Author:
Frank Hunt
Date Of Creation:
20 March 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024
Content
If it's your first time using a calculator, all the buttons and options can be a bit scary. But whether you're using a regular calculator or a scientific calculator, the basics are pretty much the same. Once you know what the buttons do and how to use them for different calculations, it will be much easier to use your calculator when you need it - in or out of school!
To step
Method 1 of 2: Learn the basic functions
 Find the power button, if there is one. While most newer calculators are solar powered - meaning the lights turn them on automatically - some also have an "ON" or "ON / OFF" button. If you see one of these power buttons, press it to turn the calculator on or off.
Find the power button, if there is one. While most newer calculators are solar powered - meaning the lights turn them on automatically - some also have an "ON" or "ON / OFF" button. If you see one of these power buttons, press it to turn the calculator on or off. - If your calculator has an "ON" button, press it when the calculator is on to turn it off.
- Some calculators turn off automatically after a few minutes of inactivity.
 Add numbers with the "+" key. Press the "+" key between any two numbers to add them. For example, to add 5 by 10, press "5", the "+", then "10".
Add numbers with the "+" key. Press the "+" key between any two numbers to add them. For example, to add 5 by 10, press "5", the "+", then "10". - Add extra numbers to a sequence. For example, press "+" and "5", for the sum of "5 + 10". When you need the final answer, press the "=" key to get the sum of "20".
 Subtract numbers with the "-" key. Press the "-" key between any two numbers to subtract the second from the first number. For example, press "7", the "-" and then "5" to subtract 5 from 7. Then press "=" to get the answer "2".
Subtract numbers with the "-" key. Press the "-" key between any two numbers to subtract the second from the first number. For example, press "7", the "-" and then "5" to subtract 5 from 7. Then press "=" to get the answer "2". - Subtract extra numbers from a sequence. For example, press "-" and "2" to subtract from the sum of "2 - 7" and then press "=" to get the answer "0".
- Try to subtract numbers after adding them.
 Divide numbers or change fractions to decimals with the "÷" or "/" keys. For example, to divide 2 by 1, press "2", the "÷" and "1", then press "=". To change the fraction 4/5 to a decimal, press "4", the "/" and "5", then "=".
Divide numbers or change fractions to decimals with the "÷" or "/" keys. For example, to divide 2 by 1, press "2", the "÷" and "1", then press "=". To change the fraction 4/5 to a decimal, press "4", the "/" and "5", then "=". - If you are using a physical calculator, the partial test is likely to be "÷". For computer calculators, the partial test is likely to be a "/".
- Divide a series by pressing "÷" or "/" followed by a number. For example, if your calculator says "2 ÷ 1", press "÷", the "2" and then "=" to get the final answer "1".
 Multiply numbers using the "x" or " *" key. For example, to multiply 6 by 5, press "6", the "x", then "5", and then "=". The final answer will be "30".
Multiply numbers using the "x" or " *" key. For example, to multiply 6 by 5, press "6", the "x", then "5", and then "=". The final answer will be "30". - Physical calculators often use "x" as a multiplication key, while computer calculators usually use " *".
- Multiply in a series by pressing "x" or " *" followed by a number. For example, if your calculator reads "6 x 5", press "x", the "2" and then "=" to get the final answer "60".
 Press "=" to get the answer to an equation. After you enter the numbers and operations of your equation, such as addition or subtraction, press "=" to get the final answer. For example, press "10", the "+", then "10", then "=", to get "20" as the final answer.
Press "=" to get the answer to an equation. After you enter the numbers and operations of your equation, such as addition or subtraction, press "=" to get the final answer. For example, press "10", the "+", then "10", then "=", to get "20" as the final answer. - Remember that you can change the sum without erasing everything after pressing the "=", but only with the ← / → keys, so always double check your numbers first!
 Clear your calculator's memory with the "Clear" or "AC" key. Whenever you want to clear the calculator's memory and remove something from the display, press "AC" or "Clear". For example, start by pressing "2 x 2" followed by "=". You should now see "4" on the screen, which is also stored in memory. Press "Clear" and the number will be reset to "0".
Clear your calculator's memory with the "Clear" or "AC" key. Whenever you want to clear the calculator's memory and remove something from the display, press "AC" or "Clear". For example, start by pressing "2 x 2" followed by "=". You should now see "4" on the screen, which is also stored in memory. Press "Clear" and the number will be reset to "0". - "AC" stands for "All Clear".
