Author:
Roger Morrison
Date Of Creation:
2 September 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- To step
- Part 1 of 4: Using home remedies
- Part 2 of 4: Using medications
- Part 3 of 4: Preventing infections and getting medical attention
- Part 4 of 4: Preventing new bites
- Warnings
Insect bites are very annoying. Depending on what bit you, the bite may be red, swollen, itchy or stinging. You may immediately realize that you have been bitten, but you may also not discover the bite until hours later. With proper care, most bites are nothing more than an annoyance.
To step
Part 1 of 4: Using home remedies
 Cool the bite with the help of a cold compress. The cold will lessen the swelling and numb the area a bit.
Cool the bite with the help of a cold compress. The cold will lessen the swelling and numb the area a bit. - If you don't have an ice pack in the freezer that you can use right away, you can make one quickly by wrapping ice cubes or a bag of frozen peas in a towel.
- Be careful not to hold the ice against your skin for too long. Don't do this for longer than 15 to 20 minutes at a time.
 Apply heat to the bite. If cold doesn't work to relieve itching, try using heat. The heat can break down some of the chemicals from the bite that are causing the itchiness, reducing the itchiness.
Apply heat to the bite. If cold doesn't work to relieve itching, try using heat. The heat can break down some of the chemicals from the bite that are causing the itchiness, reducing the itchiness. - Heat a spoon in boiling water. Hold the spoon with a pot holder so you don't burn your hand.
- Gently push the back of the spoon onto the bite. Hold the spoon on it for 15 seconds and then take it off. Be careful not to burn yourself.
- Use a hair dryer to heat the bite and the area around the bite.
 Apply essential oils to the bite. These methods have not been scientifically researched, but some people say they are useful.
Apply essential oils to the bite. These methods have not been scientifically researched, but some people say they are useful. - Tea tree oil has antibacterial properties and will help prevent infection. In addition, tea tree oil helps to reduce itching, swelling and pain. Put a small drop on your finger or a clean cotton ball and rub the oil directly on the bite.
- Try other essential oils such as lavender or coconut oil to reduce itching and swelling. These oils also have the advantage that they smell good.
 Use citrus juice or vinegar to stop the itching. The acid will help kill bacteria, prevent infection, promote healing and reduce itching.
Use citrus juice or vinegar to stop the itching. The acid will help kill bacteria, prevent infection, promote healing and reduce itching. - Lemon juice, lime juice and apple cider vinegar are often used as an ingredient in cooking and have a high acid content.
- Soak the edge of a kitchen towel or napkin in the juice or vinegar, then dab it onto the bite until it is thoroughly covered.
- Let the juice or vinegar dry and then use it again when the bite starts to itch again.
 Try raw honey. Honey helps to reduce inflammation and because honey is sticky it will be less pleasant to scratch the bite.
Try raw honey. Honey helps to reduce inflammation and because honey is sticky it will be less pleasant to scratch the bite. - Clean the bite thoroughly with soap and water.
- Spread a quarter teaspoon of honey on the bite and let the honey soak in.
- The honey will be sticky, so make sure to keep the area clean so that dirt doesn't stick to the honey and get onto the bite.
 Dry the bite with a baking soda or toothpaste paste. This will pull fluids and toxins out of the bite, allowing the area to heal more quickly.
Dry the bite with a baking soda or toothpaste paste. This will pull fluids and toxins out of the bite, allowing the area to heal more quickly. - Make a baking soda paste by mixing baking soda and water in a 2: 1 ratio. Then dab the paste onto the bite and the surrounding skin. Let the paste dry completely and then wipe the paste off your skin. This will help dry out the bite and get rid of toxins.
- Dab a pea-sized dollop of toothpaste on the bite and let the toothpaste dry on the bite. Toothpaste is an astringent and will help draw moisture from under your skin.
 Apply meat tenderizer to the bite. Meat tenderizer contains enzymes that break down proteins. This powder will break down the chemicals in the insect's saliva that has entered your skin, helping to soothe the itchiness.
Apply meat tenderizer to the bite. Meat tenderizer contains enzymes that break down proteins. This powder will break down the chemicals in the insect's saliva that has entered your skin, helping to soothe the itchiness. - Dissolve the meat tenderizer in a small amount of water.
