridians and restore circulation.
- Some medical studies have proven that acupressure method is effective in treating migraines.
Use the right force. When doing acupressure, try to use the correct pressure. Press the points with deep and strong force when stimulating the points. When pressed, you can feel a multiplicity, but not to the point of being unbearable, the sensation of having to balance pain and comfort.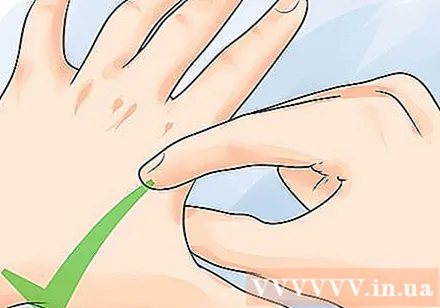
- Your overall health will determine the force of your acupressure.
- You will feel pain in some pressure points when pressed. Whenever you experience extreme pain or increased pain, slowly reduce your pressure until you feel a balance between pain and comfort.
- You should not have pain during acupressure. If the pain is uncomfortable, stop the pressure.
Correct use of reflexology. This method requires pressure on the acupressure points, so be sure to use the correct means of pressure. Reflexologists often use their fingers to massage and stimulate the acupressure points. The longest and strongest middle finger should be most effective when using pressure points, but you can also use your thumb. Some spots that are smaller and more difficult to reach may need to be pressed with your fingernail.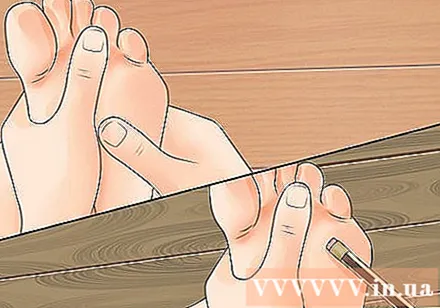
- Certain parts of the body such as knuckles, elbows, knees, legs or feet can also be used for acupressure.
- To properly do acupressure, press with a round object. In some acupuncture points, the fingertips are too thick. Try using the pencil eraser to press the small points. You may also consider using an avocado seed or a golf ball to apply pressure.
Talk to your doctor about reflexology. You can try pressing these pressure points at home or visit an acupressure specialist or a traditional medicine doctor. If you decide to try these acupressures, you should always let your doctor know so that your medications and other treatments will not interfere.
- If acupressure really works for pain relief, you should let your doctor know. But if this method doesn't work, you must see your doctor.
Method 5 of 5: Understand headaches
Distinguish two types of headaches. There are two basic types of headaches: primary headache that is not caused by any disorder, and secondary headache that results from another disorder. Migraine is the primary type of pain. Other primary types of headache include tension headaches and cluster or cyclical headaches.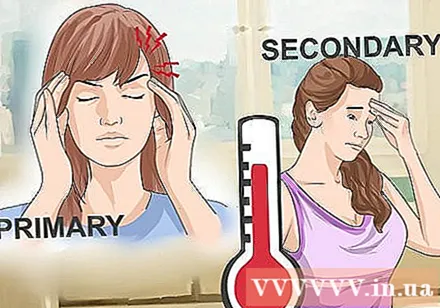
- Secondary headache can be caused by stroke, high blood pressure, fever or a problem in the temporomandibular joint (Temporomandibular Joint).
Know the symptoms of a migraine. In general, migraine attacks occur only on one side of the head, most commonly in the forehead or temples. Pain can range from moderate to severe pain, and can be heralded by aura. The majority of migraine patients also have symptoms of nausea, sensitivity to light, smell, and noise. Movement also often aggravates headaches.
- The aura is a temporary disturbance in the processing of information in its surroundings. Auroras can be a visible image, such as a flare, strobe light or zigzag light, or can be signaled by a scent. Other auras may include paralysis in the arms, confusion or confusion. Aura phenomenon occurs in about 25% of patients with migraine.
- There are many factors that trigger migraines and vary from person to person. Potential triggers include red wine, skipping meals or fasting, environmental stimuli such as bright lights or strong scents, weather changes, lack of sleep, stress, and hormonal problems. subjects, especially the menstrual cycle in women, certain foods, head injuries, including traumatic brain injury, neck pain, and temporal joint dysfunction.
Be aware of the red warning signs of an emergency headache. Any headache should be evaluated by a doctor. In some cases, the headache may be a sign of emergency. These signs include:
- Severe headache with fever and stiff neck. This may indicate meningitis.
- Headache type "lightning". A sudden and severe headache can be a sign of hemorrhage under the meninges, or bleeding under the tissue covering the brain and spinal cord.
- Pain, sometimes pain in the temples according to pulse. Especially when it occurs in the elderly and weight loss, this is a sign of a condition called giant cell arteritis.
- Red eyes and visible aura around light. This can be a sign of glaucoma (glaucoma) which, if left untreated, can lead to permanent vision loss.
- Sudden or severe headache in cancer patients or with weakened immune systems, such as post-transplant patients and HIV-AIDS patients.
See your doctor. Headaches can be symptoms of very serious medical problems. You should see a doctor to determine if your headaches are primary or secondary. If you have one or more of the following symptoms, see your doctor within a day or two, but no later than:
- Migraine attacks occur in increasing frequency and intensity.
- Headaches start after age 50.
- Vision changes
- Weight loss
Get medical treatment for migraines. Migraine treatments can include identifying and eliminating triggers, stress management, and treatment. In severe cases, your doctor may prescribe medications such as triptans (Sumatriptna / Imatrex or Zolmitriptan / Zomig), dihydroergotamine (Migranal), and anti-nausea and vomiting medications, if available.
- The drugs triptans and dihydroergotamine are not for people with coronary artery disease and should be used with caution in elderly patients or those with risk factors for cardiovascular disease, including obese people, people with cholesterol or high triglycerides or people diagnosed with diabetes.