- If you press "+", "-", "x" or "/" after the "4" and then try to start a new equation without pressing "Clear" first, it becomes part of the current equation. Always press "Clear" if you have to start over in the middle of a calculation.
 Press "Backspace", "Delete" or "CE" to delete the last number. If you want to delete the last number on your screen without deleting the entire equation, press "Backspace" or "Delete". For example, suppose you pressed "4 x 2" but wanted to press "4 x 3". Then press "Delete" to delete the "2" and then press "3" and you should see "4 x 3" on the display.
Press "Backspace", "Delete" or "CE" to delete the last number. If you want to delete the last number on your screen without deleting the entire equation, press "Backspace" or "Delete". For example, suppose you pressed "4 x 2" but wanted to press "4 x 3". Then press "Delete" to delete the "2" and then press "3" and you should see "4 x 3" on the display. - The "CE" button stands for "Clear Entry".
- If you press "Clear" instead of "Backspace" or "Delete", your equation will be reset to "0".
 Press on the '."Key to create decimal numbers. Start with the number before the decimal, press the "." Button, press the number after the decimal, and then press the "=" button. For example, to make "50.6", press "5", "0", "." And the "6", then "=".
Press on the '."Key to create decimal numbers. Start with the number before the decimal, press the "." Button, press the number after the decimal, and then press the "=" button. For example, to make "50.6", press "5", "0", "." And the "6", then "=". - If you add, subtract, multiply, or divide after making your decimal, you don't have to press the "=".
- Use the "+", "-", "x" and "÷" buttons to add, subtract, multiply and divide decimals respectively.
 Convert numbers to percentages with the "%" key. Press the "%" key to divide the number on your screen by 100, making it a percentage. For example, if you want to know what 7 percent of 20 is, first press "7" followed by "%" to make 0.07. Now press "x" and then "20" to multiply the percentage (0.07) by 20 to give the answer "1.4".
Convert numbers to percentages with the "%" key. Press the "%" key to divide the number on your screen by 100, making it a percentage. For example, if you want to know what 7 percent of 20 is, first press "7" followed by "%" to make 0.07. Now press "x" and then "20" to multiply the percentage (0.07) by 20 to give the answer "1.4". - To turn a percentage back into a number, multiply it by 100. In the last example, press "7" and "%" to get 0.07. Now press "x" and then "100" to multiply it by 100 to get the original number "7".
 Make fractions with the parentheses and division keys. In English, brackets are often referred to as "brackets". Always start with a "(" followed by the numerator, which is the number above the division line. Now press the "÷" or "/" and end with a ")". For example, create "5/6" as follows: enter "(", "5", "/", "6" and then ")".
Make fractions with the parentheses and division keys. In English, brackets are often referred to as "brackets". Always start with a "(" followed by the numerator, which is the number above the division line. Now press the "÷" or "/" and end with a ")". For example, create "5/6" as follows: enter "(", "5", "/", "6" and then ")". - Use the "+", "-", "x" and "÷" buttons to add, subtract, multiply, and divide fractions respectively. Just don't forget to put parentheses around each fraction, otherwise the calculation will be wrong!
 Add and delete data to the calculator's temporary memory using the "M" keys. The "M +" and "M-" keys add and remove the number on your screen from the calculator's temporary memory. For example, press "5" and then "M +" to add 5 to the memory. Now press "5" again and then "M-" to remove the number from the memory.
Add and delete data to the calculator's temporary memory using the "M" keys. The "M +" and "M-" keys add and remove the number on your screen from the calculator's temporary memory. For example, press "5" and then "M +" to add 5 to the memory. Now press "5" again and then "M-" to remove the number from the memory. - Temporary storage is not affected by the "Clear" or "Backspace" keys.
- To reset the calculator's temporary memory, press "MC".
- Use the temporary memory to make simple calculations, separate from more complex ones.
Method 2 of 2: Using a scientific calculator
 Create the reverse of a number by entering "1 / x" or "x ^ -1". Also called the inverse key, this gives you the inverse of any number, which is equal to 1 divided by the number. For example, the reciprocal of 2 (which is 2/1 in fraction form) is 1/2. This means you can press "2" and then "1 / x", to get 1/2 (0.5 in decimal form) as the answer.