- Dab the mixture directly on the spot where the insect bit you. It should provide instant relief.
- Let the mixture dry, then rinse it off your skin with water.
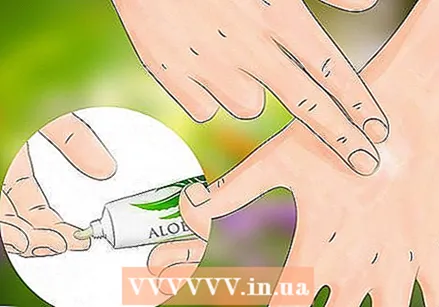 Rub aloe vera on the affected area. The aloe will have a cooling and soothing effect and is an excellent remedy to help your skin heal.
Rub aloe vera on the affected area. The aloe will have a cooling and soothing effect and is an excellent remedy to help your skin heal. - If you have commercially available aloe vera gel, apply liberally to the bite and surrounding skin.
- If you have an aloe vera plant in your home, remove a leaf from it and cut it open. Apply the sticky gel to the bite itself.
 If possible, hold the area with the bite above your heart. Hold your arm or your leg up above your heart if you got bit there.
If possible, hold the area with the bite above your heart. Hold your arm or your leg up above your heart if you got bit there. - For a comfortable position, try lying in bed and putting your arm or leg on a pile of pillows.
- Stay in this position for at least half an hour to allow the swelling to subside.
Part 2 of 4: Using medications
 Use an antihistamine to counteract the allergic reaction. Insect bites are itchy because of the body's autoimmune response to the anticoagulants in the insect's saliva. As a result, your blood will not clot when the insect drinks from it. After the insect has gone, a small amount of saliva will remain in your skin.
Use an antihistamine to counteract the allergic reaction. Insect bites are itchy because of the body's autoimmune response to the anticoagulants in the insect's saliva. As a result, your blood will not clot when the insect drinks from it. After the insect has gone, a small amount of saliva will remain in your skin. - Using a cream antihistamine, spread a pea-sized blob on the bite until the cream is completely absorbed into the skin.
- Take a non-narcotic oral antihistamine daily to help relieve symptoms. For example, you could take 10 mg of cetirizine. It is not recommended to use both oral and topical antihistamines at the same time.
 Apply hydrocortisone cream to the bite to soothe the itchy, red, swollen skin around the bite. Hydrocortisone cream takes longer to work, but this remedy will provide longer relief.
Apply hydrocortisone cream to the bite to soothe the itchy, red, swollen skin around the bite. Hydrocortisone cream takes longer to work, but this remedy will provide longer relief. - Hydrocortisone cream with a concentration of 1% can only be obtained by prescription. The cream will reduce inflammation.
- Put a pea-sized blob on your finger and rub it into the bite until it is completely absorbed by the skin.
 Dab calamine lotion on the bite. This will help remove the fluids that have accumulated under the skin. These fluids cause the bite to swell. A lotion with pramocaine will also help.
Dab calamine lotion on the bite. This will help remove the fluids that have accumulated under the skin. These fluids cause the bite to swell. A lotion with pramocaine will also help. - Apply the lotion according to the directions on the package. The lotion will dry out the bite and will also remove any chemicals from the insect's saliva that are irritating your skin.
 Use painkillers if necessary. A pain reliever should help if the bite is swollen and hurts.
Use painkillers if necessary. A pain reliever should help if the bite is swollen and hurts. - Apply a topical anesthetic to the bite to instantly relieve the discomfort. There are several effective means available.
- If a topical pain reliever doesn't help, try an over-the-counter oral pain reliever such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
Part 3 of 4: Preventing infections and getting medical attention
 Remove the insect if it still bites you. If you were bitten by a mosquito, chances are that you immediately realized this and killed the mosquito immediately. However, some insects such as ticks secrete an anesthetic in their saliva so that the animal or person being bitten does not feel it. The insect can then feed on the blood of the animal or person for longer. It is very important to get rid of ticks as soon as possible, as this will reduce the chances of getting infected with any of those diseases that the tick carries.
Remove the insect if it still bites you. If you were bitten by a mosquito, chances are that you immediately realized this and killed the mosquito immediately. However, some insects such as ticks secrete an anesthetic in their saliva so that the animal or person being bitten does not feel it. The insect can then feed on the blood of the animal or person for longer. It is very important to get rid of ticks as soon as possible, as this will reduce the chances of getting infected with any of those diseases that the tick carries. - Use tweezers to grab the tick as close to your skin as possible.
- Pull the tick out of your skin at a 90 degree angle and gradually apply more and more pressure until the tick comes out. Do not turn the tick or try to rip it out. This can cause the body of the tick to break off at the head or the mouth, so that the insect remains in your skin. You want to remove the entire tick, of course.
- If the head or mouth area does stick in your skin, disinfect the tweezers with rubbing alcohol and remove the body parts from your skin. You can also have this done by a doctor if you are unable to do this yourself.
- Do not apply nail polish or petroleum jelly to the tick or hold a smoldering match up to the tick and wait for the tick to release on its own. To reduce the risk of getting infected with a tick-borne disease, get rid of the tick yourself as soon as possible.
 Wash the bite. This way, you cleanse the area, make sure the bite heals quickly, and reduce the risk of infection.
Wash the bite. This way, you cleanse the area, make sure the bite heals quickly, and reduce the risk of infection. - Wet the bite with clean water and scrub the area gently with a mild soap. This prevents dirt particles and bacteria from entering the wound and causing an infection.
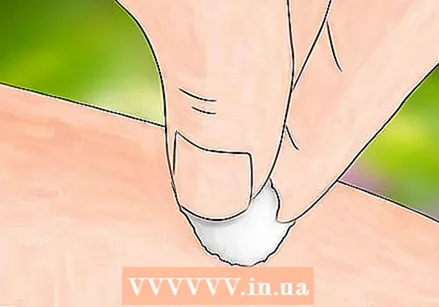 Use a disinfectant to kill bacteria or other pathogens. Put the disinfectant on a sterile cotton ball and then gently wipe the bite. It can sting a little. The following chemicals have excellent sanitizing properties and will work well.
Use a disinfectant to kill bacteria or other pathogens. Put the disinfectant on a sterile cotton ball and then gently wipe the bite. It can sting a little. The following chemicals have excellent sanitizing properties and will work well. - Rubbing alcohol
- Povidone iodine
- Hydrogen peroxide
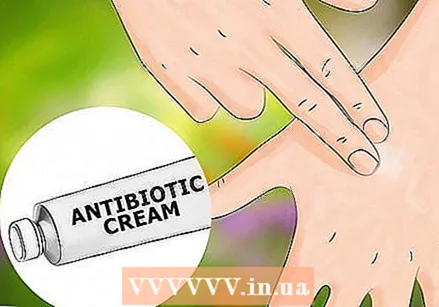 Apply a topical antibiotic to the bite to prevent bacterial growth. Triple antibiotic creams can only be obtained from pharmacies with a prescription and are very effective. Always read and stick to the directions on the packaging. Seek advice from your doctor before using these medications on a baby or if you are pregnant.
Apply a topical antibiotic to the bite to prevent bacterial growth. Triple antibiotic creams can only be obtained from pharmacies with a prescription and are very effective. Always read and stick to the directions on the packaging. Seek advice from your doctor before using these medications on a baby or if you are pregnant.  Do not scratch the bite. Scratching the bite will further irritate the area and allow bacteria from your fingers and fingernails to get into the bite. If you scratch the bite, it will even take longer to heal and the bite is more likely to become infected.
Do not scratch the bite. Scratching the bite will further irritate the area and allow bacteria from your fingers and fingernails to get into the bite. If you scratch the bite, it will even take longer to heal and the bite is more likely to become infected. - If it is difficult for you not to scratch the bite, cover the bite with a band-aid. You will be so reminded not to scratch. Moreover, you cannot scratch the bite in your sleep now.
 Get medical help right away if you develop a strange rash. Some insects carry serious illnesses characterized by a certain type of rash.
Get medical help right away if you develop a strange rash. Some insects carry serious illnesses characterized by a certain type of rash. - A red ring or circles around a tick bite is a symptom of Lyme disease. This condition must be treated with antibiotics as soon as possible.
- If you develop a fever and also have a red or black and blotchy rash, see your doctor to be tested for typhoid fever.