Create the reverse of a number by entering "1 / x" or "x ^ -1". Also called the inverse key, this gives you the inverse of any number, which is equal to 1 divided by the number. For example, the reciprocal of 2 (which is 2/1 in fraction form) is 1/2. This means you can press "2" and then "1 / x", to get 1/2 (0.5 in decimal form) as the answer. - Multiplying a number by its reciprocal is always equal to 1.
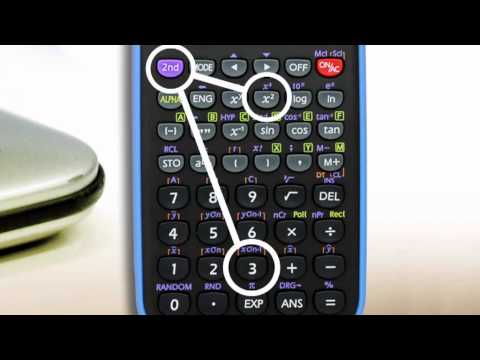
 Find the square of a number by pressing "X ^ 2" or "yx". pressing The square of a number is obtained by multiplying the number by itself. For example, the square of 2 is "2 x 2", which is 4. If you press "2" in the calculator and "X ^ 2" or "yx", the answer is "4".
Find the square of a number by pressing "X ^ 2" or "yx". pressing The square of a number is obtained by multiplying the number by itself. For example, the square of 2 is "2 x 2", which is 4. If you press "2" in the calculator and "X ^ 2" or "yx", the answer is "4". - The second function of the square test is usually "√", which is the square root. The square root is the function that converts the square (such as 4) to its square root (in this case 2). For example, the square root of 4 is 2, so pressing "4" and then "√" will give you "2" as the final result.
 Calculate the exponent of a number by pressing "^", "x ^ y" or "yX". The exponent (or power) of a number refers to the number of times it is multiplied by itself. The exponent key takes the first number (x) and multiplies it by itself a specified number of times, as determined by "y". For example, "2 ^ 6" is 2 to the power of 6, which is equal to "2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2". This can be calculated with the following sequence of operations: press "2", press "x ^ y", press "6", and press "=". The final answer is "64".
Calculate the exponent of a number by pressing "^", "x ^ y" or "yX". The exponent (or power) of a number refers to the number of times it is multiplied by itself. The exponent key takes the first number (x) and multiplies it by itself a specified number of times, as determined by "y". For example, "2 ^ 6" is 2 to the power of 6, which is equal to "2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2". This can be calculated with the following sequence of operations: press "2", press "x ^ y", press "6", and press "=". The final answer is "64". - Any number (x) to the power of 2 is called x squared, while any number (x) to the power of 3 is a cube.
- The "^" key is usually found on graphing calculators, while the "x ^ y" and "yX" keys are found on scientific calculators.
 Calculate scientific notation with the "EE" or "EXP" key. Scientific notation is a method of expressing large numbers or those with many decimal places (such as 0.0000000057) in a simpler way. In this case, scientific notation is 5.7 x 10. To convert a number to scientific notation, key in the number (5.7) and then press "EXP". Now press the exponent number (9), the "-" key, and then press "=".
Calculate scientific notation with the "EE" or "EXP" key. Scientific notation is a method of expressing large numbers or those with many decimal places (such as 0.0000000057) in a simpler way. In this case, scientific notation is 5.7 x 10. To convert a number to scientific notation, key in the number (5.7) and then press "EXP". Now press the exponent number (9), the "-" key, and then press "=". - Do not press the multiplication key (x) after pressing "EE" or "EXP".
- Use the "+/-" key to change the sign of the exponent.
 Use your trigonometry calculator with the "sin", "cos" and "tan" keys. To find the sine, cosine, or tangent of an angle, start by entering the angle value in degrees. Now press "sin", "cos" or "tan" to get the sine, cosine or tangent respectively.
Use your trigonometry calculator with the "sin", "cos" and "tan" keys. To find the sine, cosine, or tangent of an angle, start by entering the angle value in degrees. Now press "sin", "cos" or "tan" to get the sine, cosine or tangent respectively. - To convert the sine to an angle, press the sine value and then press "sin" or "arcsin".
- To convert the cosine or tangent of an angle to the angle value, key in the cosine or tangent and then press "cos" or "arccos".
- If your calculator does not have 'arcsin', 'sin', 'arccos' or 'cos' keys, press the 'function' or 'shift' key and then press the standard 'sin' or 'cos' key to convert these values to angles.