 Seek medical attention if you are traveling and get sick after being bitten. Some insects carry illnesses that do not cause a rash, but often have flu-like symptoms. The diseases that insects carry differs per country or region. So if you get sick after traveling and been bitten by insects, don't forget to tell your doctor where you've been, that you've been bitten, and what your symptoms are. See your doctor if you experience any of the following symptoms:
Seek medical attention if you are traveling and get sick after being bitten. Some insects carry illnesses that do not cause a rash, but often have flu-like symptoms. The diseases that insects carry differs per country or region. So if you get sick after traveling and been bitten by insects, don't forget to tell your doctor where you've been, that you've been bitten, and what your symptoms are. See your doctor if you experience any of the following symptoms: - Fever
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Joint and muscle pain
- Throwing up
 See a doctor right away if you think you are having a systemic allergic reaction. The doctor will give you an injection of epinephrine right away. The symptoms include:
See a doctor right away if you think you are having a systemic allergic reaction. The doctor will give you an injection of epinephrine right away. The symptoms include: - Hives or rashes in areas other than where you were bitten
- Itching or swelling on parts of the body other than where you were bitten
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing
- Difficulty swallowing
- Dizziness
- Throwing up
- Palpitations
Part 4 of 4: Preventing new bites
 Cover your skin as much as possible. Wearing long pants and a long-sleeved shirt will reduce the amount of skin that can be bitten. Some insects can still bite through your clothes, but you will definitely be bitten less.
Cover your skin as much as possible. Wearing long pants and a long-sleeved shirt will reduce the amount of skin that can be bitten. Some insects can still bite through your clothes, but you will definitely be bitten less.  Tuck your trouser legs into your socks when you go for a walk. This will protect you from ticks. After the walk you should thoroughly check your entire body for ticks and immediately remove any ticks you find.
Tuck your trouser legs into your socks when you go for a walk. This will protect you from ticks. After the walk you should thoroughly check your entire body for ticks and immediately remove any ticks you find.  Spray insect repellent on your skin and clothing. The most effective sprays contain DEET (N, N-diethyl-meta-toluenamide) or citriodiol and are available in many stores. As a result, you will be bitten less by mosquitoes, ticks and harvest mites.
Spray insect repellent on your skin and clothing. The most effective sprays contain DEET (N, N-diethyl-meta-toluenamide) or citriodiol and are available in many stores. As a result, you will be bitten less by mosquitoes, ticks and harvest mites. - Avoid getting the spray in your eyes or inhaling it.
- Do not spray on open wounds.
- Consult a doctor if you are pregnant and want to use insect repellants.
- Consult a doctor before using the spray on a baby.
- Take a shower to wash the spray off your skin when you no longer need to protect yourself.
 Sleep under a mosquito net if you are traveling and staying in a hotel without mosquito nets on the windows. This way you will not be bitten when you sleep.
Sleep under a mosquito net if you are traveling and staying in a hotel without mosquito nets on the windows. This way you will not be bitten when you sleep. - Don't forget to check the mosquito net for holes.
 Use permethrin on clothing, mosquito nets and camping gear. The protection should withstand multiple washes.
Use permethrin on clothing, mosquito nets and camping gear. The protection should withstand multiple washes.  Put a flea and tick collar on your pets. Make sure to check the straps regularly so that your pets don't bring fleas and ticks inside. This can help keep pests out.
Put a flea and tick collar on your pets. Make sure to check the straps regularly so that your pets don't bring fleas and ticks inside. This can help keep pests out.  Do not leave pools of water near your house. Mosquitoes reproduce in standing water, so removing the water will reduce the number of mosquitoes.
Do not leave pools of water near your house. Mosquitoes reproduce in standing water, so removing the water will reduce the number of mosquitoes.
Warnings
- If you are allergic to certain medications, discuss this with your doctor before taking any medications.
- Seek the advice of a doctor before using any over-the-counter medications on a baby or while pregnant.
- If you are currently taking any medications, discuss potential interactions with your doctor before taking any new medications. Even over-the-counter medications can have side effects and interactions.
- Get medical help right away if your symptoms get worse after taking any medication or if you experience side effects such as hives, rash, fever, dizziness, or vomiting.
- Always read the directions on the packaging and in the package insert before using any medication, even if it is an over-the-counter medication. Follow the directions carefully.